🐬 신입 호빵이는 1만건의 데이터를 처리하여 파일에 쓰려고 한다. 수행시간을 줄이기 위해 병렬 처리를 하려고 하는데..
Process와 Thread 그리고 Python의 GIL(Global Interpreter Lock)에 대해 알아보자. 👻
1. Process와 Thread
1 ) Process
- 프로그램의 실행 단위
- 4GB의 주소공간 그리고 파일, 메모리, 스레드 등의 객체를 가짐
- Process가 종료될 때, 운영체제에 의해 소유 자원이 파괴됨
2 ) Thread
- Process의 작업을 처리
- Thread 별로 보통 1M의 Stack 공간이 할당됨
2. Multi-Process와 Multi-Thread
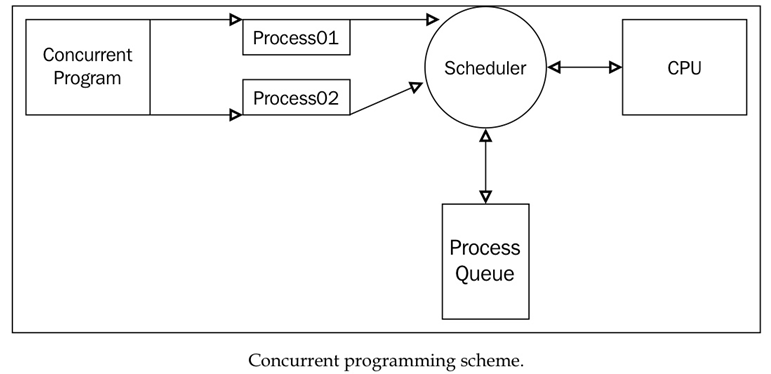
1 ) Multi-Process와 Multi-Thread
- Multi-Process는 독립적인 메모리 공간을 가짐
- Multi-Thread는 하나의 Process의 작업을 나누어 하므로 자원을 공유

각각의 Process와 Thread들은 CPU에 의해 스케줄링됨
Time Slice를 통해 정해진 시간만큼만 실행하는 Round-Robin
최소 작업을 우선으로 하는 SFJ(Shortest First Job)
우선 순위에 따라 처리하는 Priority Scheduling 등의 방식이 있음작업 전환에는 Context Switching 시간이 포함
Process Control Block, Thread Control Block에 현재 실행 중인 메모리의 주소, 코드의 위치 등을 기록하고 실행중인 Process나 Thread를 바꾸는 작업을 말함
- Thread의 경우, 자원을 공유하기 때문에 Process에 비해 작업 전환 속도가 빠름
3 ) 발생 가능한 문제
작업 처리 중 자원을 공유하는 것은 다양한 문제를 발생시킬 수 있음
- ☕
비유하자면카페에서 캐셔가 직접 주문 받은 음료만 서빙되고, 키오스크의 주문은 한 없이 밀리는 문제..
- Race Condition
- Starvation
- DeadLock
Critical Section, Mutex, Semapore 등으로 공유 자원에 대한 접근을 제어
3. Python Code 그리고 GIL
Test Version : Python 3.8.10Python에서 제공하는 모듈인
multiprocessing은 대부분threading의 API를 복제하기 때문에 코드가 비슷함
- 하지만, Python의 GIL로 인해 Thread를 사용할 경우, 수행하는 작업에 따라 싱글 스레드와 차이가 없을 수 있음
📑 GIL(Global Interpreter Lock)
CPython에서 여러 개의 thread들이 동시에 bytecode를 실행하는 것을 방지하기 위해 만들어진 것
- Thread safe 하지 않은 자원들을 보호하기 위함
- Bytecode를 실행하기 위해 interpreter의 lock을 획득해야 함 multi-thread로 동작할 수 없음
- Python Runtime과 상호 작용하는 것(GIL의 영향을 받는 것)들은 GIL로 인해 Single Thread로 동작
- PEP 703 – Making the Global Interpreter Lock Optional in CPython 제안을 통해 GIL 제거가 추진 중임
1 ) Multi-Thread
- 단일 스레드 실행 시간: 0.3817 초
- 멀티스레딩 실행 시간: 0.3829 초
import threading
import time
# CPU-bound 작업: 간단한 계산 작업을 시뮬레이션
def cpu_bound_task(start, end, result):
total = 0
for i in range(start, end):
total += i
result.append(total)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# CPU-bound 작업을 위한 범위 및 스레드 개수 설정
total_numbers = 10**7
num_threads = 2
chunk_size = total_numbers // num_threads
# 단일 스레드로 작업 실행
start_time_single = time.time()
cpu_bound_task(1, total_numbers + 1, [])
end_time_single = time.time()
execution_time_single = end_time_single - start_time_single
# 멀티스레딩으로 작업 실행
start_time_multi = time.time()
result_list = []
threads = []
for i in range(num_threads):
start = i * chunk_size + 1
# 실행 thread 개수만큼 데이터 나누기
end = (i + 1) * chunk_size + 1 if i < num_threads - 1 else total_numbers + 1
thread = threading.Thread(target=cpu_bound_task, args=(start, end, result_list))
threads.append(thread)
thread.start()
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
total_result = sum(result_list)
end_time_multi = time.time()
execution_time_multi = end_time_multi - start_time_multi
print(f"단일 스레드 실행 시간: {execution_time_single:.4f} 초")
print(f"멀티스레딩 실행 시간: {execution_time_multi:.4f} 초")
# 단일 스레드 실행 시간: 0.3817 초
# 멀티스레딩 실행 시간: 0.3829 초2 ) Multi-Process
- 단일 프로세스 실행 시간: 0.3874 초
- 멀티프로세스 실행 시간: 0.2981 초
import multiprocessing
from queue import Queue
import time
# CPU-bound 작업: 간단한 계산 작업을 시뮬레이션
def cpu_bound_task(start, end, result):
total = 0
for i in range(start, end):
total += i
result.put(total)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# CPU-bound 작업을 위한 범위 및 프로세스 개수 설정
total_numbers = 10**7
num_processes = 4
chunk_size = total_numbers // num_processes
# 단일 프로세스로 작업 실행
start_time_single = time.time()
single_result = Queue()
cpu_bound_task(1, total_numbers + 1, single_result)
end_time_single = time.time()
execution_time_single = end_time_single - start_time_single
# 멀티프로세스로 작업 실행
start_time_multi = time.time()
result_queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
processes = []
for i in range(num_processes):
start = i * chunk_size + 1
# 실행 process 개수만큼 데이터 나누기
end = (i + 1) * chunk_size + 1 if i < num_processes - 1 else total_numbers + 1
process = multiprocessing.Process(target=cpu_bound_task, args=(start, end, result_queue))
processes.append(process)
process.start()
for process in processes:
process.join()
total_result = sum([result_queue.get() for _ in range(num_processes)])
end_time_multi = time.time()
execution_time_multi = end_time_multi - start_time_multi
print(f"단일 프로세스 실행 시간: {execution_time_single:.4f} 초")
print(f"멀티프로세스 실행 시간: {execution_time_multi:.4f} 초")
# 단일 프로세스 실행 시간: 0.3874 초
# 멀티프로세스 실행 시간: 0.2981 초