🎄 이진트리
🎠 이진트리 순회(깊이 우선 탐색)
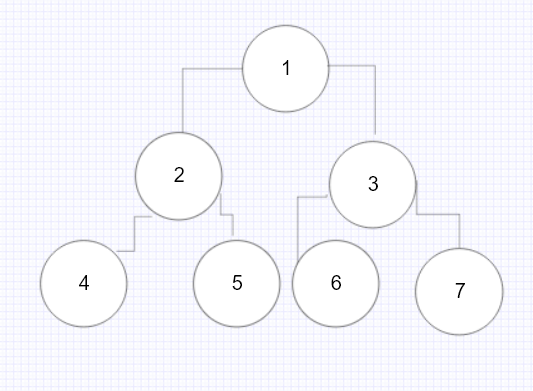
위와 같은 구조가 있다고 했을 때,
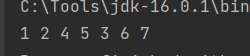
전위순회 : 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
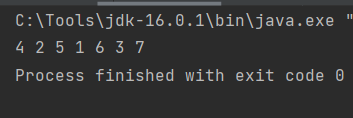
중위순회 : 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
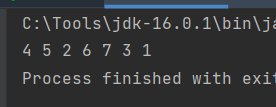
후위순회 : 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
🎠 코드를 작성해 보자.
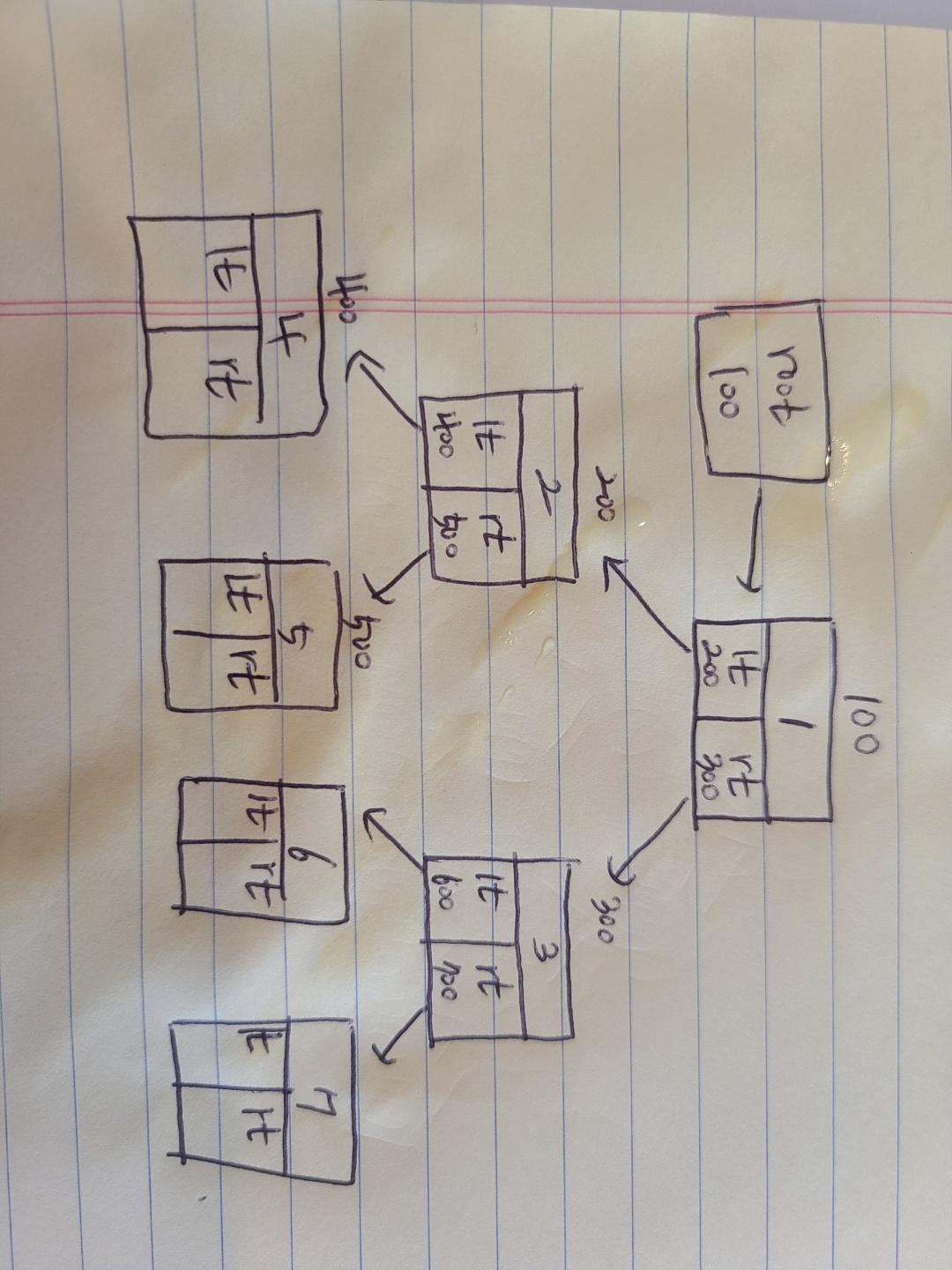
🔑 Node 클래스 코드
class Node{
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val){
data = val;
lt = rt = null;
}
}lt와 rt는 Node클래스의 객체 주소를 저장하는 변수이다.
🔑 Main 클래스 코드
public class Main{
Node root;
public void DFS(Node root){
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Main tree = new Main();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.lt = new Node(2);
tree.root.rt = new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt = new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.lt = new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(7);
tree.DFS(tree.root);
}
}Main클래스의 객체를 하나 만들고.
🔑 전위순회 코드
package algolecture;
class Node{
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val){
data = val;
lt = rt = null;
}
}
public class Main57 {
Node root;
public void DFS(Node root){
if(root == null)
return;
else{
System.out.println(root.data+" ");
DFS(root.lt);
DFS(root.rt);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main57 tree = new Main57();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.lt = new Node(2);
tree.root.rt = new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt= new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt = new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt = new Node(7);
tree.DFS(tree.root);
}
}결과
🔑 중위순회 코드
package algolecture;
class Node{
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val){
data = val;
lt = rt = null;
}
}
public class Main57 {
Node root;
public void DFS(Node root){
if(root == null)
return;
else{
DFS(root.lt);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
DFS(root.rt);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main57 tree = new Main57();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.lt = new Node(2);
tree.root.rt = new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt= new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt = new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt = new Node(7);
tree.DFS(tree.root);
}
}
🔑 후위순회 코드
package algolecture;
class Node{
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val){
data = val;
lt = rt = null;
}
}
public class Main57 {
Node root;
public void DFS(Node root){
if(root == null)
return;
else{
DFS(root.lt);
DFS(root.rt);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main57 tree = new Main57();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.lt = new Node(2);
tree.root.rt = new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt= new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt = new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt = new Node(7);
tree.DFS(tree.root);
}
}
🎠 배열을 이용해 작성해 보자.
package Nodes.tree_binary_tree;
public class BinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 정점의 갯수
int count = 7;
// 크기8, index의 시작은 0부터 이기 때문에, 1부터 사용함.
Node[] nodeList = new Node[count +1];
// Node형식의 배열을 만듬.
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++){
Node binaryTree = new Node(i);
nodeList[i] = binaryTree;
// 노트 형식의 binaryTree를 만들고, 배열에 저장함.
}
for(int i=1; i<=count; i++){
if(i *2 <= count) {
nodeList[i].leftChild = nodeList[i*2];
nodeList[i].rightChild = nodeList[(i*2)+1];
}
}
preOrder(nodeList[1]);
System.out.println();
inOrder(nodeList[1]);
System.out.println();
postOrder(nodeList[1]);
}
static void preOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
System.out.println(node.data + " ");
preOrder(node.leftChild);
preOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
static void inOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
inOrder(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data+ " ");
inOrder(node.rightChild);
}
}
static void postOrder(Node node){
if(node != null){
postOrder(node.leftChild);
postOrder(node.rightChild);
System.out.println(node.data + " ");
}
}
}
package Nodes.tree_binary_tree;
public class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild, rightChild;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
}
}