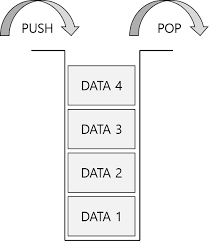
Stack
스택은 삽입과 삭제가 last-in first-out 방식으로 이루어 집니다.
Operation
주요 오퍼레이션은 다음과 같다.
push(object): 요소를 삽입하는 함수
pop(): 마지막으로 삽입된 요소를 삭제하고 반환하는 함수
top(): 마지막으로 삽입된 요소를 삭제 없이 반환하는 함수
len(): 저장된 요소의 갯수를 반환하는 함수
is_empty(): 스택이 비었는지의 유무를 검사하는 함수
Array-based Stack
Array based stack은 배열을 이용하여 구현된 스택 자료구조이다.
이 구조는 일반적으로 콜스택(Call Stack), 역추적(Backtracking), 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS, Depth First Search) 등 다양한 알고리즘에서 활용된다.
특징
◾ 삽입과 삭제가 빠르다. (각각의 연산이 의 러닝타임을 가진다.)
◾ 크기를 동적으로 조절하는 것이 어렵다.
◾ 배열의 크기를 초과할 경우 스택이 오버플로우(Overflow) 상태가 될 수 있다.
◾ n개의 요소에 대해 의 공간을 차지한다.
구현
class ArrayStack:
def __init__(self):
self.data = []
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.data) == 0
def push(self, e):
self.data.append(e)
def top(self):
if self.is_empty():
raise ValueError("Stack is Empty")
return self.data[-1]
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
raise ValueError("Stack is Empty")
return self.data.pop()Parentheses Matching Algorithm
from ArrayStack import ArrayStack
def is_mathcing(expr):
lefty = '({['
righty = ')}]'
S = ArrayStack()
for c in expr:
if c in lefty:
S.push(c)
elif c in righty:
if S.is_empty():
return False
if righty.index(c) != lefty.index(S.pop()):
return False
return S.is_empty()
def is_matched_Html(raw):
S = ArrayStack()
j = raw.find('<')
while j != -1:
k = raw.find('>', j+1)
if k == -1:
return False
tag = raw[j+1, k]
if not tag.startswith('/'):
S.push(tag)
else:
if S.is_empty():
return False
if tag[1:] != S.pop():
return False
j = raw.find('<', k+1)
return S.is_empty()Algorithm for Evaluating Expressions
# Python3 program to evaluate a given
# expression where tokens are
# separated by space.
# Function to find precedence
# of operators.
def precedence(op):
if op == '+' or op == '-':
return 1
if op == '*' or op == '/':
return 2
return 0
# Function to perform arithmetic
# operations.
def applyOp(a, b, op):
if op == '+': return a + b
if op == '-': return a - b
if op == '*': return a * b
if op == '/': return a // b
# Function that returns value of
# expression after evaluation.
def evaluate(tokens):
# stack to store integer values.
values = []
# stack to store operators.
ops = []
i = 0
while i < len(tokens):
# Current token is a whitespace,
# skip it.
if tokens[i] == ' ':
i += 1
continue
# Current token is an opening
# brace, push it to 'ops'
elif tokens[i] == '(':
ops.append(tokens[i])
# Current token is a number, push
# it to stack for numbers.
elif tokens[i].isdigit():
val = 0
# There may be more than one
# digits in the number.
while (i < len(tokens) and
tokens[i].isdigit()):
val = (val * 10) + int(tokens[i])
i += 1
values.append(val)
# right now the i points to
# the character next to the digit,
# since the for loop also increases
# the i, we would skip one
# token position; we need to
# decrease the value of i by 1 to
# correct the offset.
i-=1
# Closing brace encountered,
# solve entire brace.
elif tokens[i] == ')':
while len(ops) != 0 and ops[-1] != '(':
val2 = values.pop()
val1 = values.pop()
op = ops.pop()
values.append(applyOp(val1, val2, op))
# pop opening brace.
ops.pop()
# Current token is an operator.
else:
# While top of 'ops' has same or
# greater precedence to current
# token, which is an operator.
# Apply operator on top of 'ops'
# to top two elements in values stack.
while (len(ops) != 0 and
precedence(ops[-1]) >=
precedence(tokens[i])):
val2 = values.pop()
val1 = values.pop()
op = ops.pop()
values.append(applyOp(val1, val2, op))
# Push current token to 'ops'.
ops.append(tokens[i])
i += 1
# Entire expression has been parsed
# at this point, apply remaining ops
# to remaining values.
while len(ops) != 0:
val2 = values.pop()
val1 = values.pop()
op = ops.pop()
values.append(applyOp(val1, val2, op))
# Top of 'values' contains result,
# return it.
return values[-1]
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(evaluate("10 + 2 * 6"))
print(evaluate("100 * 2 + 12"))
print(evaluate("100 * ( 2 + 12 )"))
print(evaluate("100 * ( 2 + 12 ) / 14"))
# This code is contributed
# by Rituraj Jain