두번째 ML접근 눈문 리뷰입니다:) 이번 논문 역시 내용과 result 위주보다는 연구에서 활용한 통계 분석 방법론 위주로 정리해 보겠습니다^^
본 논문에서는 a broad panel of time-to-event ML models들을 비교하여 환자의 생존율을 예측하는 모델을 사용하였습니다. 비교적 최근 개발된 neural network 기반 모델 및 boosting algorithm에 근거한 XGBSE를 사용했다는 점에서 분명 주목할 점도 존재합니다. 활용한 모델은 아래와 같습니다.
-Elastic net penalized Cox proportional hazards regression
-Elastic net penalized Weibull accelerated failure time regression
-DeepSurv: a neural network approach using a loss function derived from a Cox proportional hazard model
-Random Survival Forests
-XGBoost Survival Embeddings: a popular stochastic gradient boosting algorithm using a loss function derived from a Weibull regression
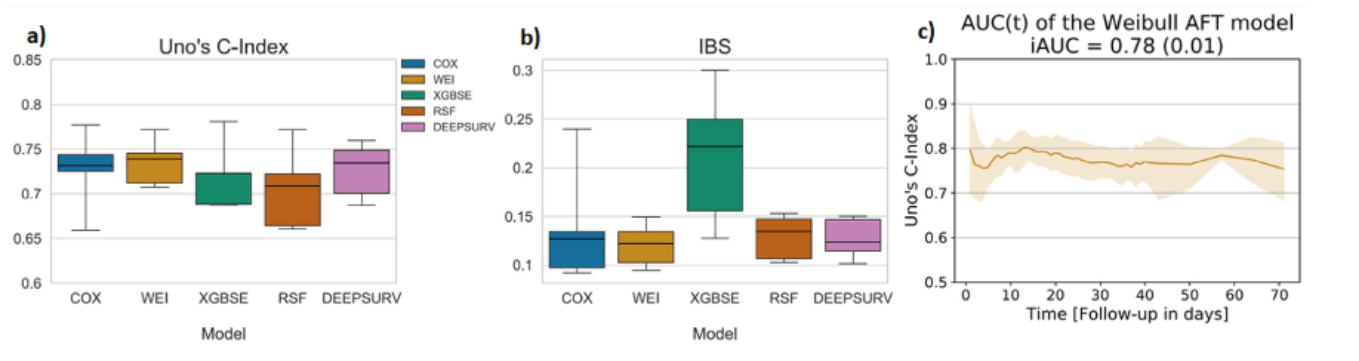
Figure-(a)는 모델 평가에 대한 Uno's C-index의 결과 값 boxplot 비교,
Figure-(b)는 Integrated Bier Score(IBS)를 통한 model calibration error의 boxplot 비교, Figure-(c)는 Weibull AFT 모델에 의한 IAUC(integrated AUC)-mean AUC over time의 95% CI입니다.
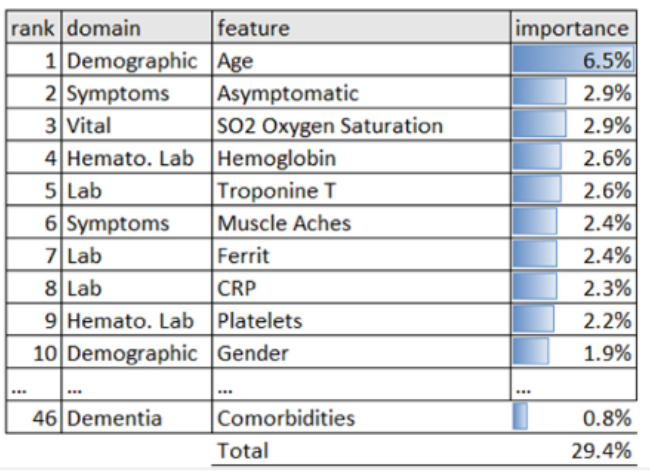
위 figure의 경우, Absolute SHAP values(Shapely Additive Explanations)를 활용하여 Feature Importance를 상위 변수와 해당하는 domain을 제시하였습니다.
SHAP에 관한 framework를 살펴보도록 하면,
individual feature attributes의 outcome에 대한 기여도를 측정하는 것입니다.
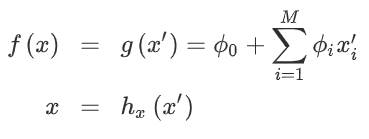
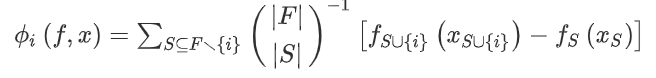
다소 식이 복잡할 수 있지만 결국 SHAP value는 위의 식들을 토대로 a weighted (binomial coefficient) sum of the differences between (in square brackets) “prediction including the feature” - “prediction excluding the feature”로 정의할 수 있습니다.
