내배캠 두 번째 팀 프로젝트
🗓️ 프로젝트 기간 🗓️
7월 9일부터 7월 21일까지
📖 오늘의 내가 한 일 📖
로얄티 멤버십 효과
- 가설: 멤버십을 가입한 고객은 미가입 고객보다 고객 생애 가치가 높다.
- 가설: 멤버십을 가입한 고객은 미가입 고객보다 재구매률이 높다.
#고객 정보 = 고객별 주문 수, CLV, 멤버십 정보 집계
customer_info = SSE.groupby('Customer ID').agg(repurchase_count = ('Total Purchase Amount','count'),
CLV = ('Total Purchase Amount','sum'),
Loyalty = ('Loyalty Member','first')).reset_index()
customer_info[결과 값]
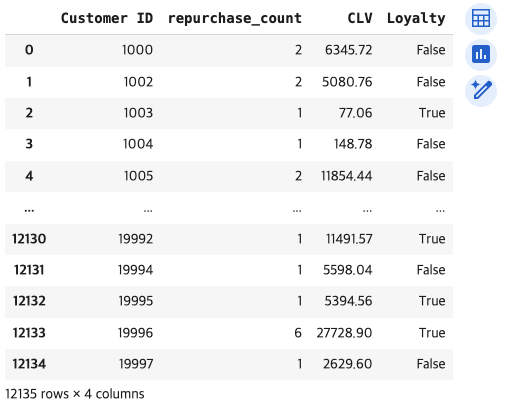
#재구매(기준 2번 이상 구매한 고객)값 확인하기
customer_info['repeat_purchase'] = customer_info['repurchase_count'] > 1
customer_info['repeat_purchase'].value_counts()[결과 값]
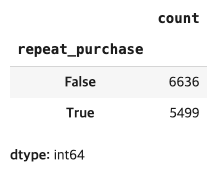
#멤버십 가입 기준 재구매율
customer_info.groupby('Loyalty').agg(repurchase_rate = ('repeat_purchase','mean'),
avg_CLV = ('CLV','mean'),
cnt_c = ('CLV','count')).reset_index()[결과 값]
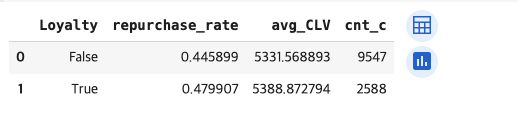
t검정 결과
#t검정(CLV 연속형 데이터와 멤버십 가입여부 범주형 데이터의 비교)
group_T = customer_info.loc[customer_info['Loyalty']==True, 'CLV'] #멤버십 가입한 고객
group_F = customer_info.loc[customer_info['Loyalty']==False,'CLV'] #멤버십 가입 안한 고객
stat, p_value = ttest_ind(group_T, group_F, equal_var=False)
print(f"CLV t-test → statistic: {stat:.3f}, p-value: {p_value:.3f}")
#t검정 결과: 멤버십 가입한 고객과 멤버십 가입 안한 고객의 CLV 평균 차이가 통계적으로 유의미 하지 않다. 귀무가설 채택[결과 값]
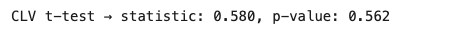
추가 의문
멤버십 가입 여부(범주형)과 재구매율(비율/확률) 비교
from statsmodels.stats.proportion import proportions_ztest
# 1) 재구매 플래그(is_repeat) 추가
customer_info['is_repeat'] = customer_info['repurchase_count'] > 1
# 2) 그룹별 재구매 수와 총 고객 수 집계
grouped = (
customer_info
.groupby('Loyalty')['is_repeat']
.agg(repeat_count='sum', # 재구매 고객 수
total_count='count') # 전체 고객 수
.reset_index()
)
# 재구매율 컬럼 추가
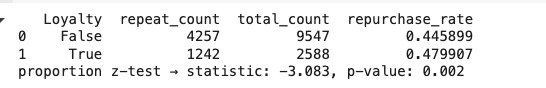
grouped['repurchase_rate'] = grouped['repeat_count'] / grouped['total_count']
print(grouped)
# 예시 출력
# Loyalty repeat_count total_count repurchase_rate
# 0 False 4262 9547 0.446
# 1 True 1242 2588 0.480
# 3) proportion z-test 실행
count = grouped['repeat_count'].values # [재구매_False, 재구매_True]
nobs = grouped['total_count'].values # [전체_False, 전체_True]
stat, pval = proportions_ztest(count=count, nobs=nobs)
print(f"proportion z-test → statistic: {stat:.3f}, p-value: {pval:.3f}")[결과 값]
결론:
-
멤버십 가입 여부와 CLV는 통계적으로 유의미한 관계가 없다.(p-value 0.562) = 귀무가설 채택
-
멤버십 가입 여부와 재구매율은 통계적으로 유의미한 관계가 있다. = 귀무가설 기각, 대립가설 채택
(p-value 0.002)
2번 가설은 발전의 가능성이 있다.

