System Call - File Descriptor
The Linux/Unix Kernel
- kernel은 computer가 처음 시작될 때, disk에서 RAM으로 program을 load해준다.
- 커널은 여러 프로세스, application 사이에서 CPU, RAM, Disk를 공유할 수 있도록 한다.
- application들이 보내는 system call을 처리한다
- peripherals(마우스, 키보드, 모니터 등 주변 기기)들을 관리한다.
Linux Operating Systems
User space와Kernel space로 나눠져 있다.
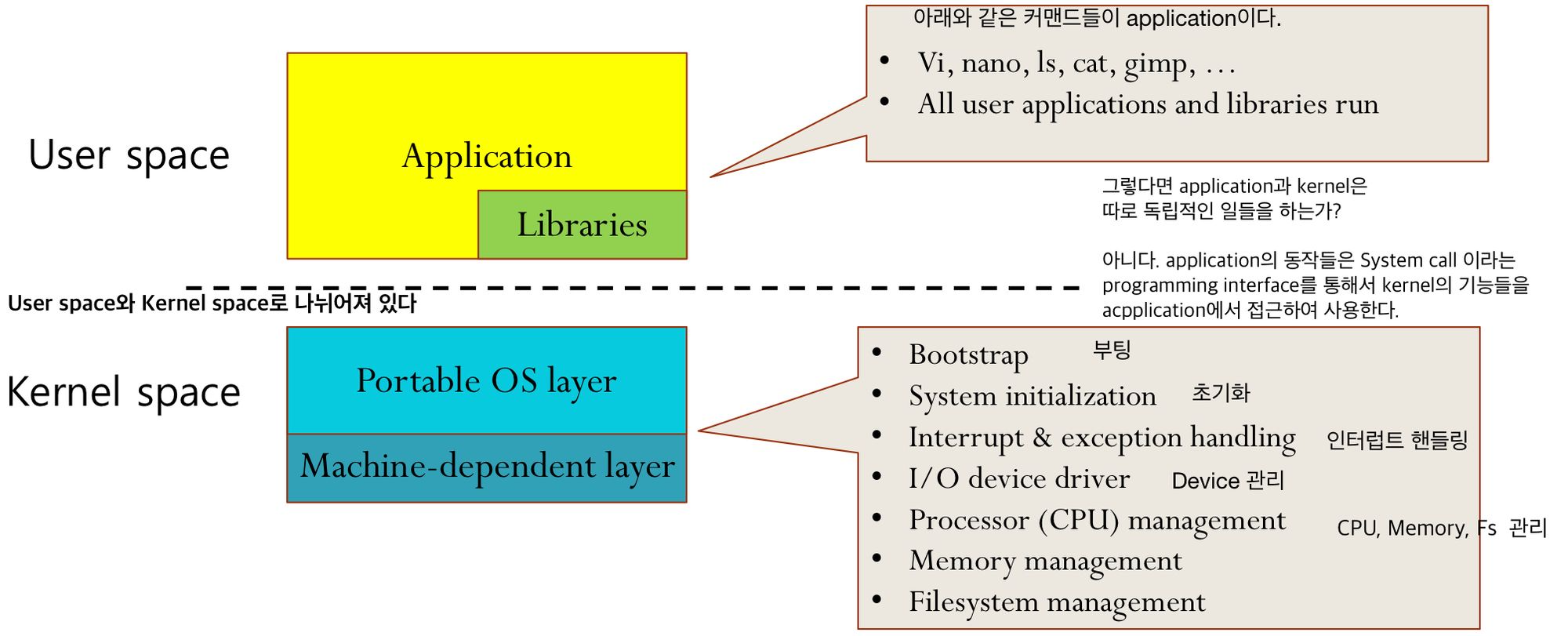
System Call
- System call은 application이 Linux kernel의 기능을 사용하기 위해 대화하는 방법이다.
- System call은 Linux kernel에 대한 programmer’s functional interface 이다.
- System call are just like binary routines, call directly into the heart of Linux Kernel.
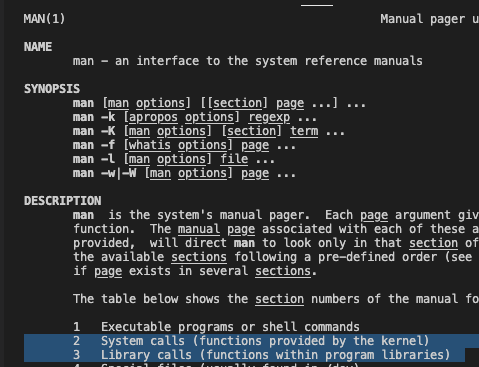
- 어떤 함수가 있을 때,
- system call인지? 확인하고 싶으면, man 2 함수
- library인지? 확인하고 싶으면, man 3 함수
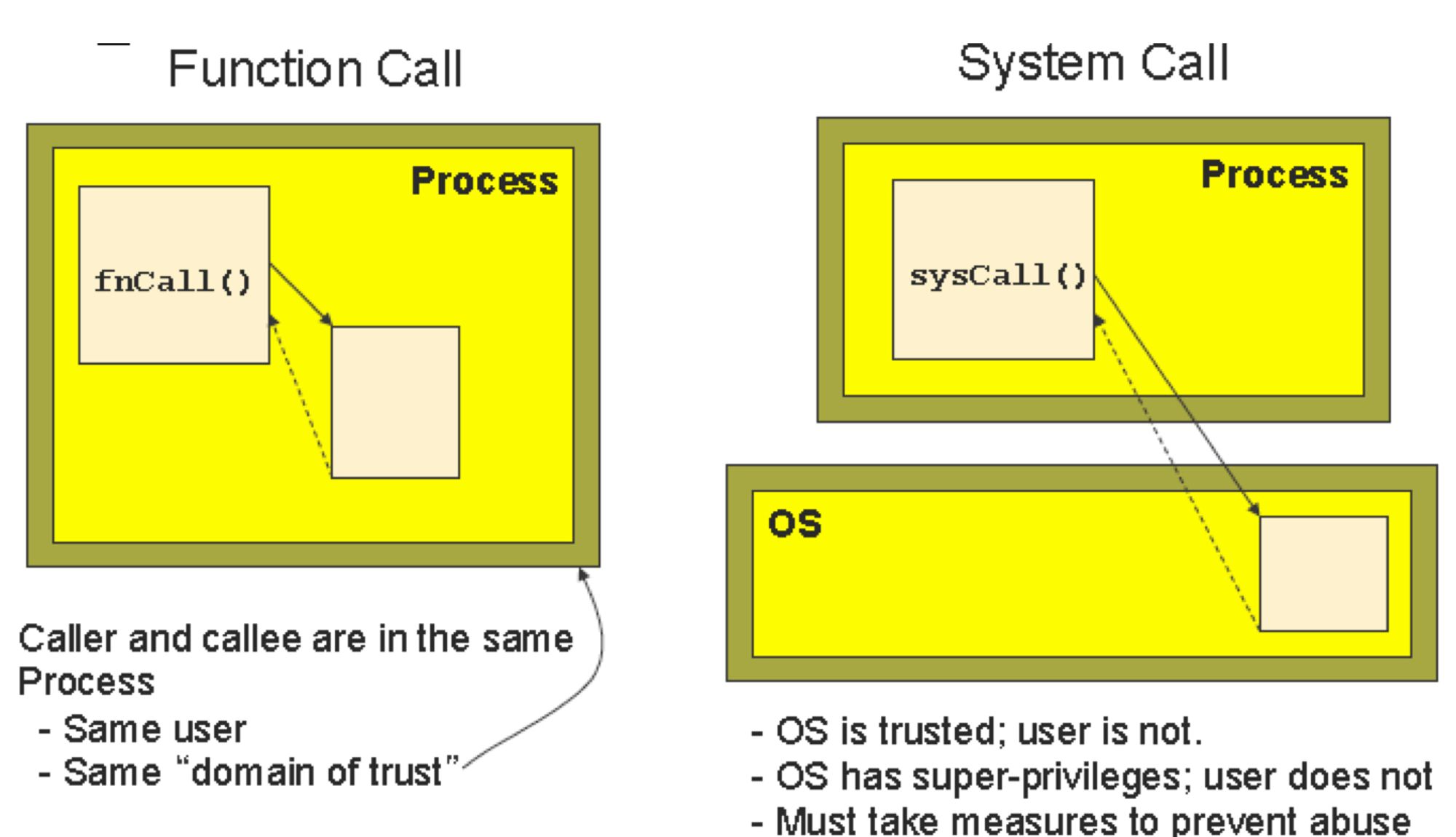
System Calls VS Function Calls
-
Function Call:- 어떤 함수에서 다른 함수를 호출할 때를 Function Call.
- Kernel Space까지 내려가지 않고, User space에 있는 함수들끼리 호출관계가 있다.
-
System Call:- User space가 아니라 Kernel에 있는 루틴으로 처리된 결과가 프로세스에 적용된다.
- Kernel Space까지 내려가 커널 내부에 존재하는 함수(sub routine)들을 호출하여 커널의 기능을 사용한다.
Linux에는 system call이 몇 개 있을까?
man syscalls
- C, C++ programming lanuguage에서 unistd.h는 POSIX OS API에 대한 access를 제공하는 header file.
단일 UNIX 사양의 기반인 POSIX.1 표준에 의해 정의되므로 모든 POSIX 호환 OS 및 compiler에서 사용.
system call은 각각이 고유한 번호를 갖고 있음.
User program이 Kernel에 어떤 system call을 요청할지 정할 때, 이 번호를 사용함.- in window, vi /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/asm/unistd.h
in ubuntu, vi /usr/include/asm-generic/unistd.h


- in window, vi /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/asm/unistd.h
Don’t mix system calls with standard library calls
-
Examples of System Calls:
getuid(), fork(), exec(), ... -
C Standard library Calls:
Is printf() a system call? No.
write(2)라는 system call이 있고, 그것의 사용을 편리하게 만든 C library function이 printf(3)이다.
write() 함수는 버퍼에 있는 내용을 그대로 출력하지만,
printf() 함수는 표준 출력 모드로 동작하여 종료 문자(\n,\0)을 만났을 때 내용을 출력하기 때문에
write() 과 printf() 을 혼합하여 사용하는 것은 좋지 않다.
POSIX
-
POSIX(Portable Operating System Interface): UNIX 계열의 운영체제에 사용되는 명령어들(system call)의 표준을 정의.
대부분은 POSIX standard를 준수 + 이외의 기능을 정의하며 서비스를 제공함.
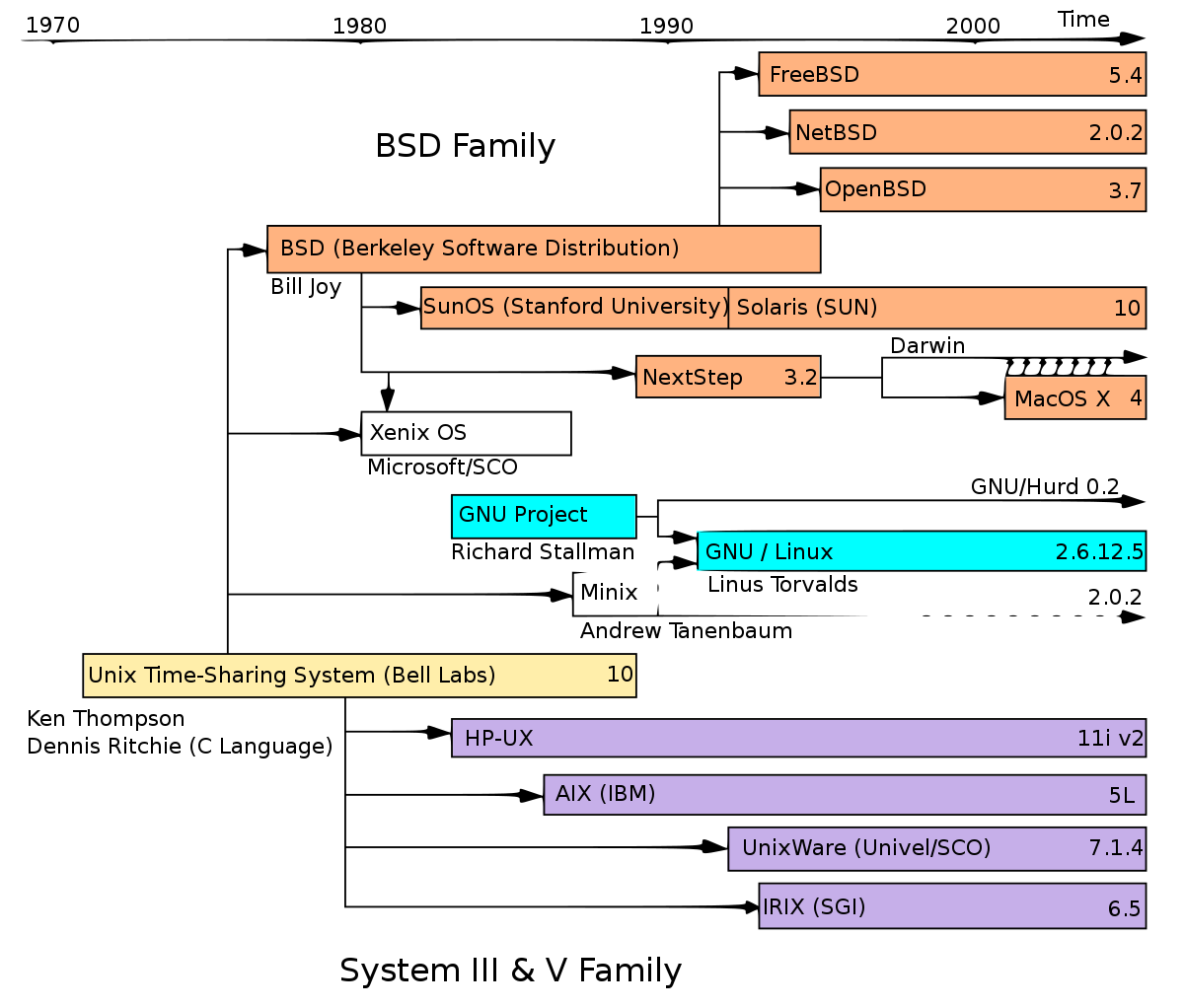 (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Timeline_of_Unix_families.svg)
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Timeline_of_Unix_families.svg)- UNIX 계열 운영체제에 여러 변종들이 많이 나오면서,
system call들이 서로 조금씩 달라지면서 소스코드 간의 호환성에 문제가 발생하였다..
이를 해결하기 위해 표준이 등장. POSIX - UNIX 운영체제에 관련된 system call, C library 등이 정의되어 있다.
- UNIX 계열 운영체제에 여러 변종들이 많이 나오면서,
-
POSIX는 여러 개의 chapter로 이루어져 있다.

Handling system call erros
- System call returns status value indicating whether the call succeeded or failed.
- all system calls return a value of -1 if an error occurs.
- Every process contains a global variable called "errno",
errno: The header file "error.h" contains a list of the predefined error
우리가 선언하지 않아도 전역변수로 선언되어 있음.

perror(): a library function that describes system-call errors.
errno은 번호로 return되기 때문에 어떤 error인지 확인하기 쉽지 않다.
따라서 perror()로 사람이 읽기 쉽게 설명된 error를 출력해준다.
정리)
System call은 그것이 성공하거나 실패했을 때 status value를 return.
모든 system call은 error가 발생하면,-1 return한다.
모든 process는“errno”이라는 global variable을 갖고 있다.
errno 변수는 우리가 define하는 것이 아니라<errno.h>에 define되어 있기 때문에 그냥 사용하면 된다.
perror()는 errno에 해당하는 사람이 읽을 수 있는 문자열로 return 해주는 function이다.
따라서 errno 변수와 perror() 함수를 사용하기 위해 <errno.h> 헤더파일을 include 해야 한다.
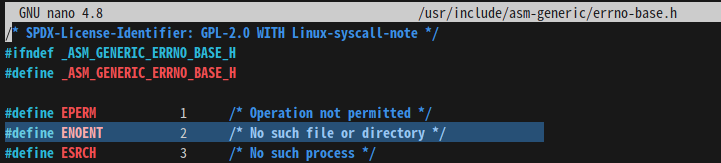
"error.h"
- vi /usr/include/asm-generic/
errno-base.h: 기본적인 errno에 대해 확인
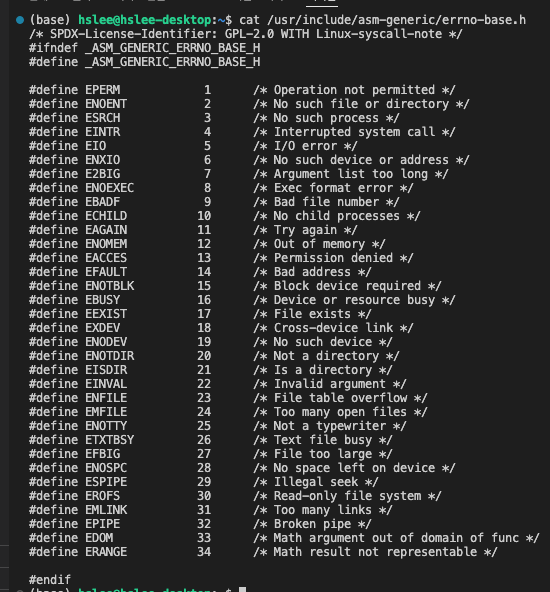
- vi /usr/include/asm-generic/
errno.h: errno에 대한 자세한 정보 확인
- vi /usr/include/asm-generic/
man 2 getpid()
-
system call 관련 manual page를 보기 위해서는
man 2
-
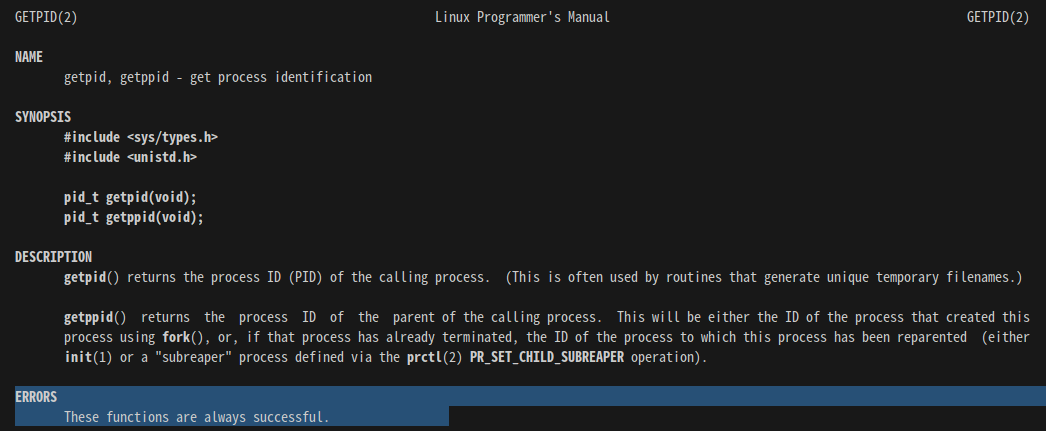
ERRORS: 항상 systemcall의 manual page에서 ERRORS를 살펴봐야 한다.
-
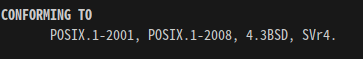
CONFORMING TO: 여러 unix 계열이 있는데, 어떤 시스템에서 사용이 가능한지? (소스레벨에서의 호환성. binary 레벨과 다름)
-
SYNOPSIS:
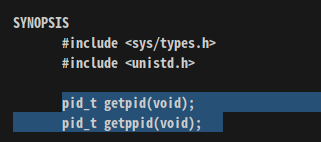 platform 간 차이(0x32, 0x86)를 없애기 위해
platform 간 차이(0x32, 0x86)를 없애기 위해 pid_t type을 사용.
size_t, pid_t같은 자료형들은 sys/types.h 헤더파일에 정의되어 있는 primitive data type이라고 한다.
운영체제에 따라 data type의 크기와 표현방식이 다르기 때문에 보다 portable한 프로그램을 만들기 위해 사용한다.
Example

pid = 845619
ppid = 843030 = bash id
"1_pid" 실행파일을 실행시킨 parent process가 bash라는 것을 알 수 있다.
strace
strace: 프로그램의 시스템콜이 호출되는 것을 추적하여 보여준다.
strace ./실행파일명:
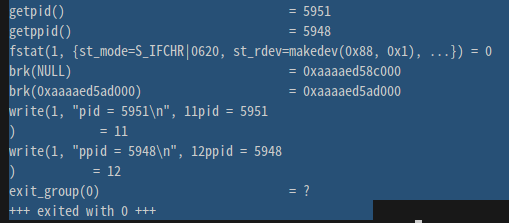
1_pid process에서 호출한 system call 정보를 보여줌
printf() library는 실제로 write()라는 system call로 동작하는 것을 알 수 있다.
In Unix, Everything is a file
- Unix에서 실제로 모든 것이 파일은 아니고
CPU, Memory, File, 통신 채널 등이 파일을 통해서 접근이 가능하다.

File Descriptors
-
파일을 사용하기 위해, 커널에 해당 파일을 사용하겠다는 의사를 표현하고,
해당 파일에 대한file descriptor를 얻어야 한다. (Non - negative integer) -
보통 descriptor는 open() 이라는 system call을 통해서 얻어와야 하는데,
그렇지 않고도 이미 open되어 있는 descriptor가 3개가 있다.Standard file descritpors
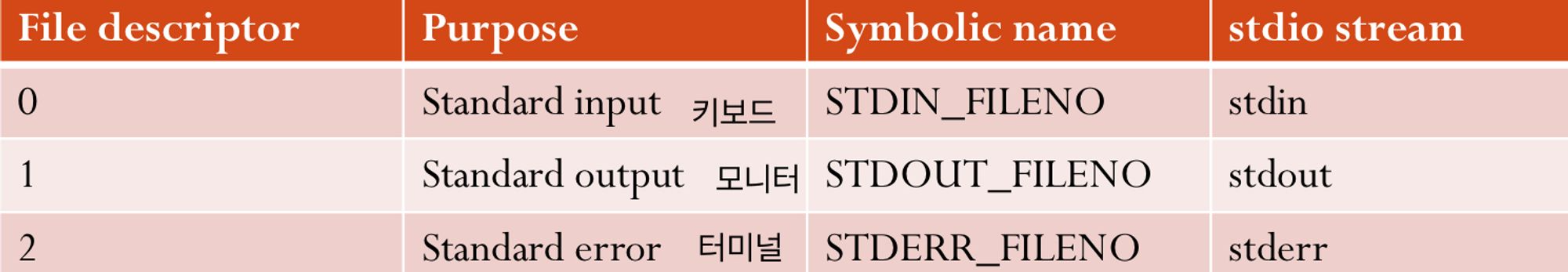
Open, Close
- int open(const char* pathname, int flags, mode_t mode)
- const char* pathname: file path
- int flags : 어떤 권한으로 파일을 open할 건지? (R? W? RW?)

위 세가지 이어서(|) 추가적으로,
- mode_t mode : 파일을 새로 생성할 때, 의미가 있음.
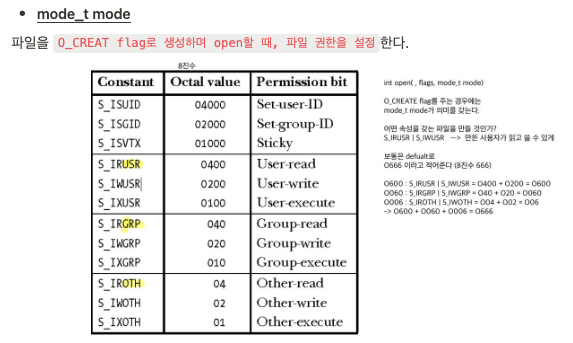
Example
- open 성공, 실패 :
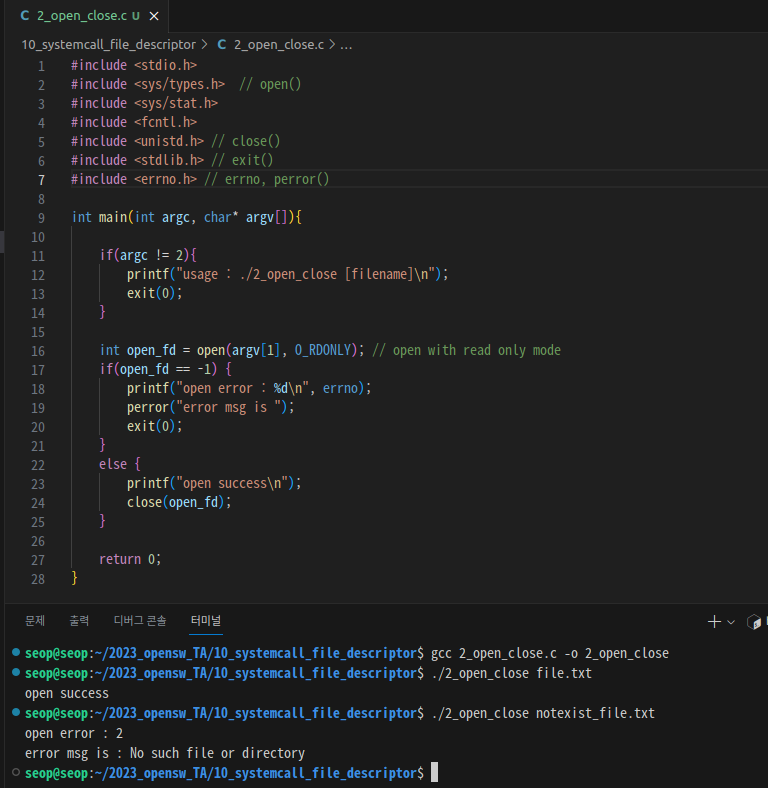
- errno = 2, perror() msg 이유 :
- errno = 2, perror() msg 이유 :
Read
- ssize_t read(int fd, void* buf, size_t nbytes);

- the number of bytes(nbytes)보다 작은 bytes가 return되는 경우
- EOF reached before requested number of bytes have been read
- Reading from a terminal device, one "line" read at a time
- socket으로 data를 받는데, network가 좋지 않아서 몇 개의 data만 받은 경우
- Interruption by a signal
- the number of bytes(nbytes)보다 작은 bytes가 return되는 경우
Example
- open, read, close :
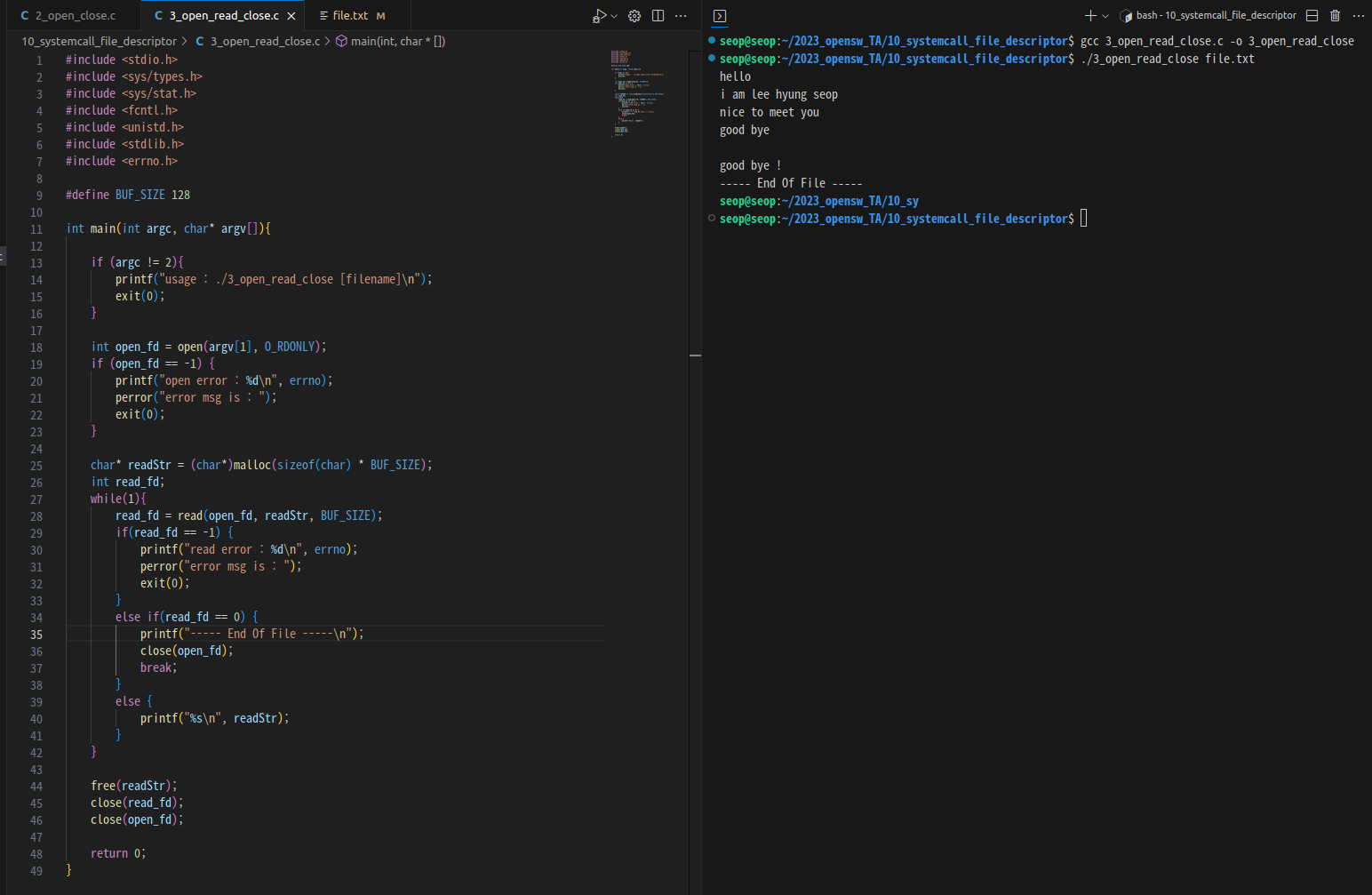
lseek
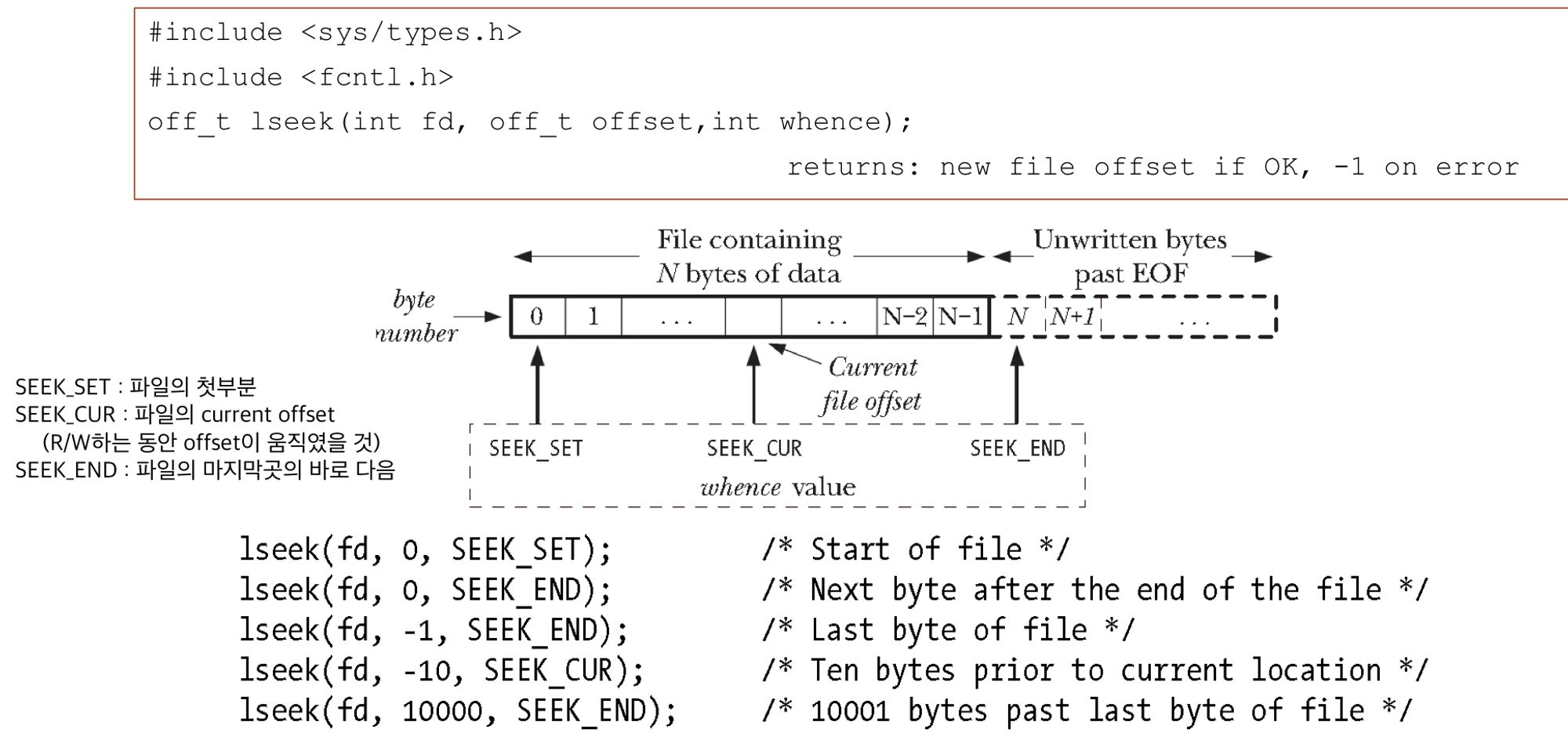
- lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence)
fd에 해당하는 filed이 offset을 원하는 위치로 이동시키는 system call.
whence는 기준점. 기준점을 기준으로 offset만큼 떨어진 곳으로 포인터 이동.
whence에는 3가지 옵션이 있다.SEEK_SET: 현재 file의 시작 지점부터 offset만큼 떨어진 곳으로 이동SEEK_CUR: 현재 file offset으로부터 offset만큼 떨어진 곳으로 이동SEEK_END: 현재 file의 마지막 지점의 그 다음부터 offset만큼 떨어진 곳으로 이동
Open, Read, Write, Close
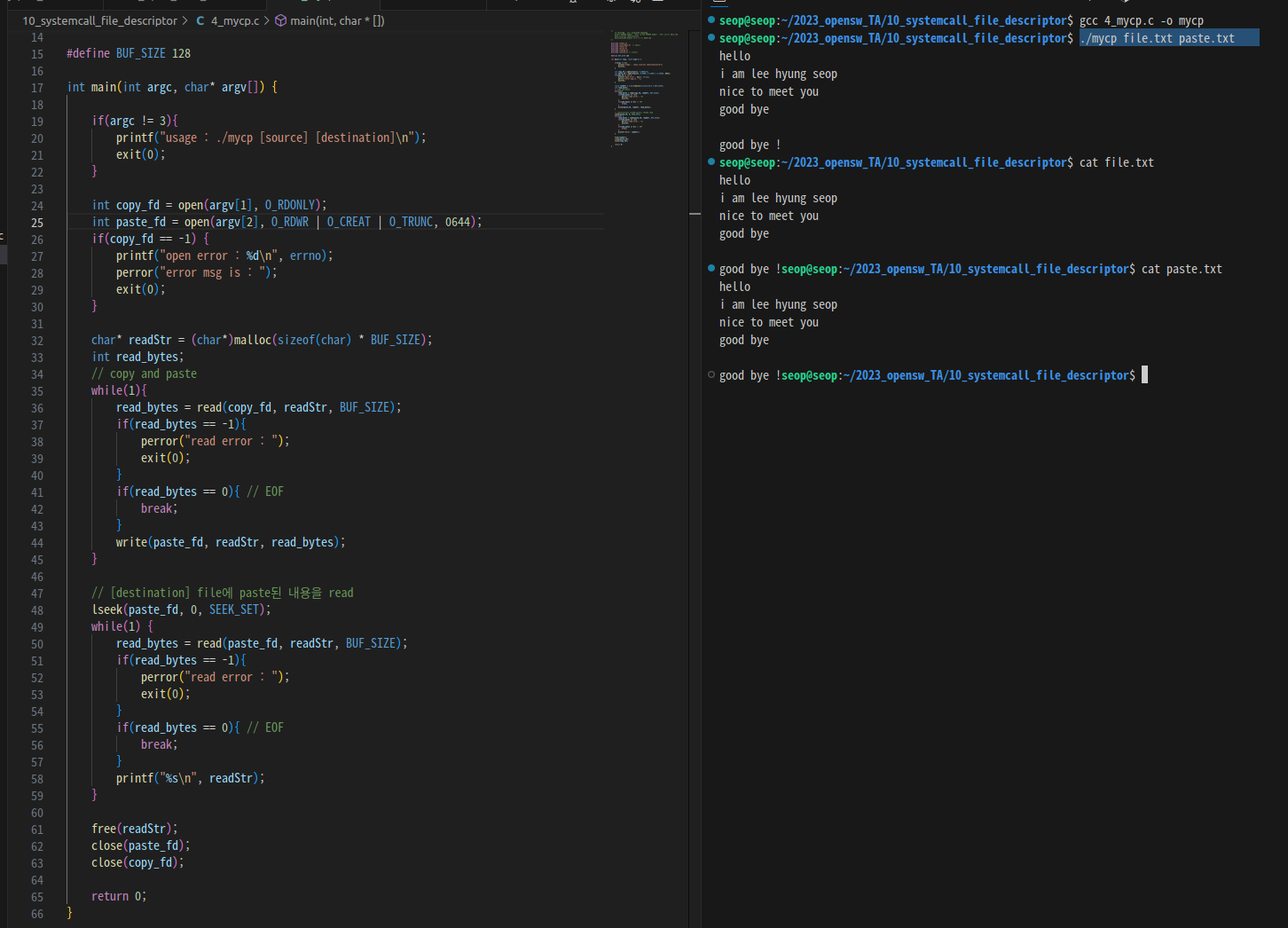
Example (cp 명령어 구현)
Example (tee 명령어 구현)
tee: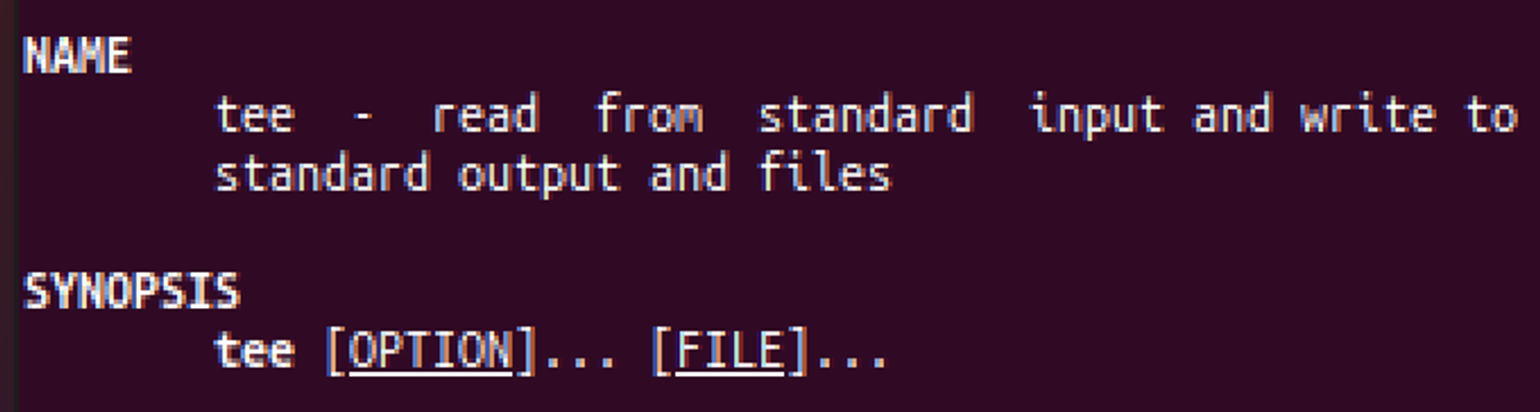
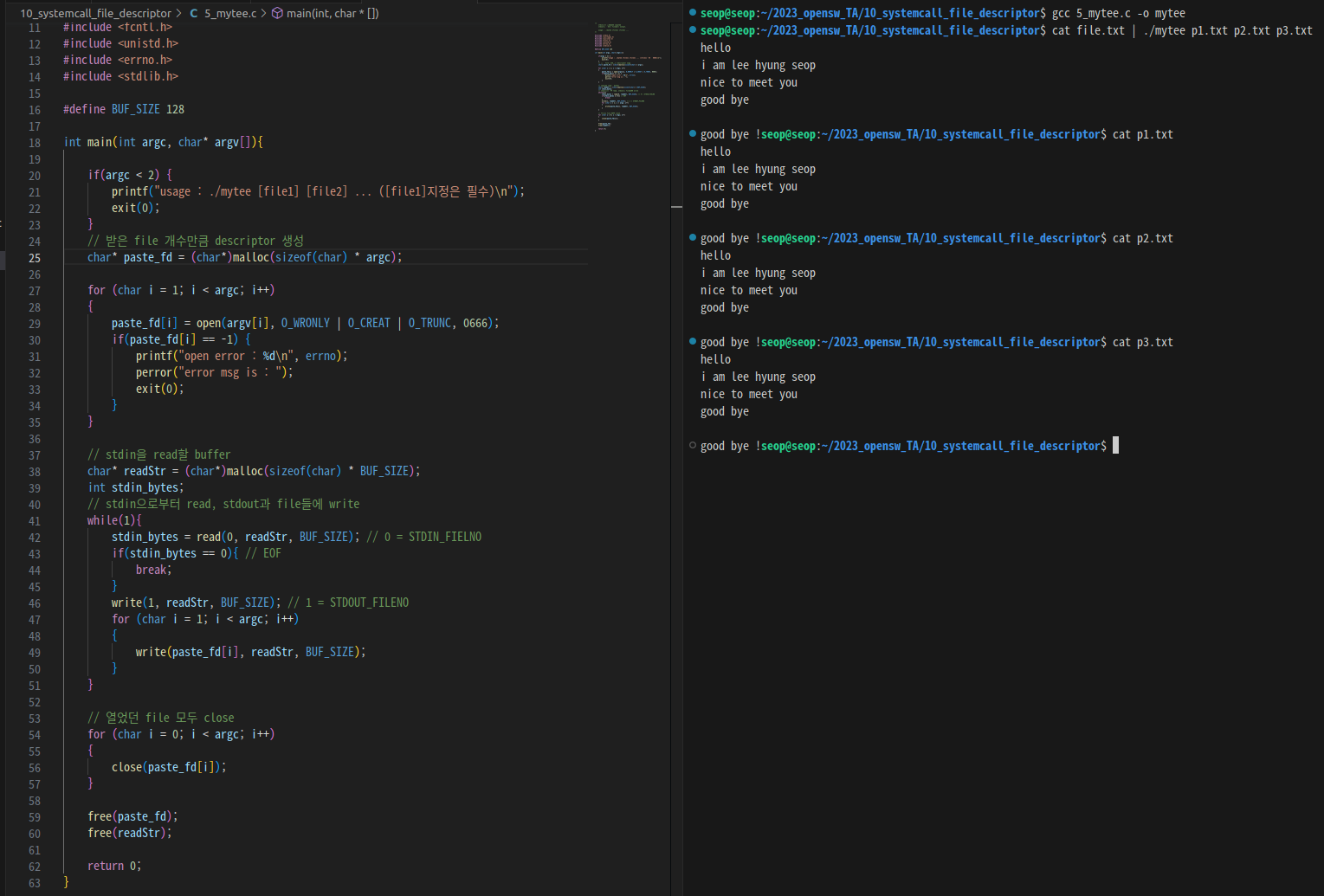
Example
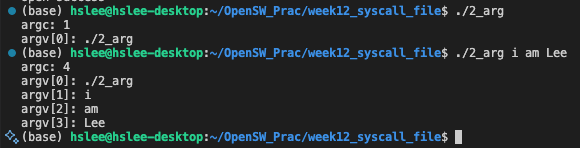
int argc, char* argv[]
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
printf("argc: %d\n", argc);
for(int i = 0; i < argc ; i++){
printf("argv[%d]: %s\n", i, argv[i]);
}
return 0;
}
open & close
#include <stdio.h>
// open(2)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
// close(2)
#include <unistd.h>
// perror(3), errno
#include <errno.h>
// exit(3)
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if(argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: ./3_open_close [file name]\n");
exit(0);
}
int open_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (open_fd == -1){
printf("error open: %d\n", errno);
perror("error msg is: ");
exit(0);
}
else{
printf("open success\n");
exit(0);
close(open_fd);
}
return 0;
}-
잘못된 사용법
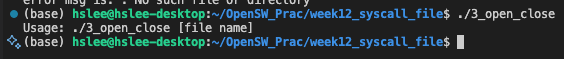
-
없는 파일

-
있는 파일 (정상작동)

open & close, read
#include <stdio.h>
// open(2)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
// close(2)
#include <unistd.h>
// read(2)
// #include <unistd.h>
// malloc(3)
#include <stdlib.h>
// exit(3)
// #include <stdlib.h>
// error handling
#include <errno.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 128 // 1char, 2Bytes -> read 64characters at once
// int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
// ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s [file name]\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
int open_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (open_fd == -1){
printf("errno: %d\n", errno);
perror("Error in opening file: ");
exit(0);
}
// success opening, and then read
char* readStr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * BUF_SIZE);
int read_result = 0;
while(1) {
read_result = read(open_fd, readStr, BUF_SIZE);
// Error handling
if (read_result == -1) {
printf("errno: %d\n", errno);
perror("Error in reading file: ");
}
// End of File
else if (read_result == 0){
printf("\n--- End of File ---\n");
close(open_fd);
break;
}
printf("%s\n", readStr);
}
free(readStr);
close(open_fd);
return 0;
}open & close, read, write
stdin로 입력받아 stdout에 write
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// read(2)
// #include <unistd.h>
// malloc(3)
#include <stdlib.h>
// exit(3)
// #include <stdlib.h>
// error handling
#include <errno.h>
// // write(2)
// #include <unistd.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 128
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if (argc != 1) {
printf("Usage: ./%s\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
char* readStr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * BUF_SIZE);
int read_result;
while(1){
read_result = read(0, readStr, BUF_SIZE);
if (read_result == -1){
perror("Error in reading : ");
exit(0);
}
else if (read_result == 0){ // Ctrl + D
printf("program end...\n");
exit(0);
}
write(1, readStr, read_result);
}
free(readStr);
return 0;
}open & close, read, write, lseek
stdin로 입력받아 한 개 이상 file 들에 (새롭게) write
- 없는 파일이면, 생성하기
- 있는 파일이면, 기존 내용 모두 지우고 새로 write
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 128
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: ./%s [file1 name] [file2 name] ... \n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
// get file descriptor for all files
int num_files = argc - 1;
int* fd_list = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_files);
// open all files (Write only, Create if no exist, Write new)
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
fd_list[i] = open(argv[i+1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (fd_list[i] == -1) {
perror("Error in openeing: ");
exit(1);
}
}
char* readStr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * BUF_SIZE);
int read_result;
while(1){
read_result = read(0, readStr, BUF_SIZE); // get str from stdin(0)
if (read_result == -1){
perror("Error in reading : ");
exit(0);
}
else if (read_result == 0){ // Ctrl + D
printf("program end...\n");
break;
}
for (int i = 0 ; i < num_files ; i++){
if (write(fd_list[i], readStr, read_result) == -1) {
perror("Error in writing: ");
}
}
}
// close all files
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
close(fd_list[i]);
}
free(readStr);
free(fd_list);
return 0;
}
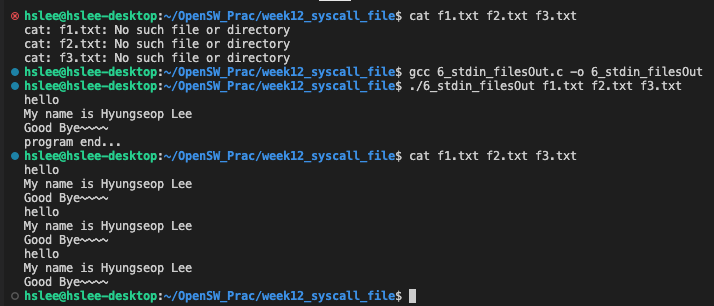
stdin로 입력받아 한 개 이상 file 들에 (이어서) write
바로 위 코드에서 아래만 수정하면 된다.
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
// fd_list[i] = open(argv[i+1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644); // write newly
fd_list[i] = open(argv[i+1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0644); // write append
if (fd_list[i] == -1) {
perror("Error in openeing: ");
exit(1);
}
}

file1로 입력받아 files에 write (cp 명령어 구현)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 128
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: ./%s [to copy file] [to paste file1] ... \n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
// open copy file
int copy_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (copy_fd == -1){
perror("Error in opening copy_fd: ");
exit(1);
}
// open paste file
int num_files = argc - 2;
int* paste_fd_list = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_files);
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
paste_fd_list[i] = open(argv[i+2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644); // write newly
if (paste_fd_list[i] == -1) {
perror("Error in openeing paste_fd: ");
exit(1);
}
}
// read from source and write destinations
char* readStr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * BUF_SIZE);
int read_result, i=1;
while(1){
read_result = read(copy_fd, readStr, BUF_SIZE);
if (read_result == -1){
perror("Error in reading : ");
break;
}
else if (read_result == 0){ // EoF
printf("program end...\n");
break;
}
for (int j = 0 ; j < num_files ; j++){
if (write(paste_fd_list[j], readStr, read_result) == -1) {
perror("Error in writing: ");
break;
}
}
i += 1;
}
// close all files
close(copy_fd);
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
close(paste_fd_list[i]);
}
// free
free(readStr);
free(paste_fd_list);
return 0;
}
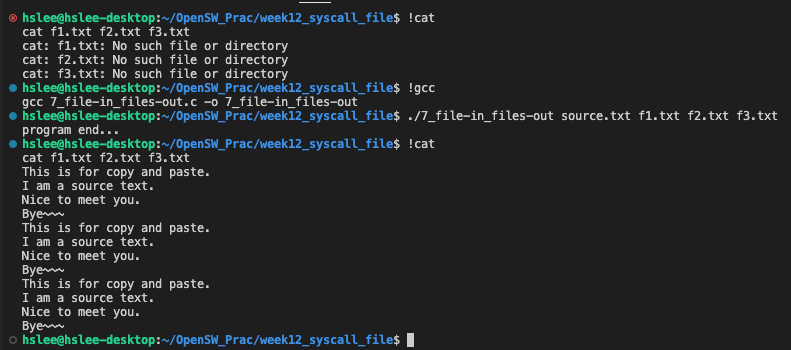
mytee: tee 명령어 구현
tee: read from standard input and write to standard output and files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define BUF_SIZE 128
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if (argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: ./%s [to paste file1] ... \n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
// open paste file
int num_files = argc - 1;
int* paste_fd_list = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_files);
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
paste_fd_list[i] = open(argv[i+1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644); // write newly
if (paste_fd_list[i] == -1) {
perror("Error in openeing paste_fd: ");
exit(1);
}
}
// read from stdin and write destinations (stdout, files)
char* readStr = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * BUF_SIZE);
int read_result, i=1;
while(1){
read_result = read(0, readStr, BUF_SIZE);
if (read_result == -1){
perror("Error in reading : ");
break;
}
else if (read_result == 0){ // EoF
printf("program end...\n");
break;
}
// write stdout
if (write(1, readStr, read_result) == -1) {
perror("Error in writing: ");
break;
}
// write files
for (int j = 0 ; j < num_files ; j++){
if (write(paste_fd_list[j], readStr, read_result) == -1) {
perror("Error in writing: ");
break;
}
}
i += 1;
}
// close all files
for (int i = 0; i < num_files; i++){
close(paste_fd_list[i]);
}
// free
free(readStr);
free(paste_fd_list);
return 0;
}