1. 센서의 개념
- 오퍼레이터의 일종
- 특정 조건이 만족되기를 기다리고 만족하면 True를 반환하는 task(주기적으로 check)
- 모든 센서는
BaseSensorOperator를 상속하여 구현되며 이때,BaseSensorOperator는BaseOperator를 상속한다.
상속시에는 __init()__(생성자)함수와 poke(context) 함수 재정의가 필요하다. - 센싱하는 로직은 poke()에서 정의한다.
2. BaseSenser 오퍼레이터 명세 확인
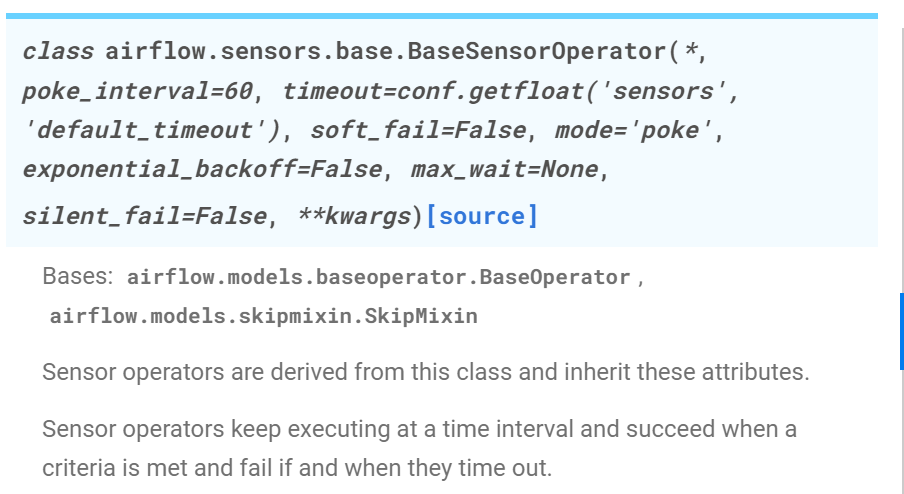
Parameters
soft_fail: fail로 마킹을 하지 말고 skip상태로 마킹을 해라.poke_interval
: 주기적으로 체크하는 주기로 초단위로 넣어준다.timeout
: 이 task가 fail로 마킹이 될 maximum 시간값을 준다.(초단위)
: 만약, daily로 수집할 경우 해당 timeout = 60 X 60 X 24 를 넣어주면 된다.(24시간만 체킹)mode
: 이 옵션은 { poke | reschedule } 중 둘 중 하나만 쓸 수 있다.exponential_backoff
: 이 옵션을 True로 주면 exponential 그러니까 2의 지수승 만큼 체킹하는 주기가 늘어나게 된다. (지수 간격만큼 커진다.)max_wait
: 이건 exponential_backoff가 True가 되었을 때, 사용할 수 있는 옵션으로 exponential_backoff로 인해 체킹 주기가 너무 커지는 걸 방지하는 역할을 한다.
체킹하는 주기의 상한선을 두는 것이다.
BaseSensorOperator method 종류

poke()
: BaseSensorOperator를 상속하는 센서들은 이 메서드를 오버라이딩해야한다.
def poke(self, context: Context) -> bool | PokeReturnValue:
"""Function defined by the sensors while deriving this class should override."""
raise AirflowException("Override me.")Execute()
: BaseOperator를 상속해서 custom_Operator를 만들 때 반드시 Execute를 재정의해야했었다. 그런데, Sensor를 만들 때는 Execute를 반드시 오버라이딩 할 필요 없다.
xcom_value = None
while True:
try:
poke_return = self.poke(context)
except (
AirflowSensorTimeout,
AirflowTaskTimeout,
AirflowSkipException,
AirflowFailException,
) as e:
raise e
except Exception as e:
if self.silent_fail:
logging.error("Sensor poke failed: \n %s", traceback.format_exc())
poke_return = False
else:
raise e
if poke_return:
if isinstance(poke_return, PokeReturnValue):
xcom_value = poke_return.xcom_value
breakpoke()에서 context를 받아서 poke_return을 받아온다. 이때, poke_return은 True/False이다. True라면 break로 빠져나오고, False 값을 만나면, 계속 while문을 빙빙 돌게 된다.
3. BaseSensor 오퍼레이터 Mode 유형
| 비교 | Poke모드 | Reschedule모드 |
|---|---|---|
| 원리 | DAG이 수행되는 내내 Running Slot을 차지. 다만 Slot안에서 Sleep, active 를 반복한다. | 센서가 동작하는 시기에만 slot을 차지한다. 그 외에는 slot을 점유하지 않는다. |
| Wait에서의 Task 상태 | running | up_for_reschedule |
| 유리한 적용 시점 | 짧은 센싱 간격(Interval, 초 단위) | 긴 센싱 가격, 주로 분 단위 Reschedule될 때 스케줄러의 부하 발생 |
Running Slot?
센서가 수행될 때, 차지하는 방('room')이라고 생각하자.
Poke모드는, 그러니까 센서가 특정조건을 만족하는지 체크할 때나 체크하지 않을 때나 항상 Running Slot을 차지한다.
running: 흔히, 초록 상태 떠올리면 된다.

Reschedule모드는 센서가 특정조건을 만족할 때에만 Running Slot을 차지한다. 만약, 조건을 만족하지 않아서 False가 되면 Running Slot을 빠져나오게 된다.
up_for_reschedule: 스케줄러에 의해 다시 한번 스케줄링이 되기를 기다리는 상태, 이건 민트 색깔을 가지고 있다.

스케줄러에 의해 다시 한번 up_for_reschedule 되는 것은 스케줄러에게 부하를 발생하기 때문에, 짧은 센싱 간격(초단위)일 경우는 Poke모드를, 긴 센싱 간격(분단위)일 때는 Reschedule모드를 선택하자.
Pool이란
모든 Task는 특정 Pool에서 수행되며 Pool은 Slot이라는 것을 가지고 있다. 기본적으로 Task 1개 당 Slot 1개를 점유하며 Pool을 지정하지 않으면 default_pool에서 수행된다.
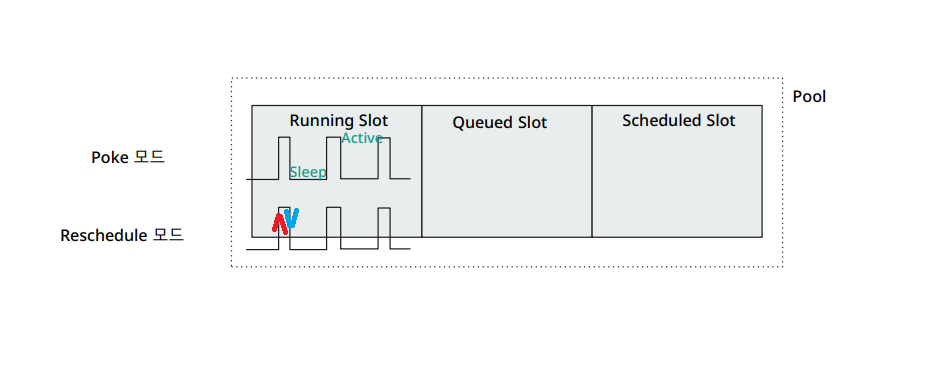
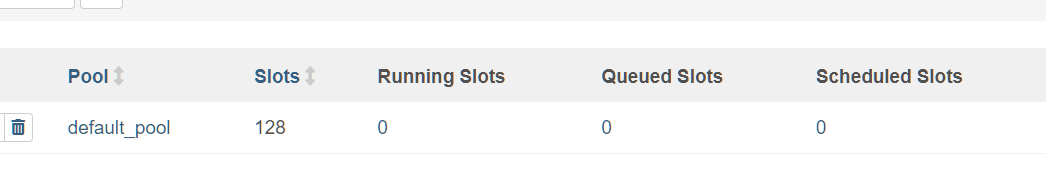
나의 경우, default_pool에 slots이 128개 존재한다. Slot에는 Running Slots 과 Queued Slots, Scheduled Slots가 있다.
Poke모드의 경우 계속해서 Running Slot을 점유하는 상태를 말하며, Reschedule모드는 True/False 결과에 따라 True면 Running Slot을 점유, False면 밖으로 Slot을 점유하지 않는다.

