기수 정렬 알고리즘(Radix Sort)
각 자릿수(기수)별로 버킷 정렬을 반복 수행하는 알고리즘
즉, 최하위 자릿수부터 시작하여 최상위 자릿수까지 자릿수별 정렬을 수행하여 정렬한다.
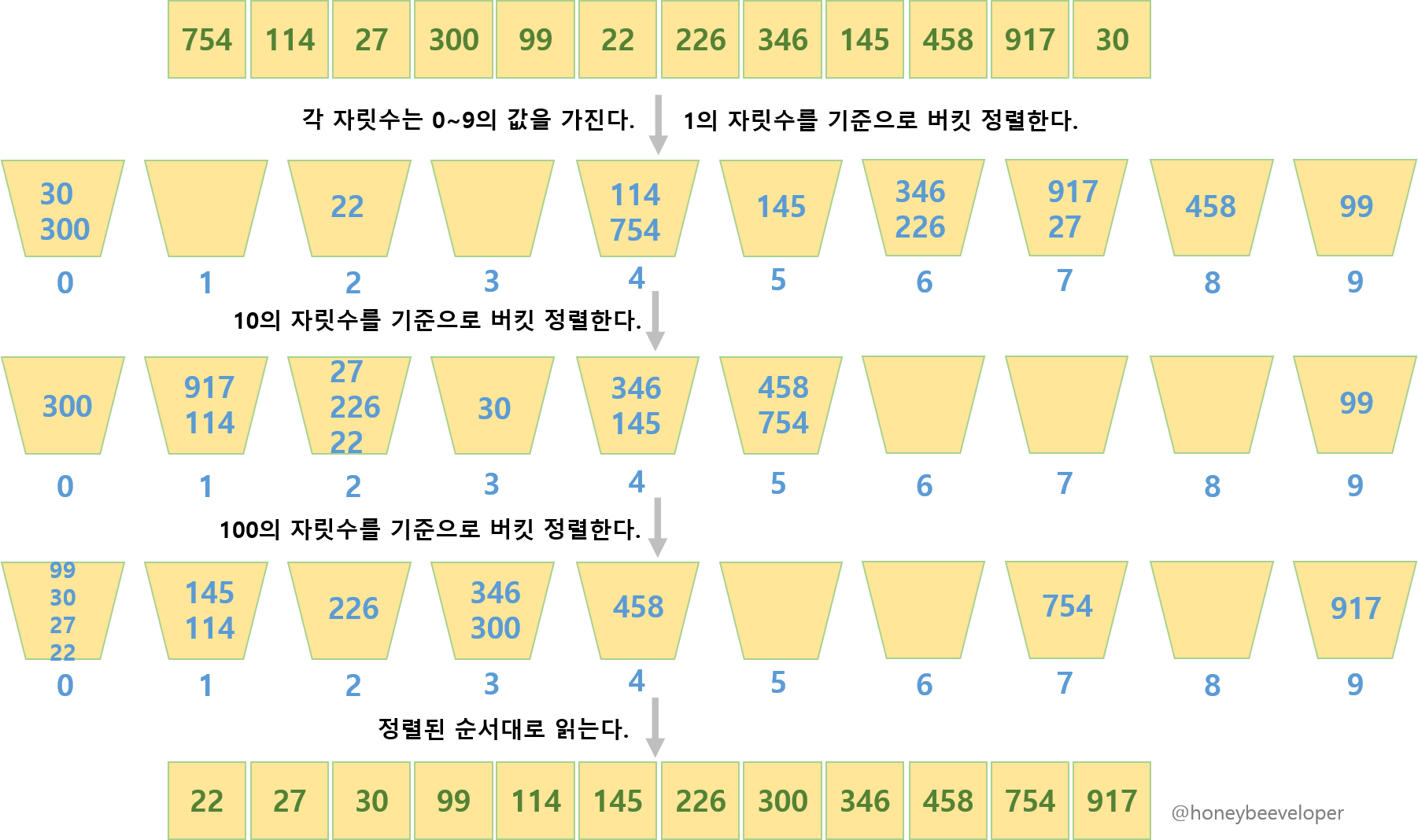
1. 사이즈 12의 정렬할 배열을 가정합니다 (size=12)

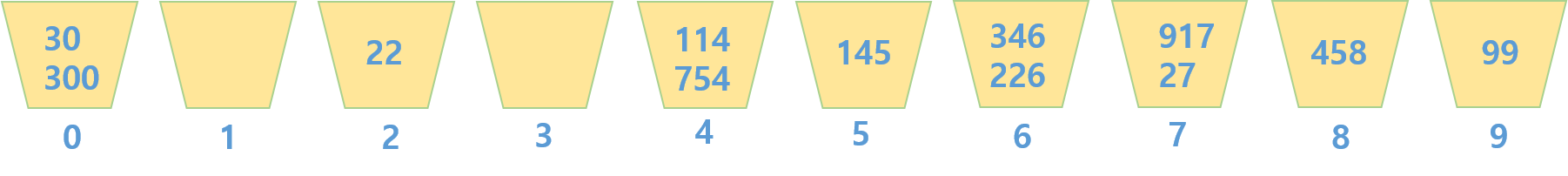
2. 1의 자릿수를 기준으로 정렬한다.
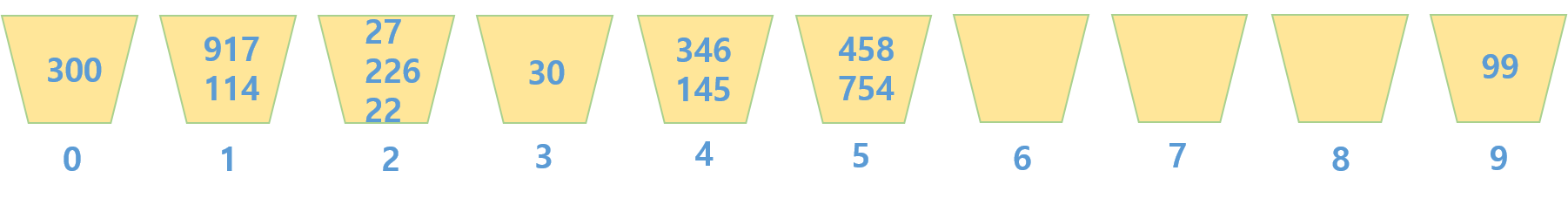
3. 10의 자릿수를 기준으로 정렬한다.
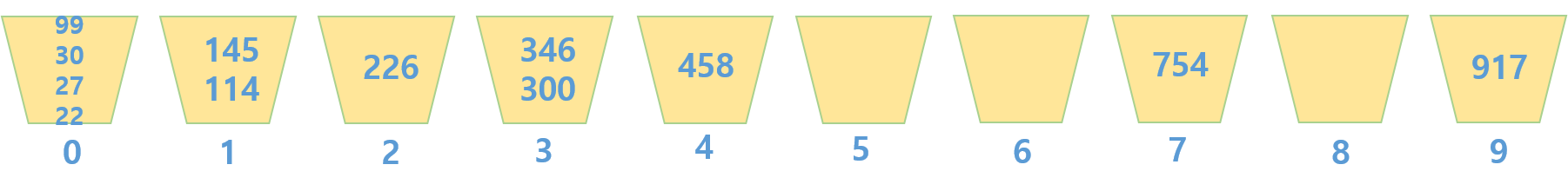
4. 100의 자릿수를 기준으로 정렬한다.
5. 정렬된 순서대로 모읍니다.

기수 정렬 알고리즘 구현
# python 3.8
def countingSort(arr, exp1):
n = len(arr)
# The output array elements that will have sorted arr
output = [0] * (n)
# initialize count array as 0
count = [0] * (10)
# Store count of occurrences in count[]
for i in range(0, n):
index = arr[i] // exp1
count[index % 10] += 1
# Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
# position of this digit in output array
for i in range(1, 10):
count[i] += count[i - 1]
# Build the output array
i = n - 1
while i >= 0:
index = arr[i] // exp1
output[count[index % 10] - 1] = arr[i]
count[index % 10] -= 1
i -= 1
# Copying the output array to arr[],
# so that arr now contains sorted numbers
for i in range(0, len(arr)):
arr[i] = output[i]
# Method to do Radix Sort
def radixSort(arr):
# Find the maximum number to know number of digits
max1 = max(arr)
# Do counting sort for every digit. Note that instead
# of passing digit number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i
# where i is current digit number
exp = 1
while max1 / exp >= 1:
countingSort(arr, exp)
exp *= 10기수 정렬 알고리즘을 제대로 이해하지 않은 좋지않은 방법...?
# python 3.8
def radix_sort(arr):
max1 = max(arr)
len_max = len(str(max1))
exp = 1
while max1 / (10 ** (exp-1)) >= 1:
arr = counting_sort(arr, exp, len_max)
exp += 1
return [j for i in arr for j in i]
def counting_sort(arr, exp, len_max):
bucket = [[], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
for i in arr:
if isinstance(i, list):
for j in i:
idx = str(j).zfill(len_max)[-1 * exp]
bucket[int(idx)].append(j)
else:
idx = str(i)[-1 * exp]
bucket[int(idx)].append(i)
return bucket
github : https://github.com/honeybeeveloper/algorithm/blob/develop/radix-sort.py
참고 : https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/radix-sort
참고 : 책 <그림으로 정리한 알고리즘과 자료구조>