MongoDB는 관계형 데이터베이스(RDBMS)처럼 직접적으로 모델 간의 관계를 설정할 수 없습니다. 하지만 Mongoose를 사용하면 다른 문서(Document)들을 참조(Reference)하여 관계를 표현할 수 있습니다.
이번 글에서는 Post(게시글) 와 Author(작성자) 모델, 그리고 Profile(프로필) 사용하여 관계를 설정하고, populate()를 활용하여 데이터를 조회하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
1. Mongoose로 MongoDB에서 관계 설정하기: Post와 Author 예제
아래 코드에서는:
- Post(게시글) 모델은 authorId를 통해 Author(작성자)를 참조합니다.
- Author(작성자) 모델은 profileId를 통해 Profile(프로필)을 참조합니다.
- 즉, Post → Author → Profile 형태의 중첩된 관계를 가진 예제입니다.
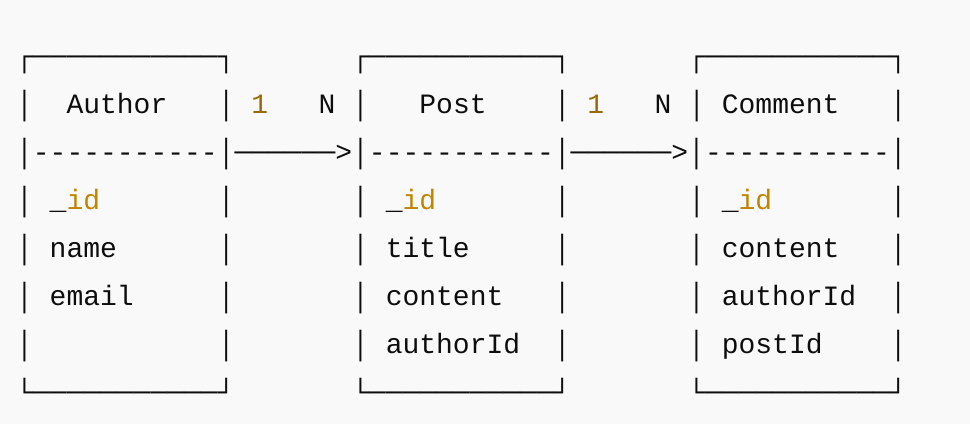
Post 모델 (작성자 정보 참조)
authorId 필드를 통해 작성자 정보를 참조하게 합니다.
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const Schema = mongoose.Schema;
const postSchema = new Schema({
_id: Schema.Types.ObjectId,
title: { type: String, required: true },
content: { type: String, required: true },
authorId: { type: Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: "Author", required: true }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("Post", postSchema);Author 모델 (작성자 프로파일 참조)
작성자의 정보를 저장하는 모델입니다. 작성자의 세부 사항은 별도의 프로파일 모델을 참조합니다.
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const Schema = mongoose.Schema;
const authorSchema = new Schema({
_id: Schema.Types.ObjectId,
name: { type: String, required: true },
email: { type: String, required: true },
profileId: { type: Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: "Profile" }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("Author", authorSchema);Profile 모델
작성자의 추가 프로필 정보를 저장하는 모델입니다.
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const Schema = mongoose.Schema;
const profileSchema = new Schema({
_id: Schema.Types.ObjectId,
bio: { type: String, required: true },
website: { type: String }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model("Profile", profileSchema);데이터 생성하기
이제 Author, Profile, Post 데이터를 생성하여 MongoDB에 저장해 보겠습니다.
....
const profile = new Profile({
_id: new mongoose.Types.ObjectId(),
bio: "web developer",
website: "https://example.com"
});
const author = new Author({
_id: new mongoose.Types.ObjectId(),
name: "jason",
email: "jason@example.com",
profileId: profile._id
});
const post = new Post({
_id: new mongoose.Types.ObjectId(),
title: "post title",
content: "post content",
authorId: author._id
});populate() 없이 조회하기
populate()를 사용하지 않으면 authorId 필드에는 단순히 ObjectId만 포함됩니다
...
app.get("/", async (req, res) => {
const posts = await Post.find();
res.send(posts);
});posts 에 담긴 내용
[
{
"_id": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a4",
"title": "post title",
"content": "post content",
"authorId": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a3",
}
]populate()를 사용하여 데이터 조회하기
이제 authorId 필드에 작성자 정보가 포함됩니다.
...
app.get("/", async (req, res) => {
const posts = await Post.find().populate("authorId");
res.send(posts);
});posts 에 담긴 내용
[
{
"_id": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a4",
"title": "post title",
"content": "post content",
"authorId": {
"_id": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a3",
"name": "jason",
"email": "jason@example.com",
"profileId": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a2",
}
}
]populate() 중첩 사용
만약 작성자의 프로필(Profile) 정보까지 가져오려면 populate()를 중첩해서 호출하면 됩니다. 이제 profileId 필드에 작성자의 프로필 정보도 포함된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
...
app.get("/", async (req, res) => {
const posts = await Post.find()
.populate({
path: "authorId",
populate: { path: "profileId" }
});
res.send(posts);posts 에 담긴 내용
[
{
"_id": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a4",
"title": "post title",
"content": "post content",
"authorId": {
"_id": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a3",
"name": "jason",
"email": "jason@example.com",
"profileId": {
"_id": "65f6e9788677062e69814c2a2",
"bio": "web developer",
"website": "https://example.com",
}
}
]2. populate()의 한계점
-
쿼리 성능 문제
populate()는 내부적으로 추가적인 쿼리 실행을 발생시킵니다.
중첩된 populate()가 많아질수록 성능이 저하됩니다. -
데이터 일관성 문제
중복된 데이터 저장(denormalization)으로 해결해야 합니다.
3. 정리
- Mongoose에서는 ref 옵션을 사용하여 다른 문서를 참조할 수 있습니다.
- 중첩된 populate()를 사용할 경우 성능 저하를 주의해야 합니다.
- 관계가 깊어질 경우 데이터 정규화보다는 필요한 데이터만 포함하는 방법을 고려해야 합니다.