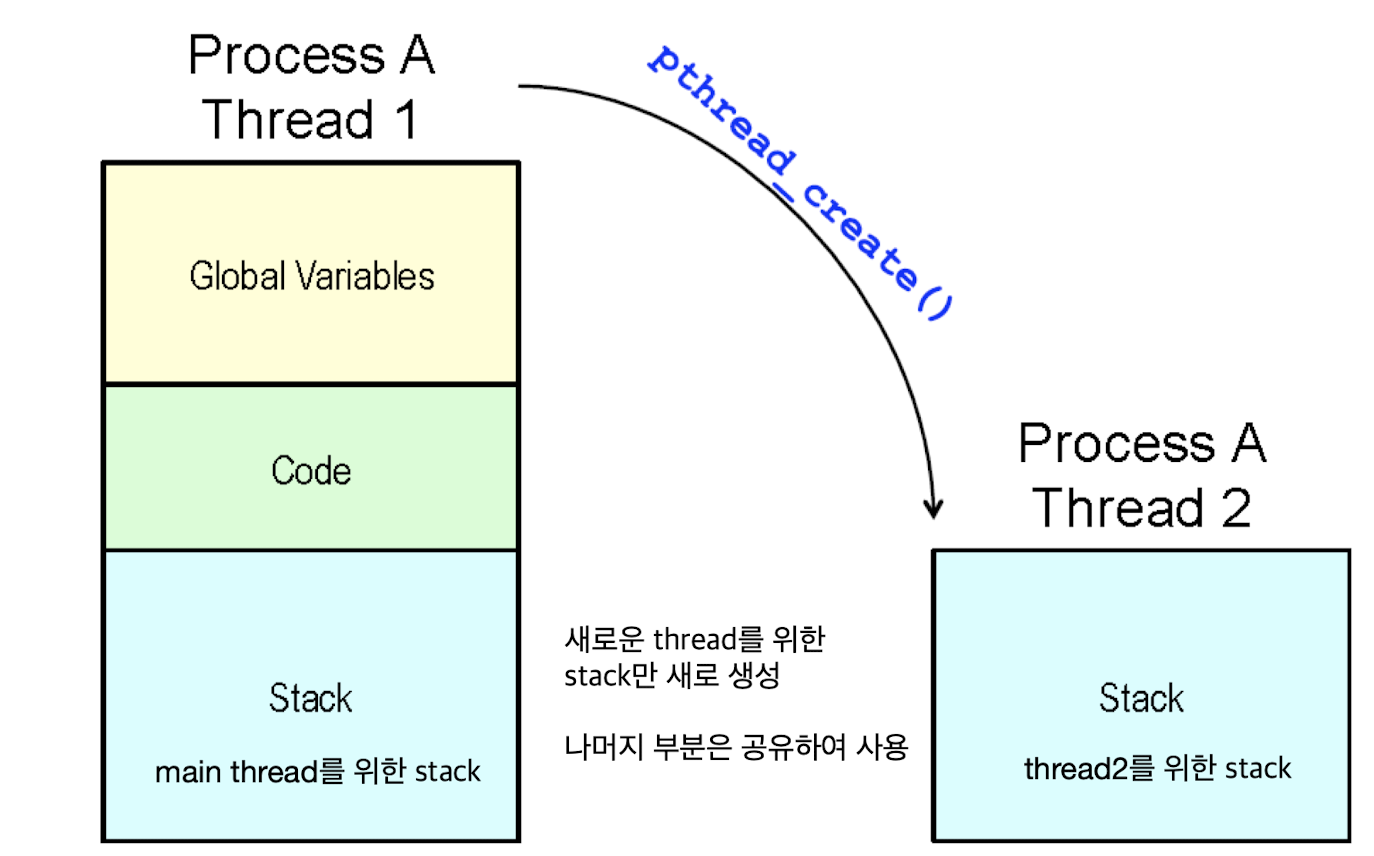
Processes and Threads
-
Process:
an instance of a running(or suspended) program
코드의 한 지점(한 thread)만 실행 -
A single process may have multiple
threadsof execution- Each thread has its own function calls & local variables
Need program counter(프로그램의 어느 부분을 실행하고 있는지?)
and stack(function call 상태) for each thread - Threads are so-called
light-weightprocesses that share access to a single memory space.
(thread는 memory space를 독립적으로 가지고 있을 필요가 없음)
- Each thread has its own function calls & local variables
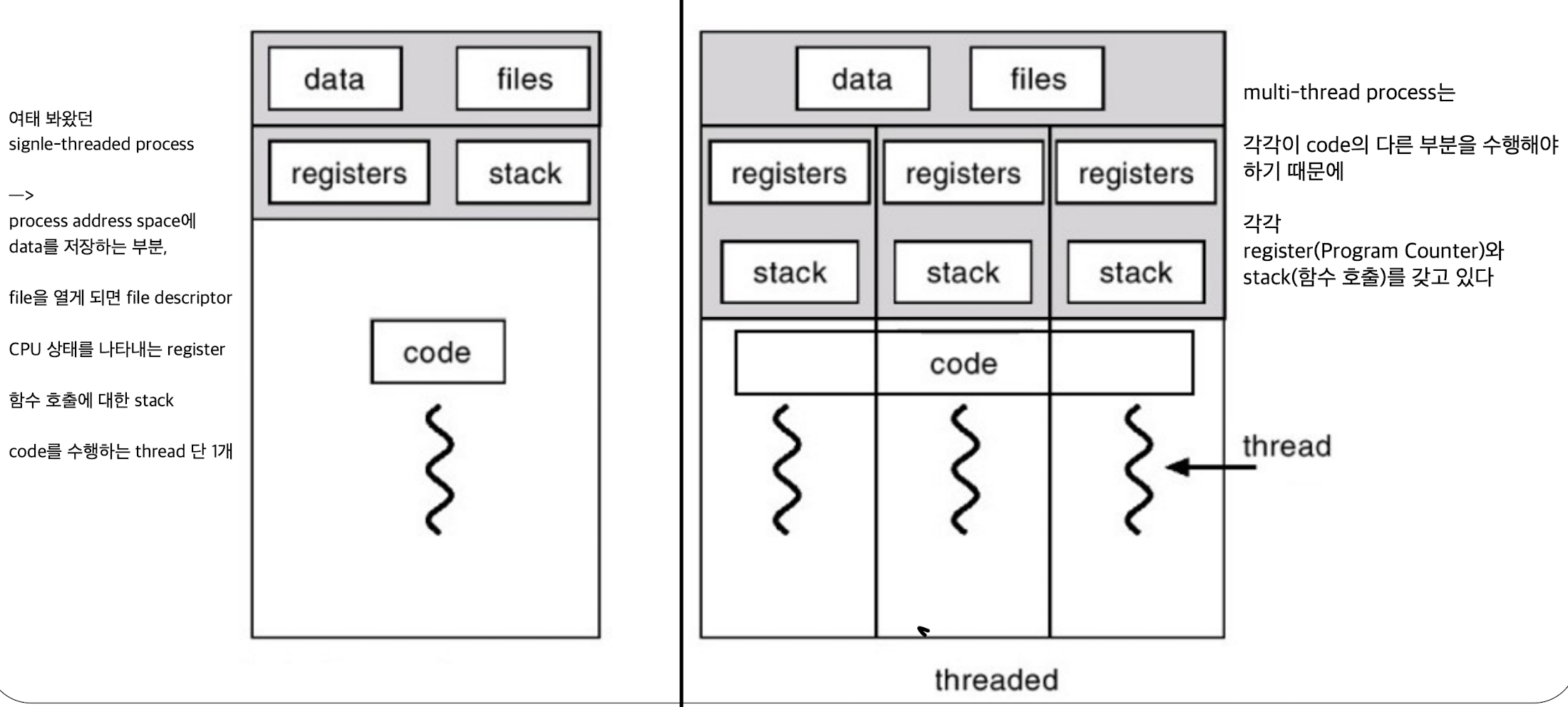
A single-threaded vs. a multi-thread processes
-
global한 data, files descriptor는 모든 thread 간의 공유가 되고 있음. (하나의 process에서 여러 thread가 생성된 것)
하지만 각각의 thread들은 각각의 register, stack segment가 있음.
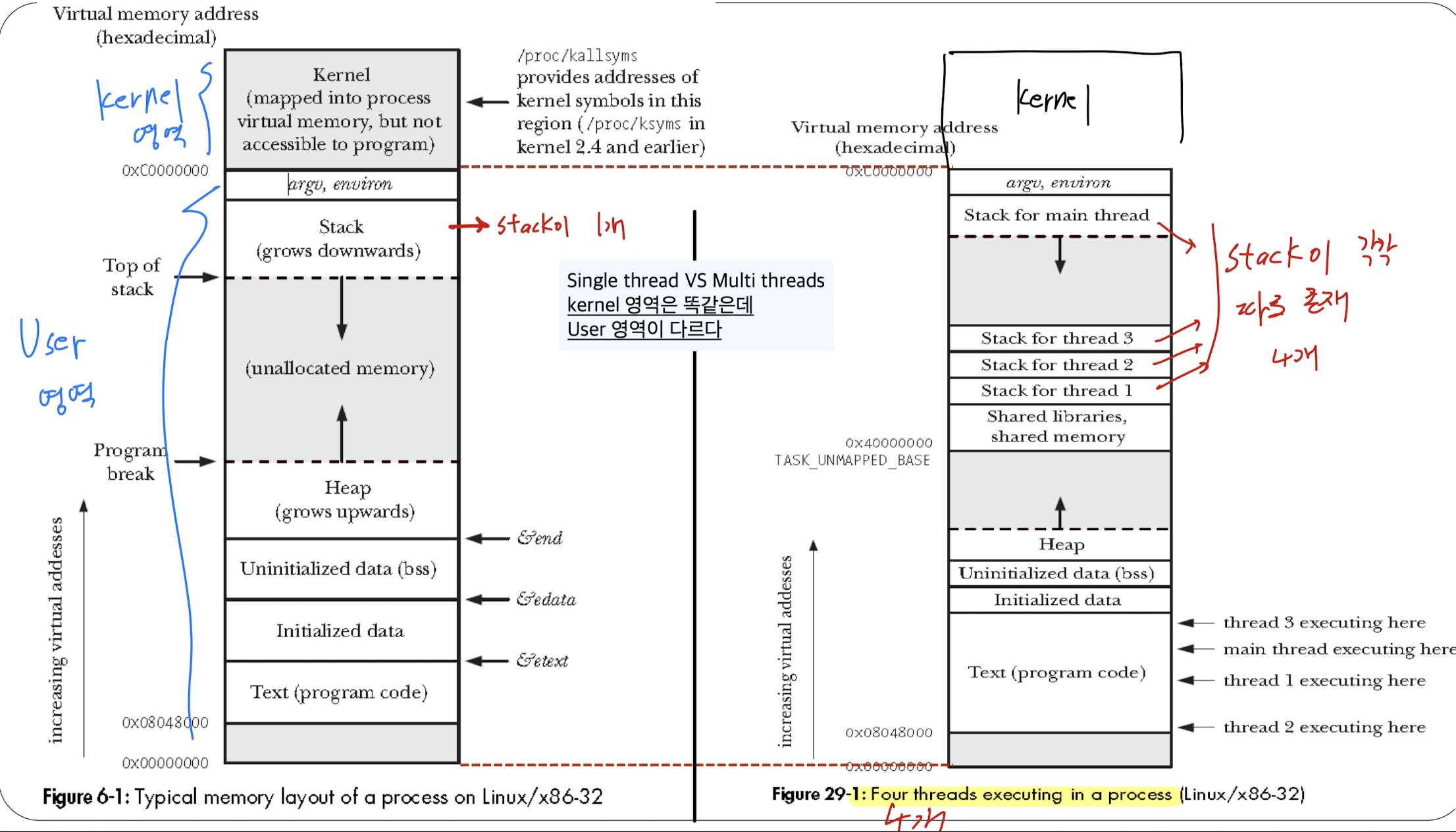
-
Kernel 영역은 똑같고, User 영역이 다름.
multi-thread process의 경우, 하나의 address space 안에서 Stack 영역에 각각의 thread별로 따로따로 존재한다.
각기 다른 function들을 호출해가기 때문.
Why use threads, not processes?
- 병렬적인 처리를 위해 여러 process를 쓰면 되는데, 왜 여러 thread를 이용할까?
process를 안 쓰는 이유:
fork()를 통해 process를 생성하는데,
overhead가 너무 크다 (복제하기 위해 time, memory 소요가 큼)
또한 process가 생성되면, 두 process 간에 data를 주고받기 어렵다.
두 process 내에서 IPC(Inter-Process Communication)로는 할 수 있지만 느리고 비효율적.thread를 사용하는 이유:
thread는 process 내에 여러 개의 thread가 동시에 존재하면서
하나의 memory space를 공유하기 때문에 data 공유(global, static)가 쉽다.
thread를 생성한다는 것은 stack 영역을 하나만 더 추가하는 것이므로 time, memory를 절약할 수 있다.
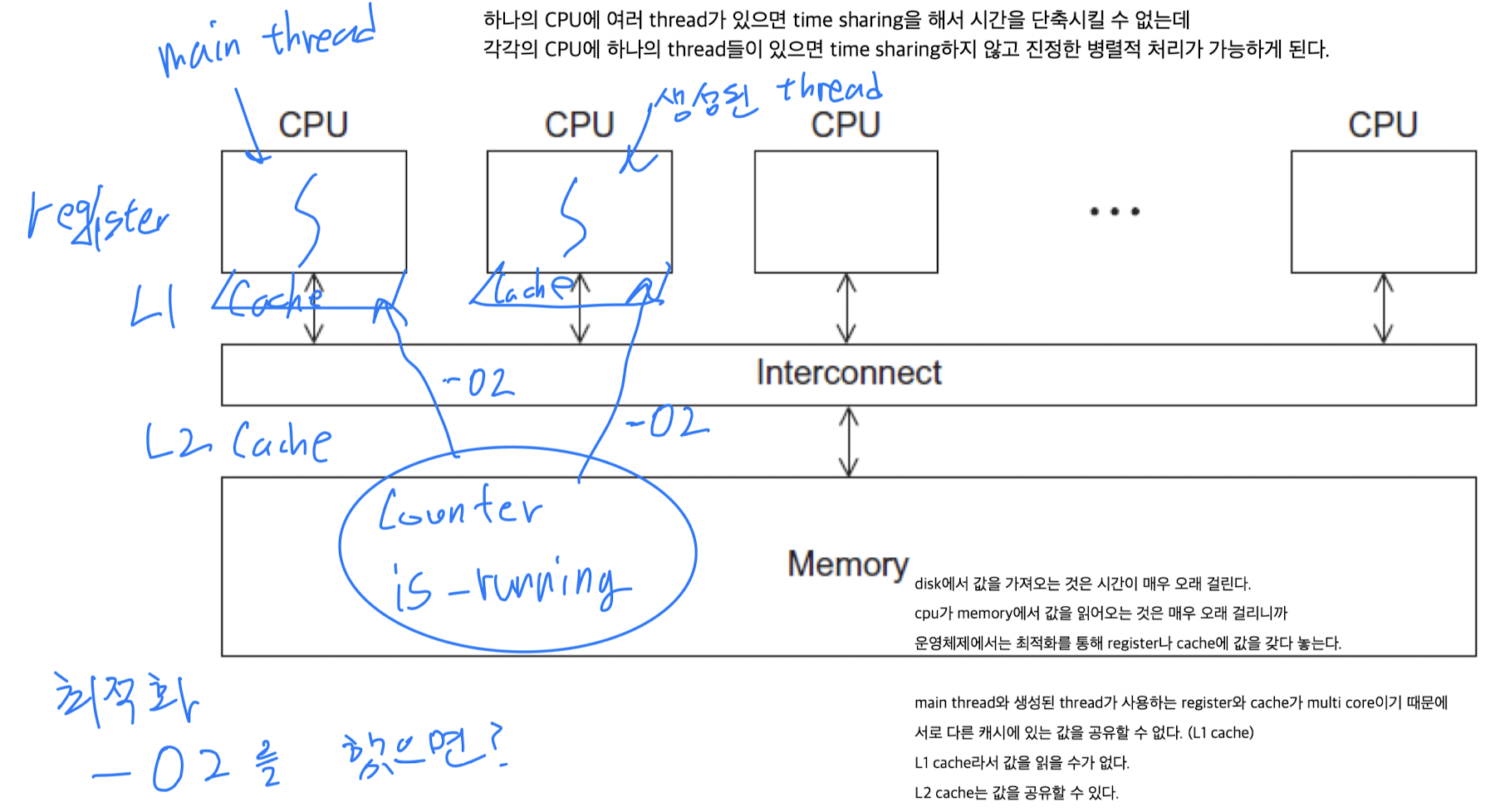
Multi-threading
- 최근에는 multiple processors (CPU cores) machine이 잘 나옴.
각각의 CPU에 thread들이 수행되도록 하여 병렬로 처리할 수 있다.- 만약 하나의 CPU에 여러 thread들이 있다면, time sharing을 해서 수행되기 때문에 시간을 단축시킬 수 없는데
- 각각의 CPU에 하나의 thread들이 있다면 time sharing하지 않고 진정한 병렬적 처리가 가능하게 된다.
POSIX threads
- Unix 계열의 운영체제 중에서 multi thread programming을 하기 위해 필요한 API(함수)들을 정의해 놓음
- POSIX threads를 줄여서 Pthreads라고 함
Pthread API
Thread Management (create, exit, join, detach)
-
Creating and Destroying Threads:

-
Using Pthreads:
gcc -o <threaded_program.c> -pthread : "pthread library와 link하여 compile하라"
1. pthread_create(3)
-
pthread_create(3): Create a new thread of control

void* (*start_routine)(void*):
function pointer인데,
넘겨줄 argument는 void* 아무 pointer 변수를 넘겨줘도 된다. 사용할 때 type casting하여 사용.
반환할 때도 void* 마찬가지로 아무 pointer 변수를 넘겨줘도 된다.error codes:
Returns 0 for success, else error code.

pthread_t type:
Opaque : pthread_t type이 내부적으로 어떠한 type으로 만들어졌는지 알 필요가 없다.
pthread_t가 어떻게 구성되어 있는지 확인하려 하지 말고(Opaque: 알 필요 없음),
pthread_t를 다루기 위한 보조함수(pthread_self(), pthread_equal())를 활용한다.
pthread_self(3), pthread_equal(3):

2. pthread_exit(3) : Thread termination
-
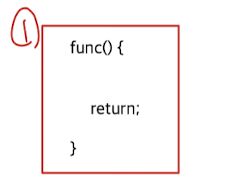
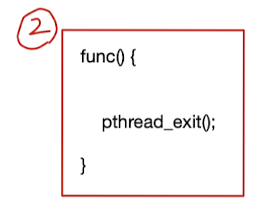
4가지 방법
The thread function performs return with a return value:
The thread calls pthread_exit() with a return value:

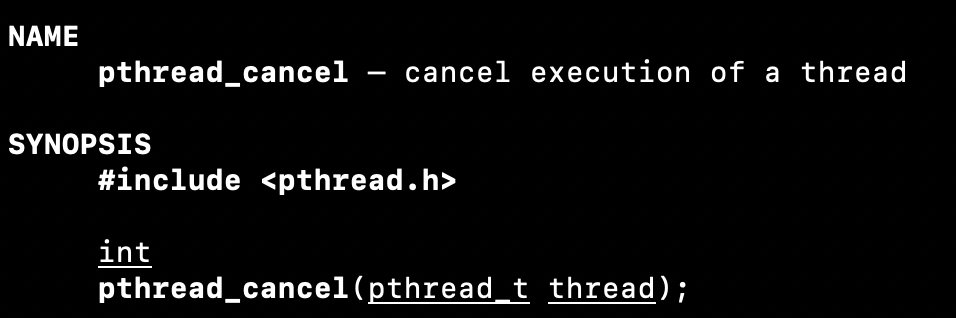
Any of the threads calls exit() or the main thread performs a return:
그 어떠한 thread라도 exit()를 call하면 해당 process가 종료.
process가 종료되니까 그 안에 있는 모든 thread들도 종료.The thread is canceled using pthread_cancel(3):
하나의 thread가 다른 thread를 종료시킬 수 있다.
-
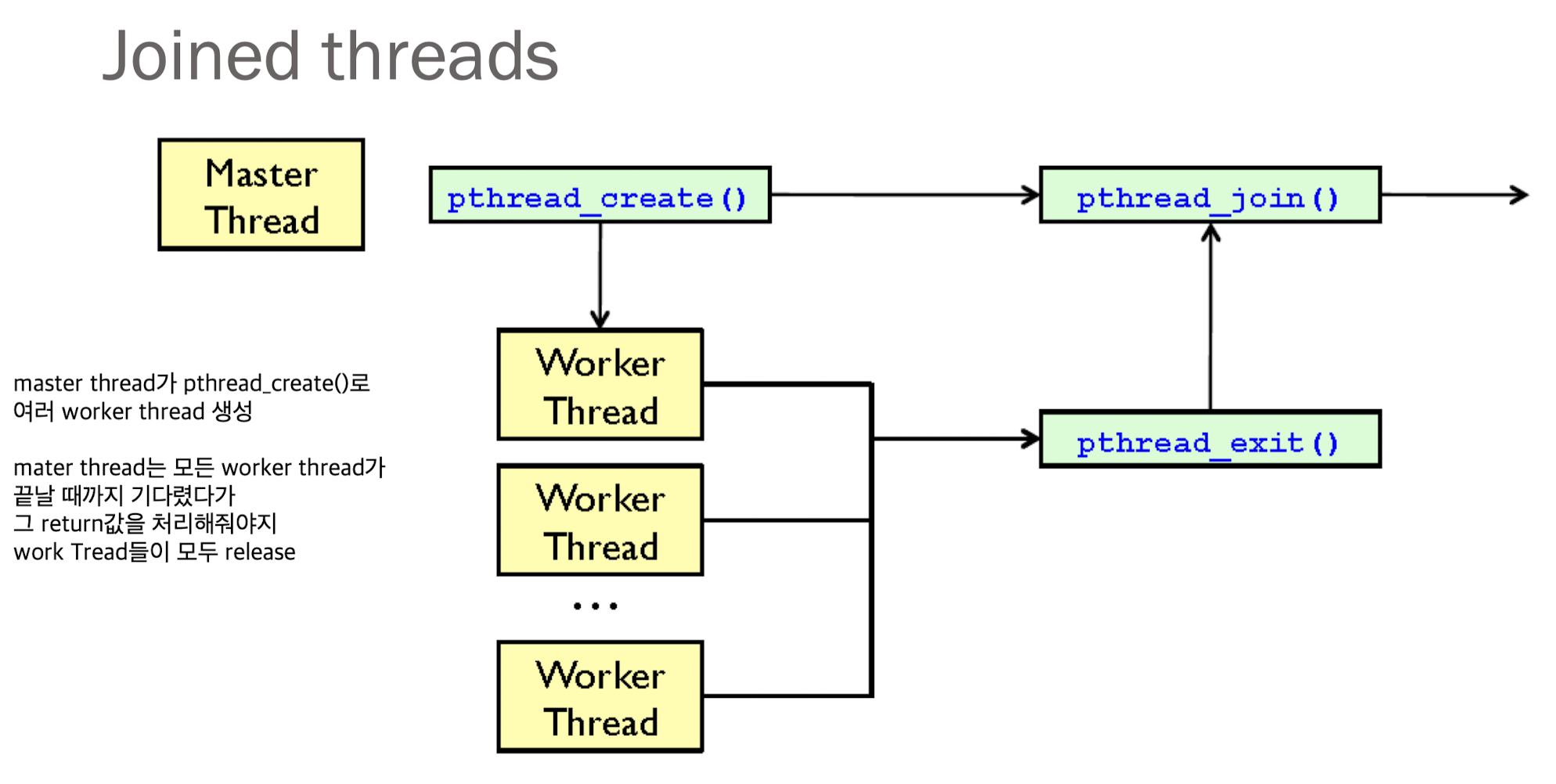
pthread_join(3): waiting for threads
 만약 여러 thread를 기다리려면 각각의 thread에 대해서 join해줘야 한다.
만약 여러 thread를 기다리려면 각각의 thread에 대해서 join해줘야 한다.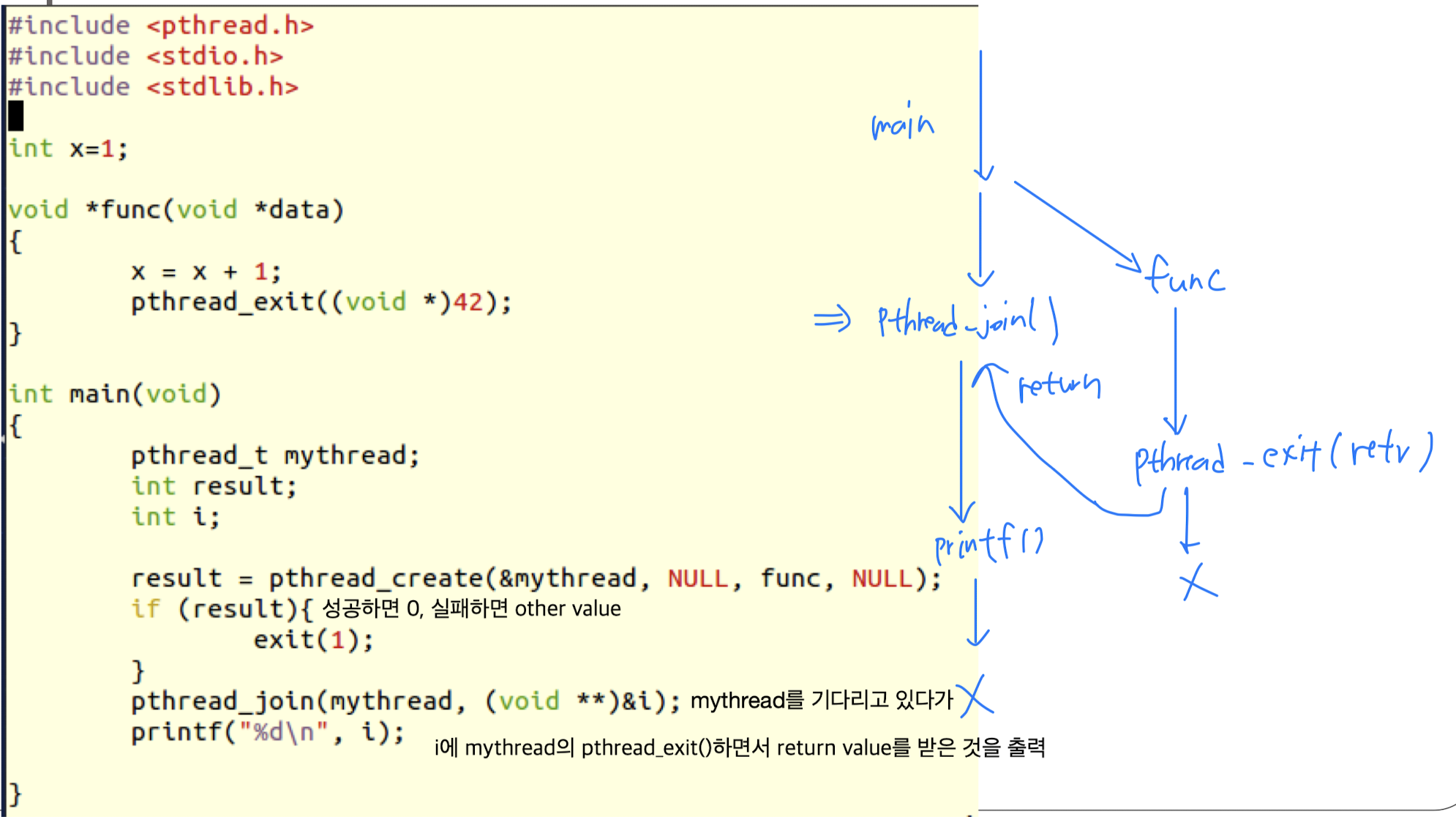
-
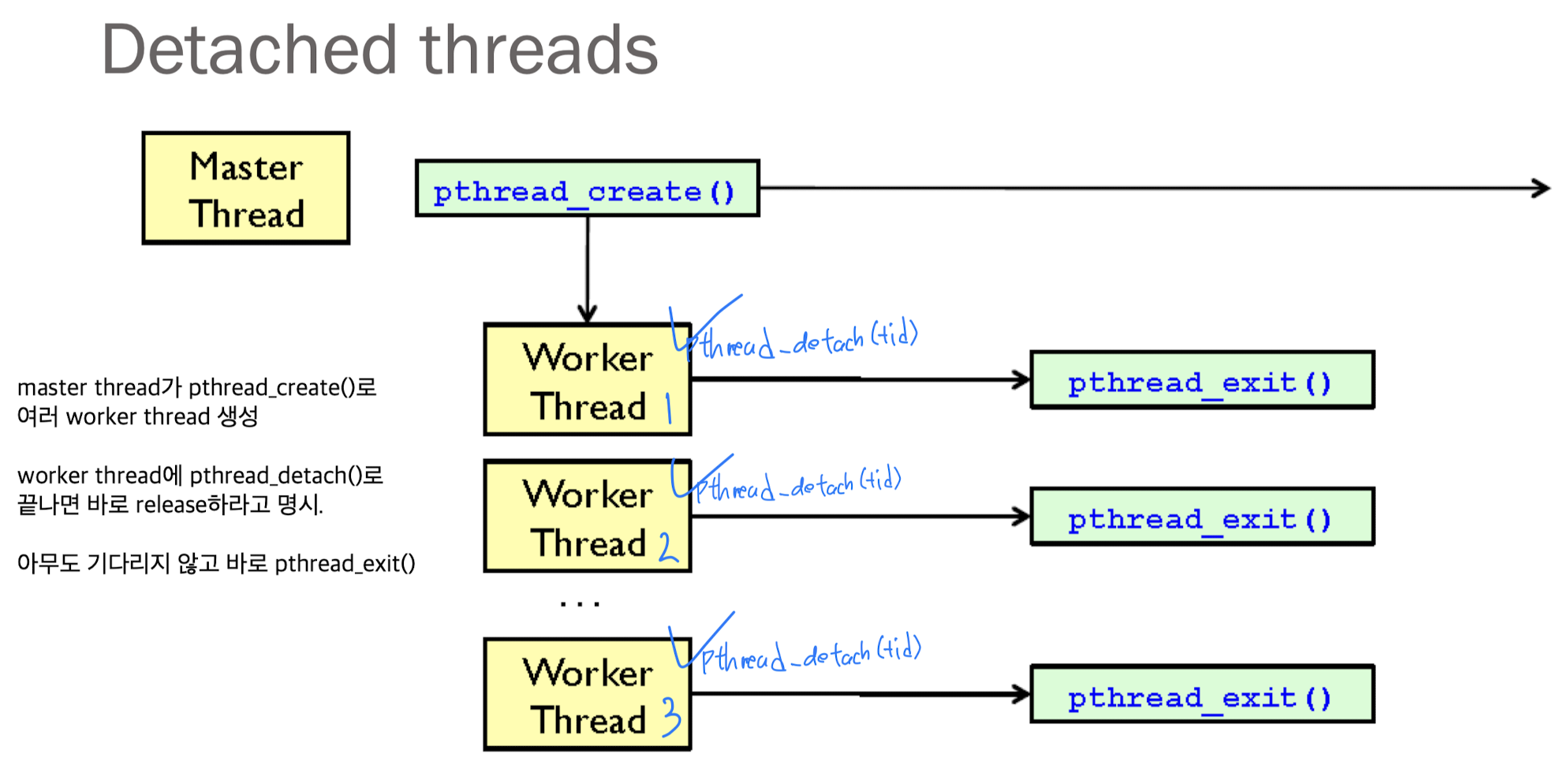
pthread_detach(3):
명시된 thread가 종료되었을 때, 그 thread는 join하는 thread 없이 바로 갖고 있는 resource들을 release.
누군가가 pthread_join(3)하며 기다려줄 필요가 없는 경우.

Examples
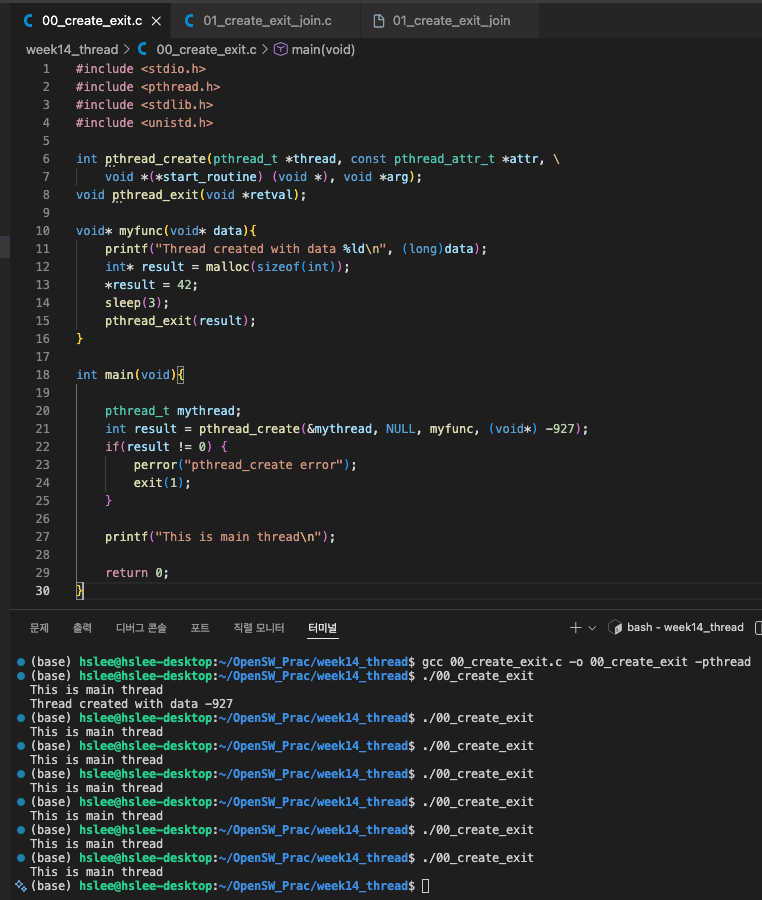
문제1: pthread_create, pthread_exit
- main thread에서 pthread_exit(3); 또는 pthread_join(3)을 안해줬기 때문에
곧바로 main 함수의 return 0;를 실행해 process가 종료되기 때문에
우리가 원하는 결과인 myfunc()가 실행되기도 전에 종료된다.
pthread_exit(3) in main()
- main에서 process가 종료되지 않도록, pthread_exit(3)를 통해 다른 thread가 계속 진행되도록 한다.
하지만
(문제 1) main에서 pthread_exit(3)를 쓰면 child thread의 return value를 받을 수 없음.
(문제2) chidl thread가 언제 끝나는지 보장할 수 없음.
(문제3) child thread 종료 보장할 수 없음.
(문제4) resource 정리 못함.
...
pthread_join(3) in main(3)
- 위 문제를 해결하기 위해, main thread는 pthread_join(3)을 통해 생성된 thread의 routine에서 pthread_exit(3)하기를 기다린다.
pthread_join(3)으로 pthread_exit(3)시 반환한 값을 출력하고 프로그램을 종료한다.
thread routine에서 exit하면, 전체 종료
- process 내 어떠한 thread routine에서 exit()하면 전체 process 모두 종료.
scheduler
- scheduler 간 차이 때문에
thread가 생성되었을 때, Main thread와 생성된 thread의 진행과정을 알 수 없다.
Globlal variable sharing
- multi thread들끼리 global variable을 sharing하는 예제
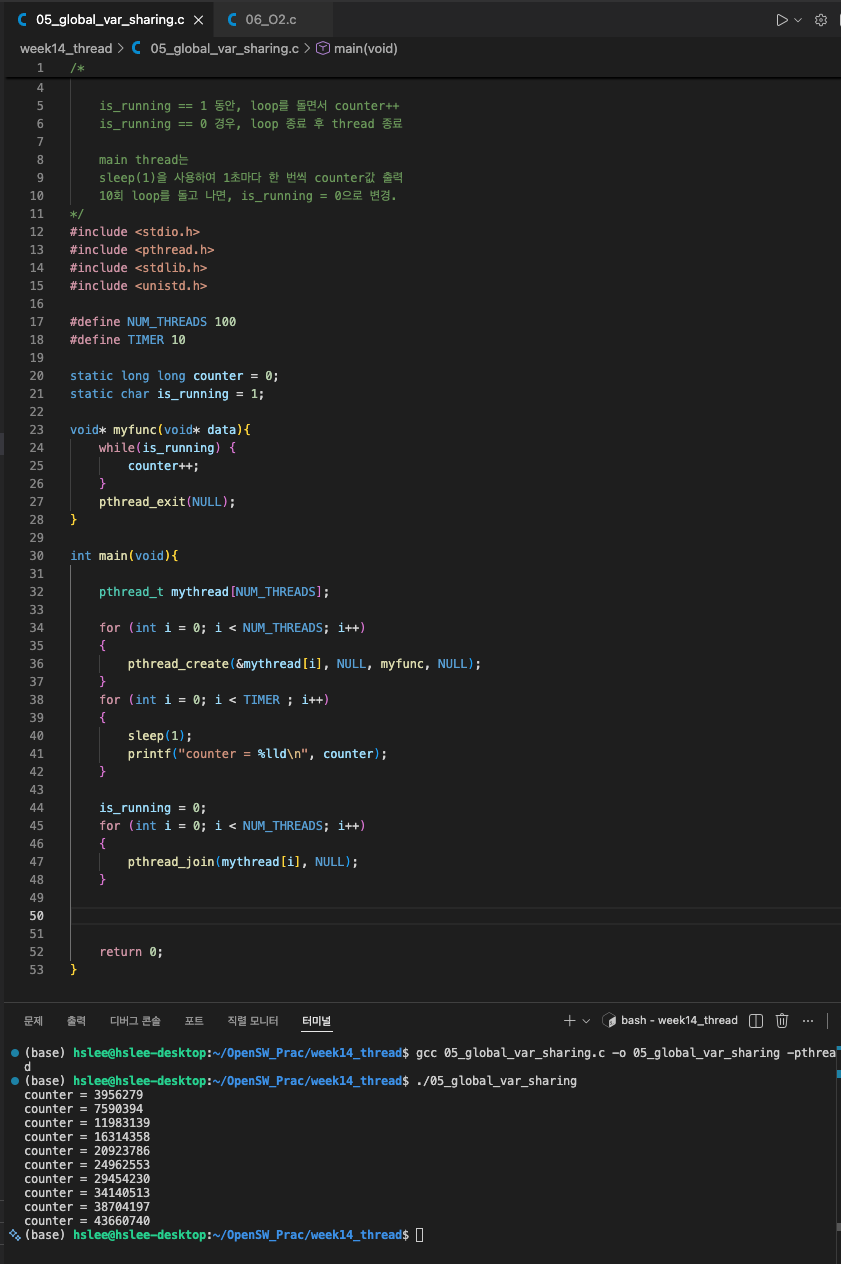
Optimization option
- gcc 명령어에
-O2라는 2-level optimization option을 주었더니,
counter 값이 모두 0으로 출력되었다.
그리고 프로세스가 무한 루프에 빠진 것처럼 종료되지 않는다.
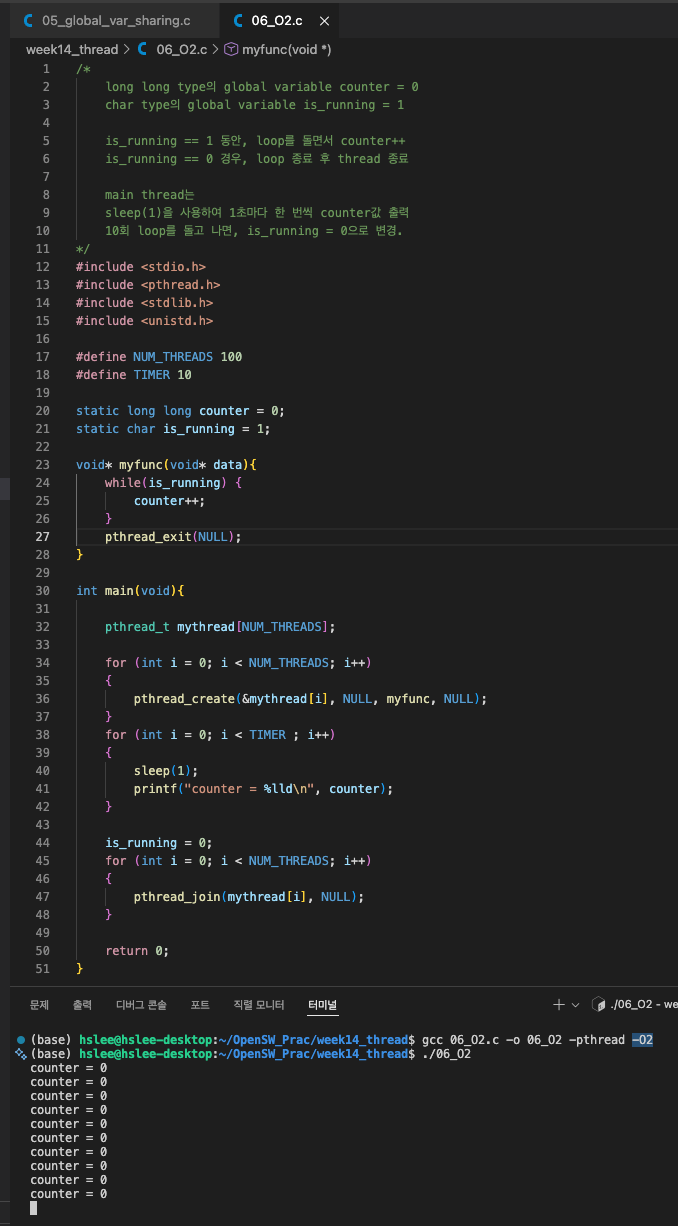 왜 그럴까?
왜 그럴까?
program이 multi-core에서 multi-thread로 실행되고 있는데,
disk에서 값을 가져오는 것은 시간이 매우 오래 걸리고,
CPU가 memory에서 값을 읽어오는 것도 시간이 걸리기 때문에
OS는 optimization을 통해 각각의 core의 register나 cache에 값을 갖다 놓는다.
is_running은 여러 thread가 읽고 쓰는 공유 변수다.
하지만 volatile이나 메모리 장벽(mfence)이 없을 경우,
컴파일러는 is_running이 loop 내부에서 변경되지 않는다고 판단하여
memory에서 반복해서 읽지 않고 register에 caching한다.
그 결과 worker thread는 is_running = 1을 register에서 계속 읽기 때문에
main thread가 is_running = 0으로 바꿔도 loop가 끝나지 않는다.
따라서 thread 간 공유 변수를 안전하게 사용하려면
volatile 또는 atomic 변수를 사용하거나 메모리 장벽을 사용해야 한다.
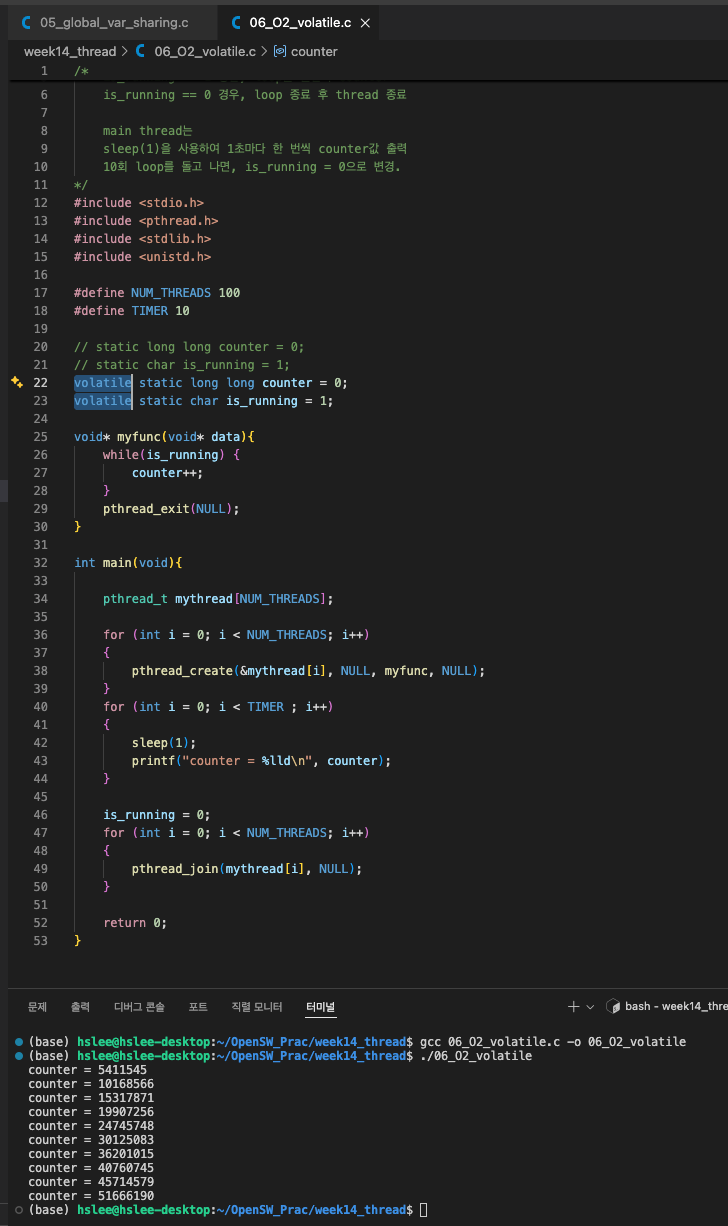
Optimization option (Volatile)
- 위 memory optimization의 문제를 해결하기 위해 counter, is_running을 선언할 때,
volatile을 선언함으로써 compiler에게 해당 변수를 register에 caching하지 말고,
매번 memory에서 읽으라고 최적화를 방지할 수 있다.
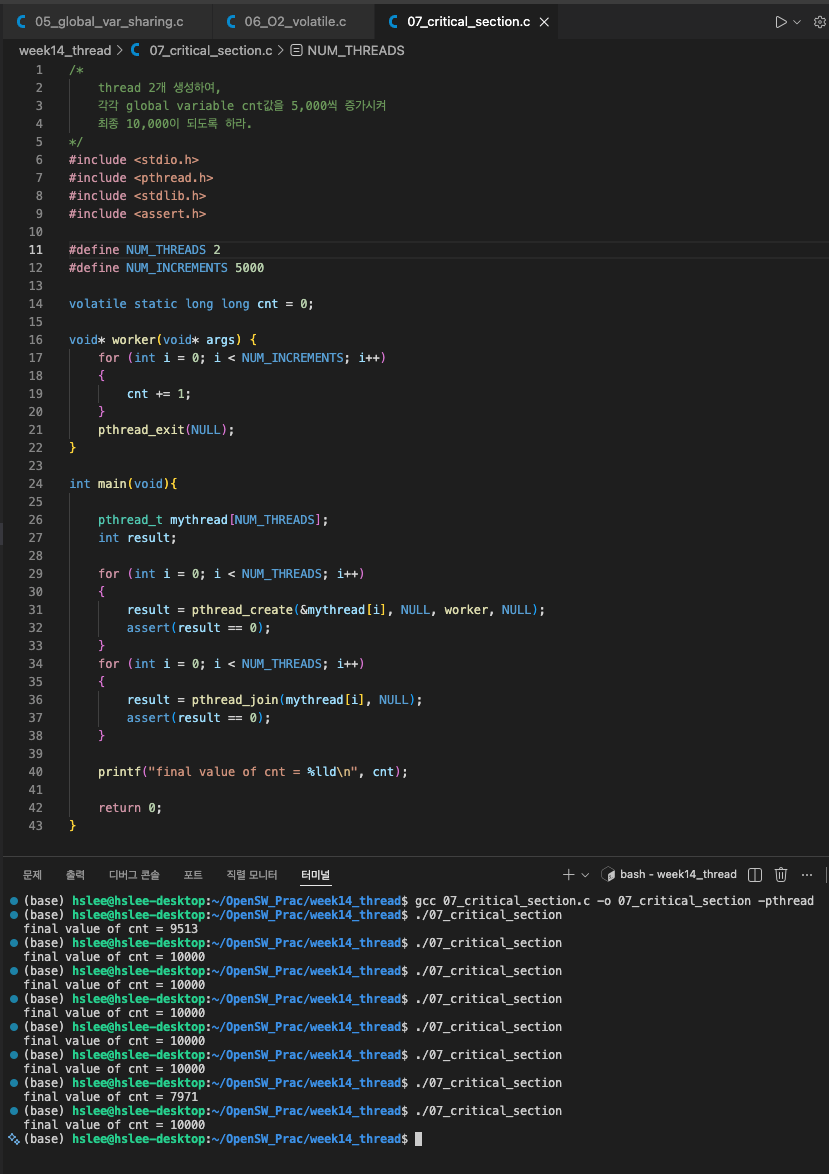
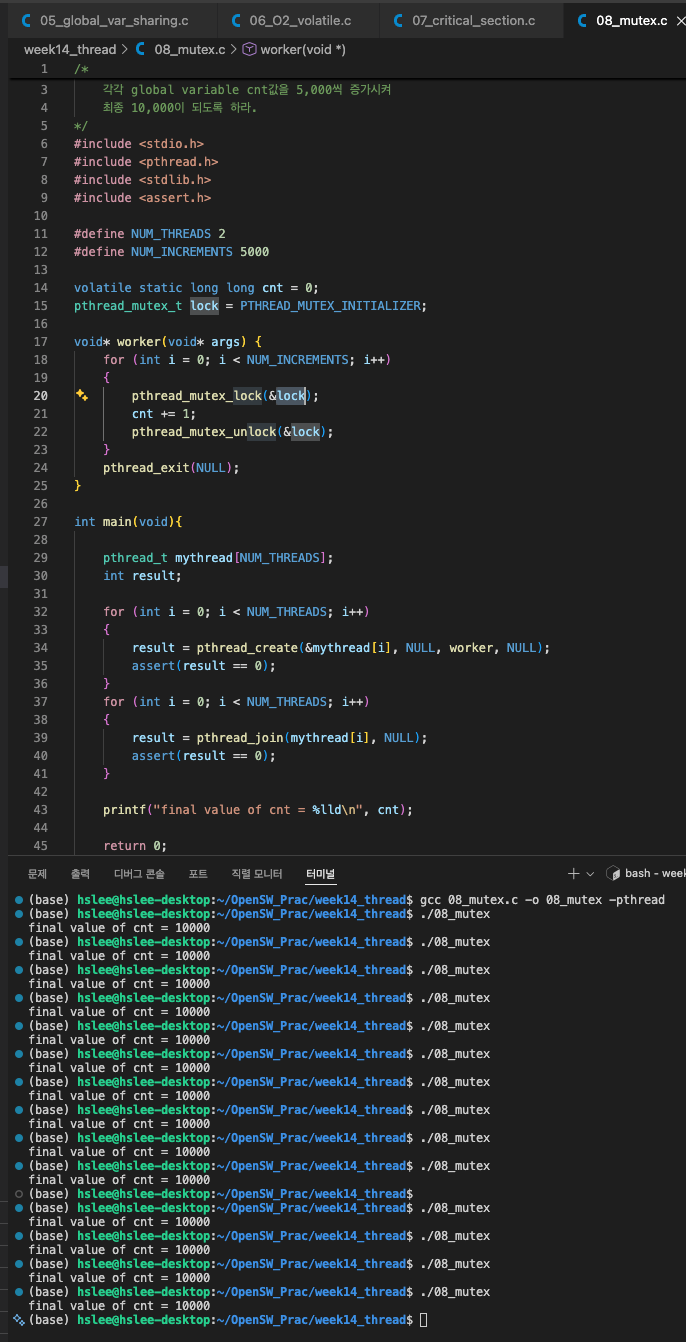
Critical section, mutex, synchronization
critical section
- 우리의 예상과 달리 10,000이 아니라 더 작은 숫자가 출력되었다...
이는 두 thread 간의 synchronization이 되지 않아 cnt라는 global variable을 동시에 처리하게 되어 문제가 발생한 것이다.
mutex
- mutex (mutual exclusion)을 이용해서 global variable에 대한 race condition을 방지한다.
mutex 주의사항
-
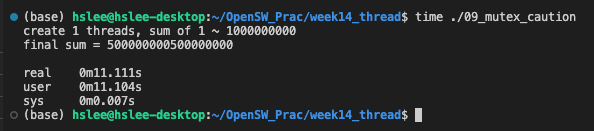
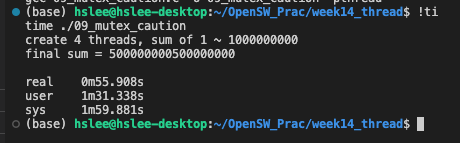
아래 예시에서는 이론대로라면, 4개 Threads를 이용한게 single thread보다 약 4배 빨라야 하지만 실제로는 훨씬 느리다.
그 이유는 아래 예시와 같이, mutex lock을 매 반복마다 호출하면 엄청나게 느려진다.
mutex는 kernel level에서 scheduling이 들어가기 때문에 엄청나게 느려진다.single threadabout 11.11s
4 trheadsabout 55.9s
-
위 문제를 해결하기 위해, 각 thread에서는 global variable인 sum에 직접 값을 더하는게 아니라,
local variable에 값을 누적해서 최종적으로 global variable sum에 더해주는 딱 한 순간만 mutex를 호출하면 된다.
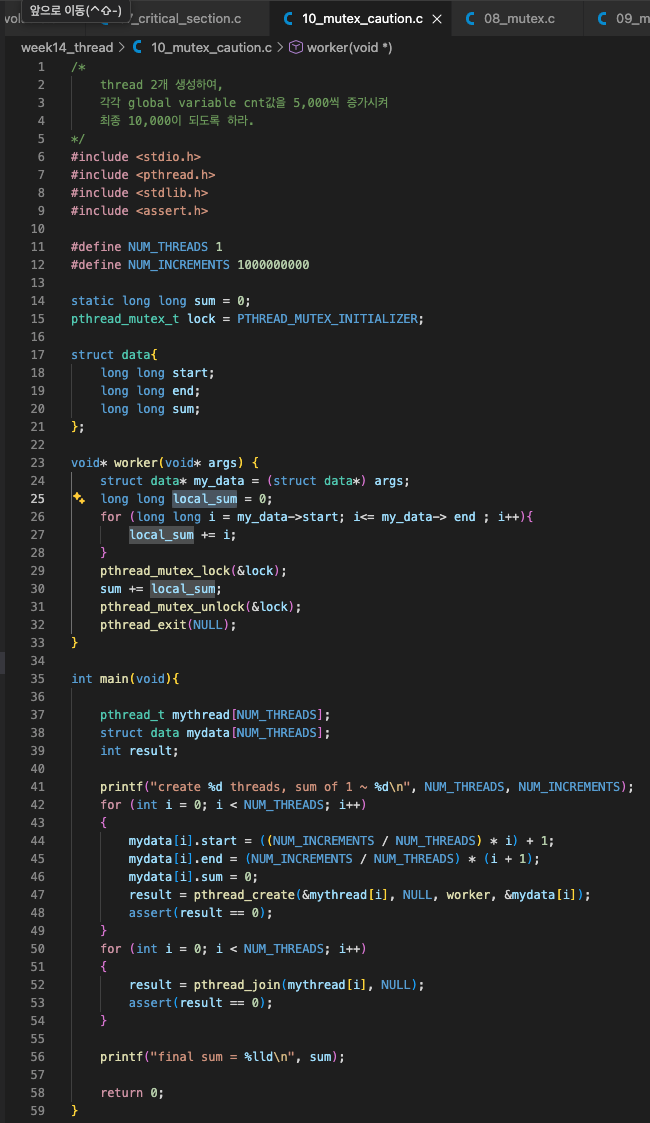
single threadabout 1.29s
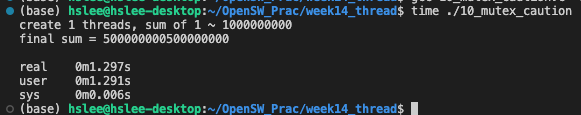
4 threadsabout 0.38s