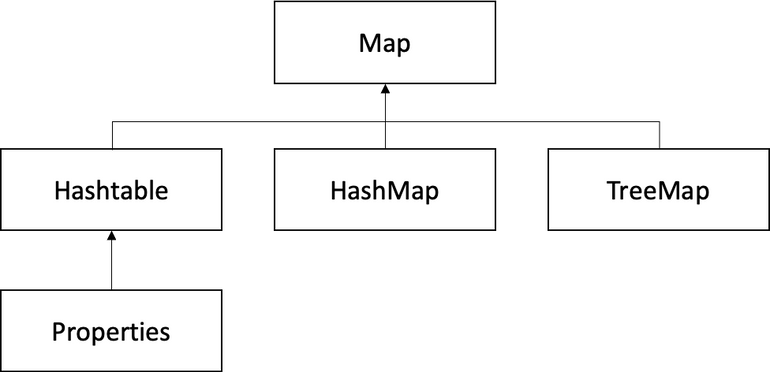
Map 인터페이스
Map 인터페이스는 하나가 아닌 쌍(Pair)으로 되어 있는 자료를 관리하는 메소드로 선언되어 있습니다.
하나의 쌍(Pair)는 키(key)와 값(value)으로 이루어져 있습니다.
키는 중복 될 수 없으며, 값은 중복될 수 있습니다.
Hash?
데이터에 대한 검색과 저장에서 아주 우수한 성능을 보여 쓰임새가 많습니다.
Hash로 값을 생성하면 고유 주소 값이 생기는데 이것을 숫자로 변환한 것을 해시코드라고 합니다.
즉, 자바에서 해시코드는 Heap 영역에 인스턴스에 대한 참조 값이라고도 부를 수 있습니다.
Hash 함수란? 데이터의 효율적인 관리를 위해 임의의 길이를 가진 데이터를 고정된 길이를 가진 테이터로 매핑해주는 함수 입니다. (암호화 기법이라고도 볼 수 있습니다.
Hash Collision?
가장 이상적인 해시테이블은 한 버켓에 딱 한개의 노드가 있는 경우 입니다. 이 경우 데이터 검색의 경우 인덱스만 계산하면 바로 값을 찾을 수 있으므로 O(1)의 시작복잡도를 보장 할 수 있습니다. 이 경우를 제외하고 한 버켓에 여러개의 노드가 있는 경우를 충돌이라고 합니다.
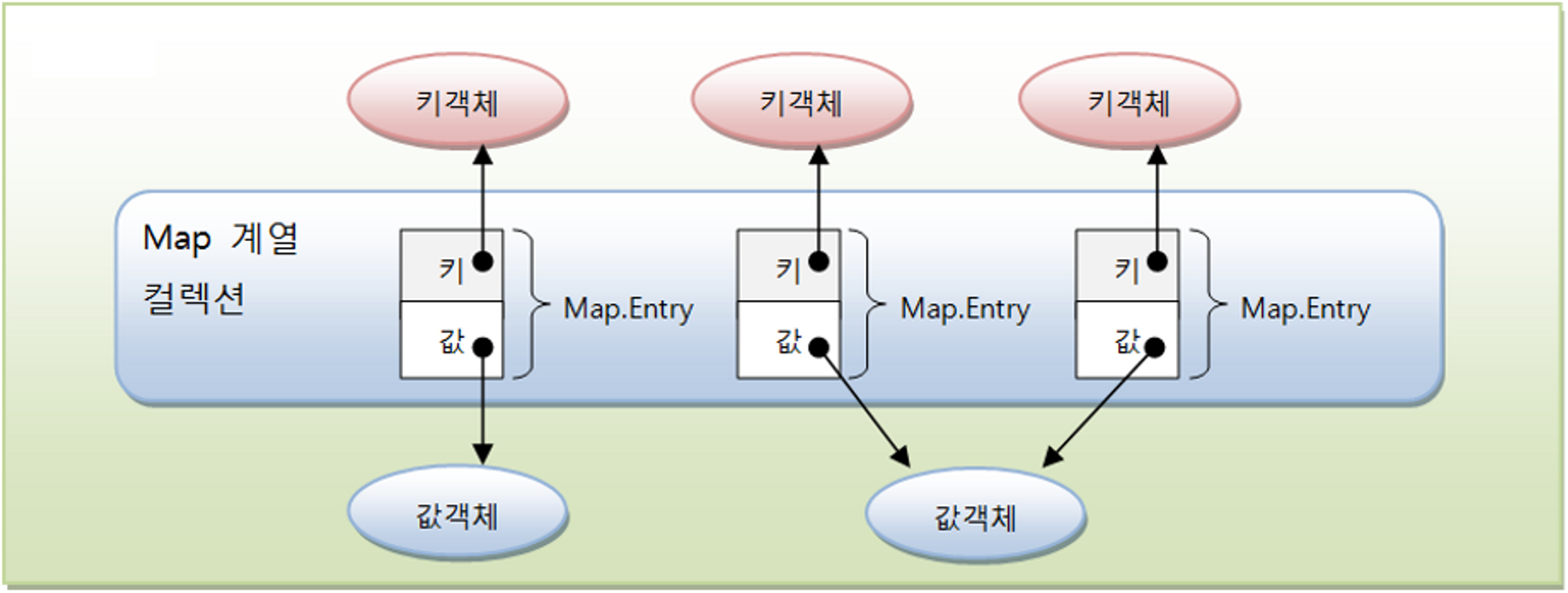
Map 컬렉션
Map은 리스트나 배열처럼 순차적으로(sequential) 해당 요소 값을 구하지 않고 key를 통해 value를 얻는다. 맵(Map)의 가장 큰 특징이라면 key로 value를 얻어낸다는 점이다.
- 순서가 보장 되지 않음
- 키와 값으로 구성되어 있으며 키는 중복 허용하지 않고 값은 중복 가능
- HashMap, HashTable, TreeMap, Properties
- 키의 동일 조건은 hashCode()의 리턴값이 같고, equals()메소드의 결과가 true
HashMap
HashMap은 Map 인터페이스를 구현한 대표적인 Map 컬렉션 입니다.
haseCode() 리턴값과 equals()리턴값이 같은 경우 같은 키로 간주 합니다.

public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 컬렉션 생성
HashMap<String, Integer>map = new HashMap<>();
// 객체 추가
map.put("Americano", 2500);
map.put("Latte", 4000);
// 객체 찾기
System.out.println(map.get("Latte"));
// 객체 삭제
map.remove("Latte");
}주요 메소드

기본 예제
public class HashMapEx1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Map 컬렉션 생성
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 객체 저장
map.put("우영우", 99);
map.put("동그라미", 55);
map.put("최수연", 95);
map.put("이준호", 80);
map.put("동그라미", 96); // 키가 같기 때문에 나중에 저장된 값으로 대치
System.out.println("총 Entry 수 : " + map.size());
// 객체 찾기
System.out.println(map.get("동그라미"));
// 객체를 하나씩 처리
Set<String> keySet = map.keySet(); // 모든 키를 Set 객체에 담아서 리턴
Iterator<String> iterator = keySet.iterator();
System.out.println("iterator를 이용하는 방법");
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
String key = iterator.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "\t" + value);
}
System.out.println();
// 향상된 for문을 이용하는 방법
System.out.println("향상된 for문을 사용하는 방법");
for(String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "\t" + map.get(key));
}
//객체 삭제
map.remove("최수연"); // 키로 Map.Entry를 제거
System.out.println("총 Entry 수 : " + map.size());
System.out.println();
// replace() 메소드를 이용한 요소 수정
map.replace("이준호", 91);
// 객체를 하나씩 처리, 키와 값의 쌍으로 구성된 모든 Map.Entry 객체를 set에 담아서 리턴
System.out.println("iterator entrySet() ");
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entryIterator = entrySet.iterator();
while (entryIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = entryIterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "\t" + value);
}
System.out.println();
//객체 전체 삭제
map.clear();
System.out.println("총 Entry 수 : " + map.size());
}HashMap - 응용예제(커피 메뉴 만들기)
package 해시맵메뉴;
import java.util.*;
// 해시맵을 이용한 커피 메뉴 (보기/추가/삭제/변경)
public class HashMenuMain {
static Map<String, MenuInfo> map = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
makeMenu();
selectMenu();
}
// 초기 메뉴를 추가 함
static void makeMenu() {
map.put("Americano", new MenuInfo("Americano", 2000, "Coffee", "기본커피"));
map.put("Espresso", new MenuInfo("Espresso", 2500, "Coffee", "진한커피"));
map.put("Latte", new MenuInfo("Latte", 4000, "Coffee", "우유 포함"));
}
static void selectMenu() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String key;
while(true) {
System.out.println("메뉴를 선택 하세요 : ");
System.out.println("[1]메뉴보기, [2]메뉴조회, [3]메뉴추가, [4]메뉴삭제, [5]메뉴수정, [6]종료 :");
int selMenu = sc.nextInt();
switch (selMenu) {
case 1 :
// Set<String> keySet = map.keySet(); // 맵의 모든 key를 모아서 반환
// Iterator<String> iterator =keySet.iterator();
// while(iterator.hasNext()) {
// key = iterator.next();
// System.out.println("메뉴 : " + map.get(key).name);
// System.out.println("메뉴 : " + map.get(key).price);
// System.out.println("메뉴 : " + map.get(key).group);
// System.out.println("메뉴 : " + map.get(key).desc);
// }
System.out.println("========== 메뉴 보기 ==========");
for(String e : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println("메뉴 : " + map.get(e).name);
System.out.println("가격 : " + map.get(e).price);
System.out.println("분류 : " + map.get(e).group);
System.out.println("설명 : " + map.get(e).desc);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
}
break;
case 2 :
System.out.print("조회 할 메뉴를 입력 하세요 : ");
key = sc.next();
// containsKey(키) : map 내에 해당 키가 있는지 확인하여 결과를 반환 함
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
System.out.println("메뉴 : " + map.get(key).name);
System.out.println("가격 : " + map.get(key).price);
System.out.println("분류 : " + map.get(key).group);
System.out.println("설명 : " + map.get(key).desc);
} else System.out.println("해당 메뉴가 존재하지 않습니다.");
break;
case 3 :
System.out.print("추가 할 메뉴를 입력 하세요 : ");
key = sc.next(); // key 이면서 메뉴이름이 된다.
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
System.out.println("해당 메뉴가 이미 존재 합니다.");
} else {
System.out.print("가격 입력 : ");
int price = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("분류 입력 : ");
String grp = sc.next();
//sc.nextInt(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.print("설명 입력 : ");
String desc = sc.next();
map.put(key, new MenuInfo(key, price, grp, desc));
}
break;
case 4 :
System.out.print("삭제할 메뉴를 입력 하세요 : ");
key = sc.next();
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
map.remove(key);
System.out.println(key + " 메뉴를 삭제 하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("삭제할 메뉴가 없습니다.");
}
break;
case 5 :
System.out.print("수정할 메뉴를 입력 하세요 : ");
key = sc.next();
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
System.out.print("가격 입력 : ");
int price = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("분류 입력 : ");
String grp = sc.next();
//sc.nextInt(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.print("설명 입력 : ");
String desc = sc.next();
map.replace(key, new MenuInfo(key, price, grp, desc));
} else {
System.out.println("수정 할 메뉴가 없습니다.");
}
break;
case 6 :
System.out.println("메뉴를 종료 합니다.");
return; // break 사용하면 반복문을 벗어나지 못함..
}
}
}
}HashTable
- Hashtable은 HashMap과 동일한 구조를 가지고 있습니다.
- HashTable도 키로 사용할 객체는 hashCode()와 equals() 메소드를 재정의해서 동등 객체가 될 조건을 정해야 합니다.
- 동기화된 메소드로 구현되어 있어 멀티 스레드 환경에서 안전 합니다.
Properties
- 키와 값을 String 타입으로 제한한 Map 컬렉션 입니다.
- 내부 설정 정보 읽기(database.properties가 생성되어 있지 않으면 에러 발생)
- 주로 Properties의 정보를 읽어 들일때 사용 됩니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[]args) throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
String path = Main.class.getResource("./database.properties").getPath();
path = URLDecoder.decode(path, "utf-8");
properties.load(new FileReader(path));
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String username = properties.getProperty("username");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("drive : " + driver);
System.out.println("url : " + url);
System.out.println("username : " + username);
System.out.println("password : " + password);
}
}driver=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@local:1521:xe
username=scott
password=tigerApplication 등에서 관련 정보 저장 및 읽기
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("timeout", "30");
properties.setProperty("language", "kr");
properties.setProperty("size", "10");
properties.setProperty("capacity", "10");
for(Object e : properties.keySet()) {
String key = (String) e;
System.out.println(properties.getProperty(key));
}
// properties에 저장된 요소들을 Enumeration을 이용해 출력
Enumeration enumeration = properties.propertyNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String element = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
System.out.println(element + "=" + properties.getProperty(element));
}
// Iterator<String> iter = (Iterator<String>) properties.propertyNames();
// while(iter.hasNext()) {
// String element = iter.next();
// System.out.println(element + "=" + properties.getProperty(element));
// }
System.out.println();
properties.setProperty("size", "20");
System.out.println("size=" + properties.getProperty("size"));
System.out.println("capacity=" + properties.getProperty("capacity", "20"));
System.out.println("loadfactor=" + properties.getProperty("loadfactor", "0.75"));
System.out.println(properties);
System.out.println();
properties.list(System.out);
}