TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)은 연결 지향적 프로토콜 입니다.
클라이언트가 연결 요청을 하고, 서버가 연결을 수락하면 통신 선로 고정되고, 모든 데이터는 통선 선로를 통해 순차적으로 전달 합니다.
데이터를 전송하기 전 연결이 형성되어하고 이제 소요되는 시간이 많이 걸립니다.
ServerSocket 과 Socket의 용도
클라이언트의 연결 요청을 기다리면서 요청이 오면 요청 수락
- java.net.ServerSocket클래스의 역할
연결된 클라이언트와 통신
- java.net.Socket 클래스의 역할
바이딩 포트
서버는 클라이언트가 접속 할 포트를 가지고 있어야 하는데, 이 포트를 바인딩 포트라고 합니다.
동작 절차
서버는 고정된 포트 번호에 바인딩해서 실행 ->ServerSocket을 생성할 때 포트번호 하나를 지정해야함
서버가 실행되면 클라이언트는 서버의 IP 주소와 바인딩 포트 번호로 Socket을 생성하여 연결 요청
ServerSocket은 클라이언트가 연결 요청을 하면 accept() 메서드로 연결 수락, 통신용 socket 생성
그 후 클라이언트와 서버는 각각 Socket을 이용해 데이터를 주고 받음.
ServerSocket 생성과 연결 요청
ServerSocket 얻기
첫번째 방법 : 생성자에 바인딩 포트를 대입하고 객체를 생성
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(5001);두번째 방법 : 디폴트 생성자로 객체 생성 후 포트 바인딩을 위해 bind() 메서드 호출
serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5001));서버PC에 멀티IP가 할당되어 있을 경우, 특정 IP로만 접속할 때만 연결 수락을 하고 싶다면 “localhost”대신 정확한 IP를 적으면 됩니다.
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
// localhost대신 정확한 IP를 주면 됨.
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",포트번호));ServerSocket 생성 시 해당 포트가 이미 할당되어 있을 경우 BindException이 발생함
=> 다른 포트로 바인딩하거나 다른 프로그램을 종료하고 다시 실행하면 됨.
연결 수락
포트 바인딩이 끝났으면 ServerSocket은 클라이언트 연결 수락을 위해 accept() 메서드 실행하면 됩니다.
accept()는 클라이언트가 연결 요청하기 전까지 블로킹
블로킹 : 스레드가 대기 상태가 된다는 뜻
때문에 UI를 생성하는 스레드나, 이벤트를 처리하는 스레드에서 accept()를 호출하지 않아야 함.
연결된 클라이언트 IP와 포트 정보 확인
InetSocketAddress isa = (InetSocketAddress) socket.getRemoteSocketAddress();| 리턴 타입 | 메소드(매개변수) | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| String | getHostName() | 클라이언트 IP 리턴 |
| Int | getPort() | 클라이언트 포트 번호 리턴 |
| String | toString() | "IP:포트번호" 형태의 문자열 리턴 |
Server
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5001));
while(true) {
System.out.println( "[연결 기다림]");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InetSocketAddress isa = (InetSocketAddress) socket.getRemoteSocketAddress();
System.out.println("[연결 수락함] " + isa.getHostName());
}
} catch(Exception e) {}
if(!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {}
}
}Client
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = new Socket();
System.out.println( "[연결 요청]");
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5001));
System.out.println( "[연결 성공]");
} catch(Exception e) {}
if(!socket.isClosed()) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {}
}
}Socket 데이터 통신
클라이언트가 연결 요청 connect()하고 서버가 연결 수락 accept() 했다면, 양쪽의 Socket객체로 부터 각각 입력 스트림과 출력 스트림을 얻을 수 있습니다.
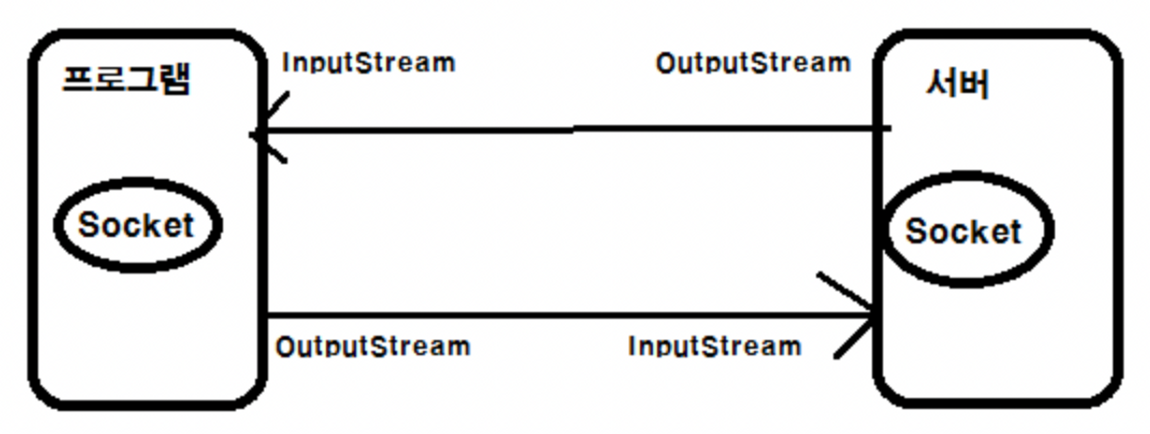
// 입력 스트림 얻기
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
// 출력 스트림 얻기
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();Stream이란? 개별 바이트나 문자열인 데이터의 원천 파일을 읽거나 쓸 때, 네트워크 소켓을 거쳐 통신 할 때 쓰이는 추상적인 개념을 의미 합니다.
상대방에게 데이터를 보내기 위한 byte[] 생성
String data = "보낼 데이터";
byte[] byteArr = data.getBytes("UTF-8");
OutputStream os =socket.getOutputStream();
os.wirte(byteArr);
os.flush();상대방이 보낸 데이터를 받기 위한 byte[] 생성
- InputStream은 데이터를 바이트 단위로 읽어 들이는 통로 입니다.
- InputStream은 추상 클래스이며 입력 스트림을 나타내는 모든 클래스의 수퍼 클래스 입니다.
- InputStream은 데이터 읽기, 특정 시점으로 되돌아가기, 남아 있는 데이터 보여주기 , 끊기 기능 제공 합니다.
byte[] byteArr = new byte[100];
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
int readByteCount = is.read(byteArr);
String data = new String(byteArr, 0, readByteCount, "UTF-8");Server
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null; // ServerSocket에 대한 참조 변수 생성
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5600));
while(true) {
System.out.println("[연결 기다림]");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InetSocketAddress isa = (InetSocketAddress) socket.getRemoteSocketAddress();
System.out.println("[연결 수락] " + isa.getHostName());
byte[] bytes = null;
String message = null;
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
message = "안녕하세요.클라이언트님 !!!";
bytes = message.getBytes("UTF-8");
os.write(bytes);
os.flush();
System.out.println("[데이터 보내기 성공]");
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
bytes = new byte[100];
int readByteCount = is.read(bytes);
message = new String(bytes, 0, readByteCount, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("[데이터 받기 성공] : " + message);
os.close();
is.close();
}
} catch(BindException e) {
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}Client
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = new Socket();
System.out.println( "[연결 요청]");
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5500));
System.out.println( "[연결 성공]");
byte[] bytes = null;
String message = null;
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
message = "Hello Server";
bytes = message.getBytes("UTF-8");
os.write(bytes);
os.flush(); // 스트림 버퍼의 내용을 강제적으로 출력 시킴
System.out.println( "[데이터 보내기 성공]");
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
bytes = new byte[100];
int readByteCount = is.read(bytes);
message = new String(bytes, 0, readByteCount, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("[데이터 받기 성공]: " + message);
os.close();
is.close();
} catch(Exception e) {}
if(!socket.isClosed()) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {}
}
}