4장. 코루틴의 실제 구현
코루틴 내부 구현과 동작 과정에 대해 알아보자
- 중단 함수는 함수가 시작할 때와 중단 함수가 호출되었을 때 상태를 가진다는 점에서 상태 머신(state machine)과 비슷하다
- continuation 객체는 상태를 나타내는 숫자와 로컬 데이터를 가지고 있다
- 함수의 continuation 객체가 이 함수를 부르는 다른 함수의 continuation 객체를 장식(decorate)한다. 그 결과, 모든 continuation 객체는 실행을 재개하거나 재개된 함수를 완료할 때 사용되는 콜 스택으로 사용된다
컨티뉴에이션 전달 방식
코틀린 팀은 중단 함수 구현 방식으로 컨티뉴에이션 전달 방식(continuation-passing style)을 선택
suspend fun getUser(): User?
suspend fun setUser(user: User)
suspend fun checkAvailability(flight: Flight): Boolean
// 자세히 들여다 보면
fun getUser(continuation: Continuation<*>): Any?
fun setUser(user: User, continuation: Continuation<*>): Any
fun checkAvailiability(flight: Flight, continuation: Continuation<*>): Any- 반환 타입이 Any 또는 Any? 로 바뀜
- 중단 함수를 실행하는 도중에 중단되면 선언된 타입의 값을 반환하지 않을 수 있기 때문
아주 간단한 함수
suspend fun myFunction() {
println("Before")
delay(1000) // 중단 함수
println("After")
}
// myFunction 함수 시그니처
fun myFunction(continuation: Continuation<*>): Any- 함수는 상태를 저장하기 위해 자신만의 컨티뉴에이션 객체가 필요
- 본체가 시작될 때,
MyFunction은 파라미터인 continuation을 자신만의 continuation으로 포장 - 현재 상태를 저장하기 위해
label이라는 필드를 사용 - 함수가 처음 시작될 때 이 값은
0으로 설정 - 이후에는 중단되기 전에 다음 상태로 설정되어 코루틴이 재개될 시점을 알 수 있게 도움
// myFunction의 세부 구현을 간단하게 표현하면 다음과 같음
fun myFunction(continuation: Continuation<Unit>): Any {
val continuation = continuation as? MyFunctionContinuation
?: MyFunctionContinuation(continuation)
if(continuation.label == 0) {
println("Before")
continuation.lable = 1
if(delay(1000, continuation) == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) {
return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
}
if (continuation.lable == 1) {
println("After")
return Unit
}
error("Impossible")
}delay에 의해 중단될 경우COROUTINE_SUSPENDED가 반환되며,myFunction은COROUTINE_SUSPENDED를 반환- 중단이 일어나면 콜 스택에 있는 모든 함수가 종료되며, 중단된 코루틴을 실행하던 스레드를 실행 가능한 코드가 사용할 수 있게 함
// 코드를 간략화한 최종 모습
fun myFunction(continuation: Continuation<Unit>): Any {
val continuation = continuation as? MyFunctionContinuation
?: MyFunctionContinuation(continuation)
if(continuation.label == 0) {
println("Before")
continuation.lable = 1
if(delay(1000, continuation) == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) {
return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
}
if (continuation.lable == 1) {
println("After")
return Unit
}
error("Impossible")
}
class MyFunctionContinuation(
val completion: Continuation<Unit>
) : Continuation<Unit> {
override val context: CoroutineContext
get() = completion.context
val label = 0
var result: Result<Any>? = null
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
this.result = result
val res = try {
val r = myFunction(this)
if (r == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) return
Result.success(r as Unit)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
Result.failure(e)
}
completion.resumeWith(res)
}
}상태를 가진 함수
함수가 중단된 후에 다시 사용할 지역 변수나 파라미터와 같은 상태를 가지고 있다면, 함수의 컨티뉴에이션 객체에 상태를 저장해야 함
suspend fun myFunction() {
println("Before")
var counter = 0
delay(1000) // 중단 함수
counter++
println("Counter: $counter")
println("After")
}counter는 0 과 1로 표시된 두 상태에서 사용되므로 컨티뉴에이션 객체를 통해 상태를 저장해야 함
// 상태를 저장하는 코드를 간략화한 코드
fun myFunction(continuation: Continuation<Unit>): Any {
val continuation = continuation as? MyFunctionContinuation
?: MyFunctionContinuation(continuation)
var counter = continuation.counter
if(continuation.label == 0) {
println("Before")
counter = 0
continuation.counter = counter
continuation.label = 1
if(delay(1000, continuation) == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) {
return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
}
if (continuation.lable == 1) {
counter = (counter as Int) + 1
println("Counter: $counter")
println("After")
return Unit
}
error("Impossible")
}
class MyFunctionContinuation(
val completion: Continuation<Unit>
) : Continuation<Unit> {
override val context: CoroutineContext
get() = completion.context
var result: Result<Any>? = null
var label = 0
var counter = 0
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
this.result = result
val res = try {
val r = myFunction(this)
if (r == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) return
Result.success(r as Unit)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
Result.failure(e)
}
completion.resumeWith(res)
}
}값을 받아 재개되는 함수
suspend fun printUser(token: String) {
println("Before")
val userId = getUserId(token) // 중단 함수
println("Got userId: $userId")
val userName = getUserName(userId, token) // 중단 함수
println(User(userId, userName))
println("After")
}파라미터와 반환값 모두 컨티뉴에이션 객체에 저장되어야 하는 이유
- token은 상태 0과 1에서 사용됨
- userId 는 상태 1과 2에서 사용됨
- Result 타입인 result는 함수가 어떻게 재개되었는지 나타냄
함수가 값으로 재개되었다면 결과는 Result.Success(value) 가 되며, 이 값을 얻어 사용할 수 있음
함수가 예외로 재개되었다면 결과는 Result.Failure(exception)이 되며, 예외를 던지게 됨
// 예시 코드
fun printUser(
token: String,
continuation: Continuation<*>
): Any {
val continuation = continuation as? PrintUserContinuation
?: PrintUserContinuation(
continuation as Continuation<Unit>,
token
)
var result: Result<Any>? = continuation.result
var userId: String? = continuation.userId
val userName: String
if(continuation.label == 0) {
println("Before")
continuation.label = 1
val res = getUserId(token, continuation)
if (res == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) {
return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
result = Result.success(res)
}
if (continuation.lable == 1) {
userId = result!!.getOrThrow() as String
println("Got userId: $userId")
continuation.label = 2
continuation.userId = userId
val res = getUserName(userId, token, continuation)
if (res == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) {
return COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
result = Result.success(res)
}
if (continuation.label == 2) {
userName = result!!.getOrThrow() as String
println(User(userId as String, userName))
println("After")
return Unit
}
error("Impossible")
}
class PrintUserContinuation(
val completion: Continuation<Unit>,
val token: String
) : Continuation<Unit> {
override val context: CoroutineContext
get() = completion.context
var label = 0
var result: Result<Any>? = null
var userId: String? = null
override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Unit>) {
this.result = result
val res = try {
val r = printUser(token, this)
if (r == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) return
Result.success(r as Unit)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
Result.failure(e)
}
completion.resumeWith(res)
}
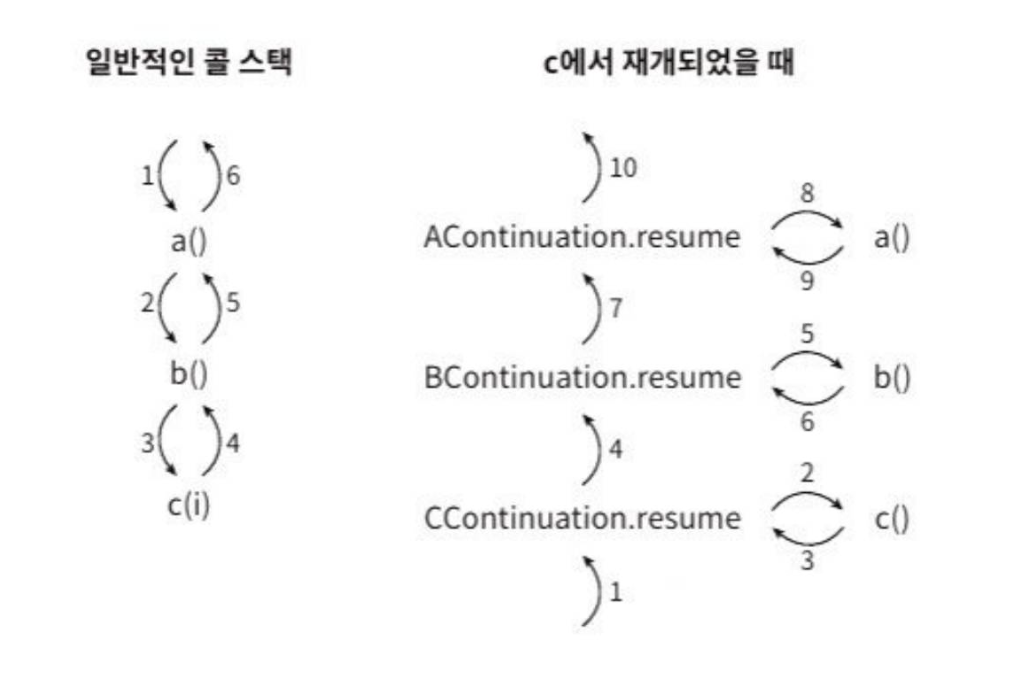
}콜 스택
- 함수 a가 함수 b를 호출하면 가상 머신은 a의 상태와 b가 끝나면 실행이 될 지점을 어딘가에 저장해야 함
- 이런 정보를 모두 콜 스택(call stack)이라는 자료 구조에 저장됨
- 코루틴을 중단하면 스레드를 반환해 콜 스택에 있는 정보가 사라지기 때문에 코루틴을 재개할 때 콜 스택을 사용할 수 없음
continuation객체가 콜 스택의 역할을 대신함continuation객체는 중단이 되었을 때의 상태(label)와 함수의 지역 변수와 파라미터(필드), 그리고 중단 함수를 호출한 함수가 재개될 위치 정보를 가지고 있음- 하나의
continuation객체가 다른 하나를 참조하고, 참조된 객체가 또 다른continuation객체를 참조 ⇒continuation객체는 거대한 양파와 같으며 일반적으로 콜 스택에 저장되는 정보를 모두 가짐
// 일반 코드
suspend fun a() {
val user = readUser()
b()
b()
b()
println(user)
}
suspend fun b() {
for (i in 1 .. 10) {
c(i)
}
}
suspend fun c(i: Int) {
delay(i * 100L)
println("Tick")
}
// continuation 객체를 사용해 나타낸 결과
CContinuation(
i = 4,
label = 1,
completion = BContinuation(
i = 4,
label = 1,
completion = AContinuation(
label = 2,
user = User@1234,
completion = ...
)
)
)예) 함수 a가 함수 b를 호출하고, 함수 b는 함수 c를 호출하며, 함수 c에서 중단된 상황
- 실행이 재개되면 c의 continuation 객체는 c 함수를 먼저 재개
- 함수가 완료되면 c continuation 객체는 b 함수를 호출하는 b continuation 객체를 재개
- b 함수가 완료되면 b continuation은 a continuation을 재개
- a 함수가 호출됨
예외를 던질 때도 처리되지 못한 예외가
resumeWith에서 잡히면 Result.failure(e)로 래핑되며, 예외를 던진 함수는 포장된 결과를 받게 됨
실제 코드
continuation 객체와 중단 함수를 컴파일한 실제 코드는 최적화되어 있으며, 몇 가지 처리과정이 더 포함됨
- 예외가 발생했을 때 더 나은 스택 트레이스 생성
- 코루틴 중단 인터셉션
- 사용하지 않는 변수를 제거하거나 테일콜 최적화 등의 최적화
internal abstract class BaseContinuationImpl(
val completion: Continuation<Any?>?
): Continuation<Any?>, CoroutineStackFrame, Serializable {
final override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any?>) {
var current = this
var param = result
while (true) {
// 컨티뉴에이션 객체를 재개할 때마다 "resume" 디버그 조사를 실행
// 디버깅 라이브러리가 중단된 콜 스택 중 어떤 부분이 이미 재개되었는지 추적
probeCoroutineResumed(current)
with(current) {
// 완료되지 않은 상태에서 컨티뉴에이션 객체를 재개하면 실패
val completion = completion!!
val outcome: Result<Any?> =
try {
val outcome = invokeSuspend(param)
if (outcome == COROUTINE_SUSPENDED)
return
Result.success(outcome)
} catch (exception: Throwable) {
Result.failure(exception)
}
releaseIntercepted()
// 상태 머신이 종료되는 중일 때 실행됨
if (completion is BaseContinuationImpl) {
// 반복문을 통해 재귀 호출을 풂
current = completion
param = outcome
} else {
// 최상위 컨티뉴에이션 객체인 completion에 도달
// 실행 후 반환
completion.resumeWith(outcome)
return
}
}
}
}
// ...
}중단 함수의 성능
일반 함수 대신 중단 함수를 사용하면 비용은 어떻게 될까?
- 함수를 상태로 나누는 것은 쉬우며, 실행점이 변하는 비용도 거의 들지 않음
- 상태를 저장하는 것은 간단함 (지역 변수를 복사하지 않고 새로운 변수가 메모리 내 특정 값을 가리키게 함)
- 컨티뉴에이션 객체를 생성하는 것에 비용이 어느 정도 들지만 RxJava나 콜백 함수의 성능과 비슷한 수준으로 걱정하지 않아도 됨
요약
- 중단 함수는 상태 머신과 유사하게 함수가 시작될 때와 중단 함수를 호출한 뒤의 상태를 가짐
- 상태를 나타내는 값과 로컬 데이터는 컨티뉴에이션 객체에 저장됨
- 호출된 함수의 컨티뉴에이션 객체는 호출한 함수의 컨티뉴에이션을 장식 ⇒ 모든 컨티뉴에이션 객체는 함수가 재개될 때 또는 재개된 함수가 완료될 때 사용되는 콜 스택의 역할을 함

