Annotate
참고링크
$ python manage.py migrate
$ python manage.py loaddata users.json articles.json comments.json
- 현재 요청/응답에 대한 다양한 디버그 정보를 표시하고 다양한 패널에서 자세한 정보를 표시

practice1
- 단순히 SQL로 계산해 하나의 테이블의 필드를 추가하여 붙여 올 수 있는 경우
'게시글 별로 댓글 수를 출력해보기 '
def index_1(request):
articles = Article.objects.order_by('-pk')
context = {
'articles': articles,
}
return render(request, 'articles/index_1.html', context)
{% block content %}
<h1>Articles</h1>
{% for article in articles %}
<p>제목 : {{ article.title }}</p>
<p>댓글개수 : {{ article.comment_set.count }}</p>
<hr>
{% endfor %}
{% endblock content %}
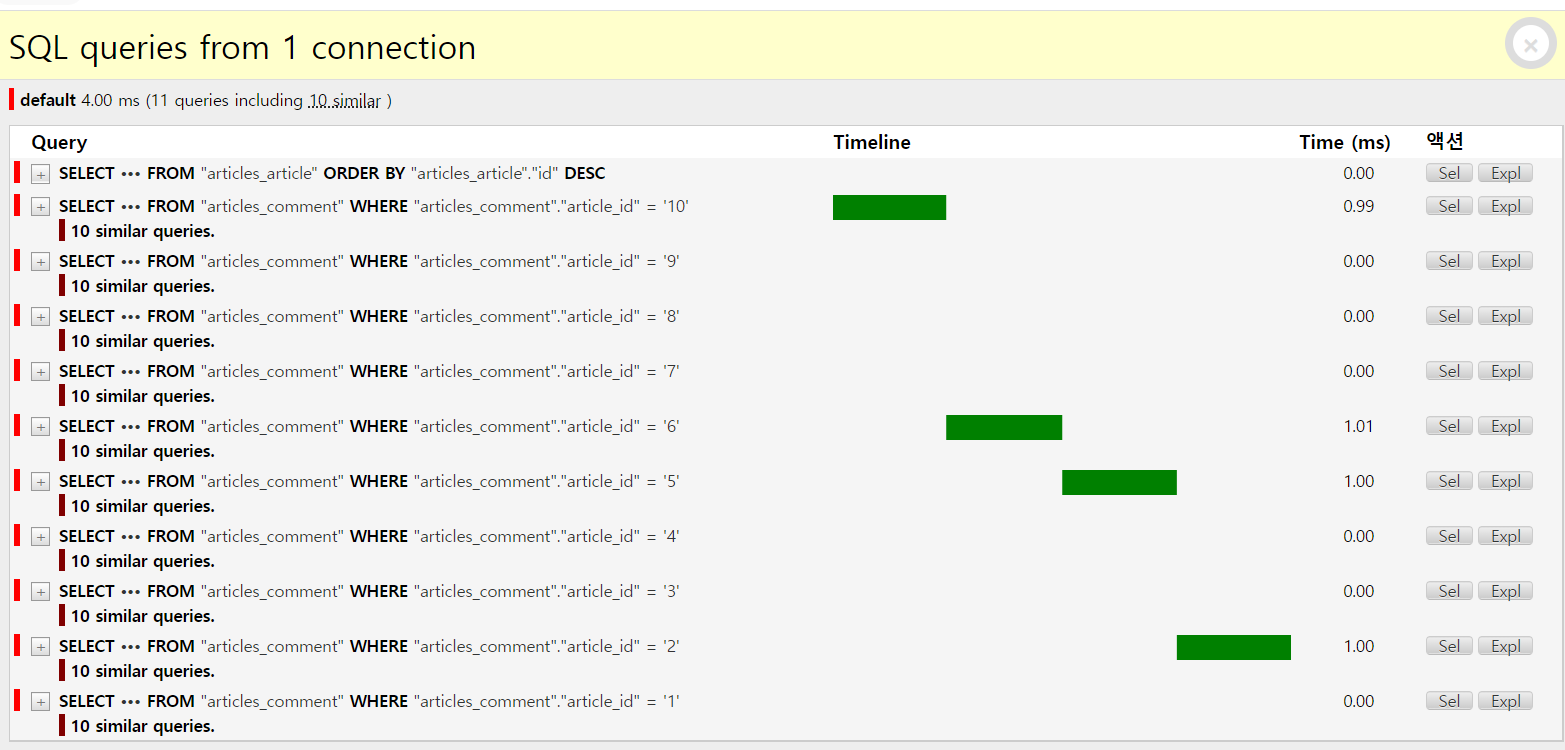
현재 article.comment_set.count가 11번 유사하게 반복되고 있음
why?
- django_html에서 댓글 개수를 출력하는
article.comment_set.count에서의 평가가 매 반복마다 (article의 번호마다) 이루어지고 있는 문제가 있음
- 따라서 반복을 줄일 필요가 있음
- 여기서 원하는 것은 게시글의 댓글 개수이기 때문에, 처음에 조회할 때 한 번에 받아오면 된다.
view함수 개선 (annotate 사용)
def index_1(request):
articles = Article.objects.annotate(Count('comment')).order_by('-pk')
context = {
'articles': articles,
}
return render(request, 'articles/index_1.html', context)
{% block content %}
<h1>Articles</h1>
{% for article in articles %}
<p>제목 : {{ article.title }}</p>
<p>댓글개수 : {{ article.comment__count }}</p>
<hr>
{% endfor %}
{% endblock content %}
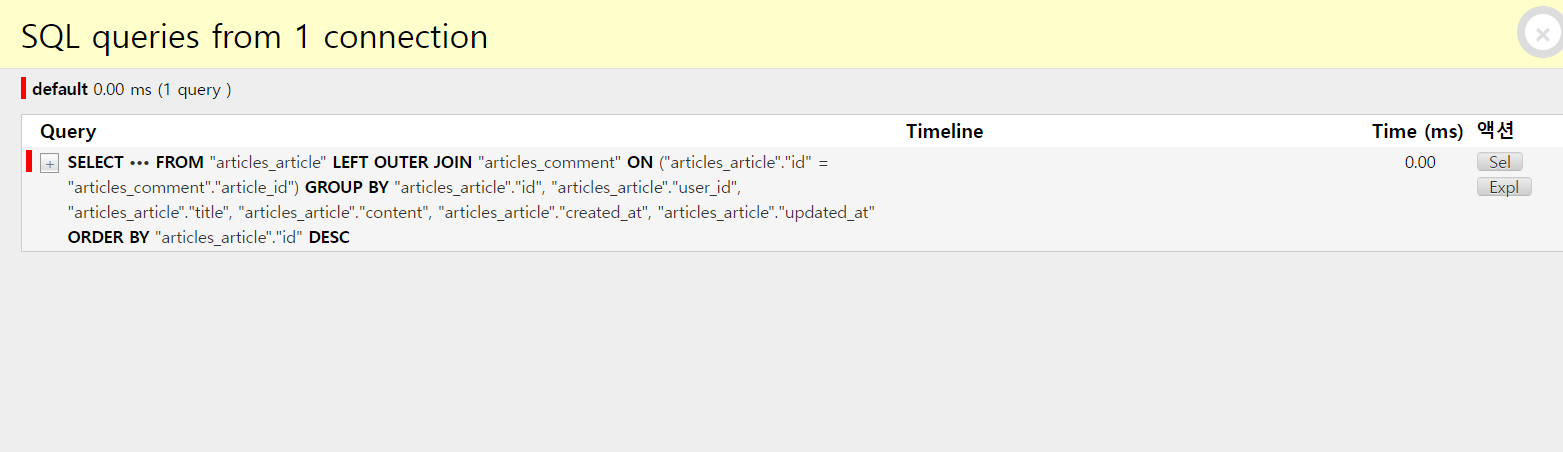
- 11개의 쿼리가 1개로 바뀌었음을 알 수 있음
JOIN
- 두 개 이상의 테이블들을 연결 또는 결합하여 데이터를 출력하는 것을 JOIN이라고 함
- 관계형 데이터베이스의 가장 큰 장점이자 핵심적인 기능
- 일반적으로 PK나 FK 값의 연관에 의해 JOIN이 성립
- SQL JOIN에 대해서는 다양한 Visualization 사이트 참고



