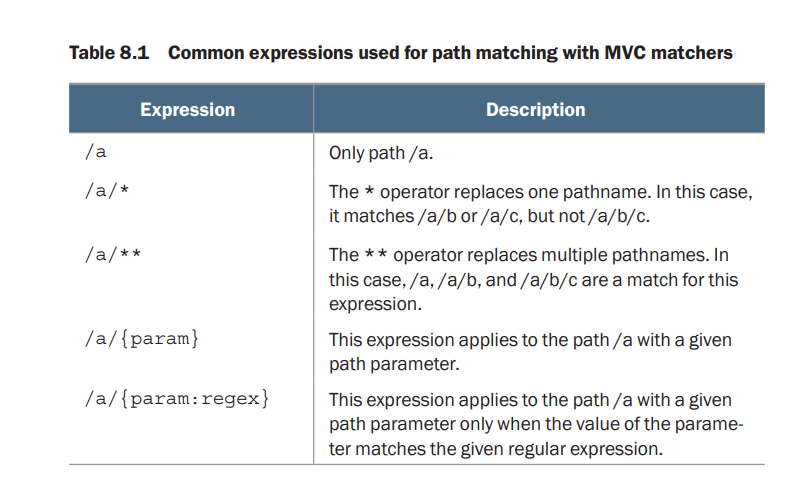
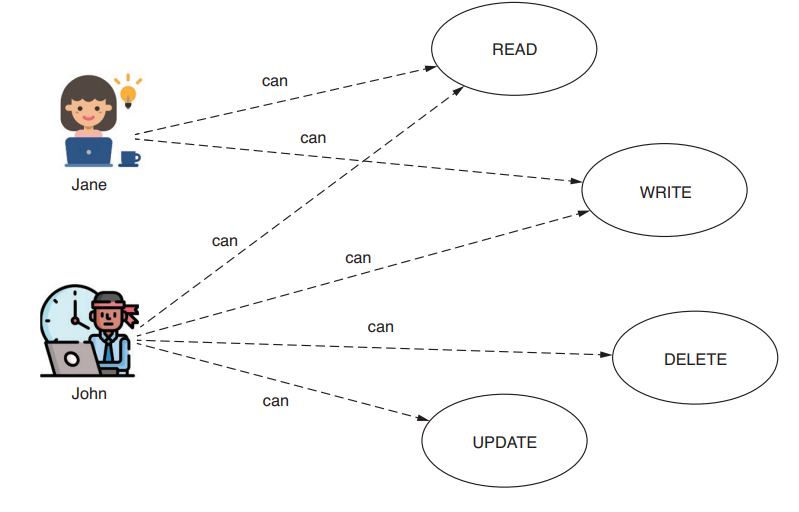
air-dnb 애플리케이션에서 권한은 크게 두가지다.
user와 host 이렇게 설정을 해두고
api에 대한 권한을 조정할 계획이다.
public interface GrantedAuthority extends Serializable {
String getAuthority();
}
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
}
@Entity
@NoArgsConstructor
@Getter
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "user_id")
private Long id;
private String loginId;
private String name;
private String password;
private String address;
private LocalDate birthdate;
private String authority = "user";
(중략)
public void enrollHost() {
if (this.host == null) {
Host host = new Host();
host.setUser(this);
this.host = host;
this.authority = "host";
}
}
만약, host가 된다면 권한은 "host"로 변경된다.
}
//기본적으로 user가 되면 "user" 권한을 디폴트 값으로 갖는다.@Bean
SecurityFilterChain configure(HttpSecurity http, AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider) throws Exception {
http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable).httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults());
http.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
http.authorizeHttpRequests(c->
c
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST,"/user").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/error").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/user/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
);
return http.build();
}authorizeHttpRequests() 이 메서드는 엔드포인트에 대해서 권한과 관련된 규칙을 설정하게 해준다. anyRequest()는 모든 요청에 적용된다.
여기서 .anyRequest().hasAnyAuthority("read", "write"));를 해줄 수도 있는데 대신에 role을 사용하는 것도 괜찮을 거 같다.
user는 a,b권한을 갖고 host는 a,b,c 권한을 갖는 식으로 말이다. 그러면 user의 디폴트 권한은 "ROLE_USER"이고, host로 등록할 때 기 값이 "ROLE_HOST"로 변경된다.
http.authorizeHttpRequests(c->
c
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST,"/user").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/error").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/user/login").permitAll()
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/accommodations").hasRole("ROLE_HOST")
.anyRequest().permitAll());
return http.build();