오늘의 문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2583
영역 구하기
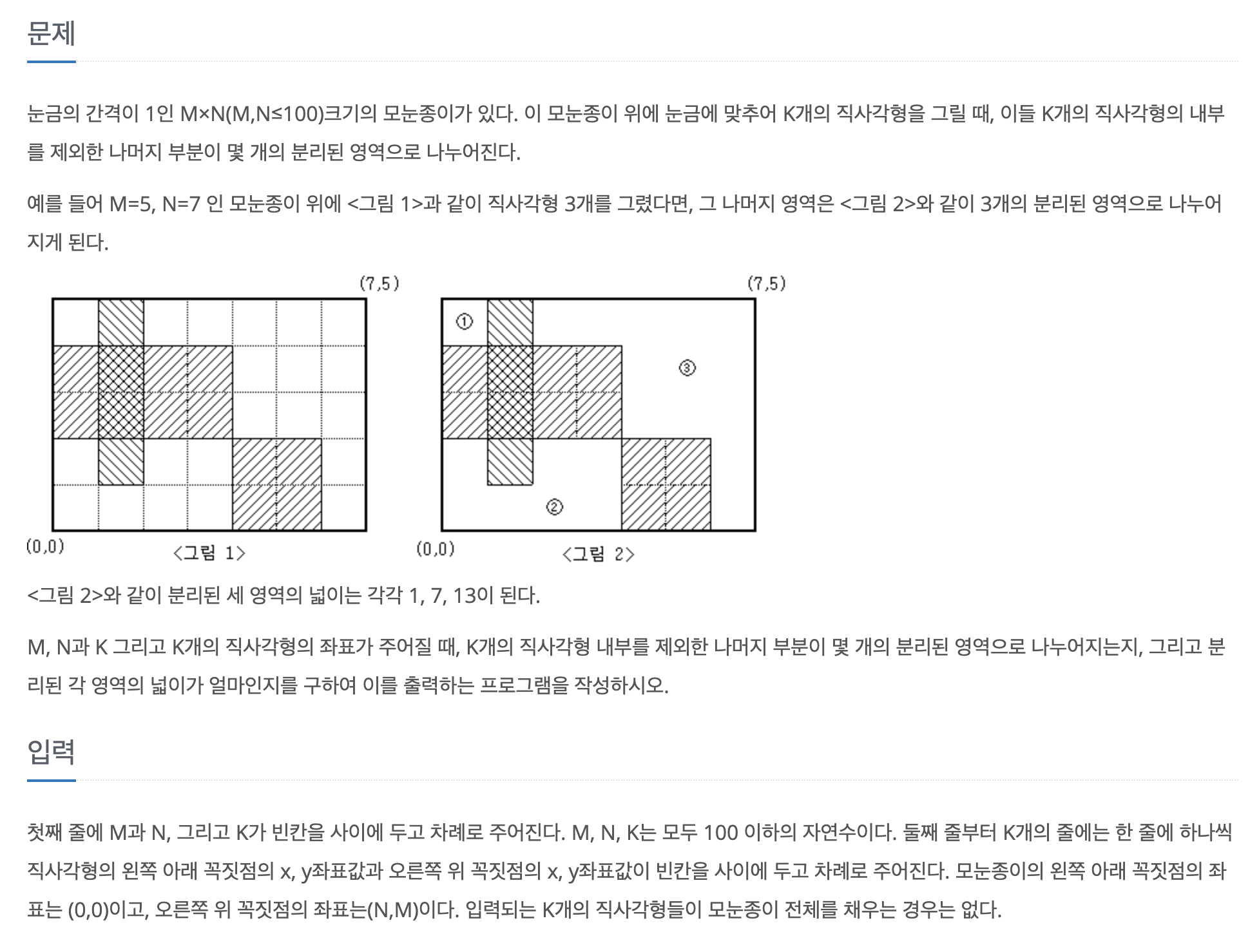
접근 방식
- 사각형을 그려서 영역을 표시하는것 빼고는 일반 영역구하기와 같다. 사각형 영역만 잘 표시해주면 된다.
나의 풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 100;
bool map[MAX][MAX] = {true, };
int dx[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int m,n,k;
// 영역 구하기
int dfs(int a, int b){
int ans = 1;
map[a][b] = false;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int ma = a+ dy[i];
int mb = b+ dx[i];
if(ma >= m || ma <0 || mb >= n || mb <0)
continue;
if(map[ma][mb])
ans+=dfs(ma, mb);
}
return ans;
}
void solution(){
int answer = 0;
vector<int> ans;
for(int a = 0;a<m;a++){
for(int b = 0;b<n;b++){
if(map[a][b]){
ans.push_back(dfs(a, b));
answer++;
}
}
}다른 풀이
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
int m, n;
char v[100][101];
int px[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int py[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int bfs(int x, int y)
{
int q[10000]{};
int b = 0, e = 0;
int res = 0;
q[e++] = x*1000 + y;
v[x][y] = 1;
res++;
while (b < e)
{
int r = q[b] / 1000;
int c = q[b] % 1000;
b++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
int tx = r + px[i];
int ty = c + py[i];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < m && ty >= 0 && ty < n)
{
if (v[tx][ty] == 0)
{
q[e++] = tx*1000 + ty;
v[tx][ty] = 1;
res++;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int k;
scanf("%d %d %d", &m, &n, &k);
int ax, ay, bx, by;
while (k--)
{
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &ax, &ay, &bx, &by);
for (int i = ax; i < bx; ++i)
{
for (int j = ay; j < by; ++j)
{
v[j][i] = 1;
}
}
}
int p = 0, cnt = 0;
int arr[5000]{};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
{
if (v[i][j] == 0)
{
cnt++;
arr[p++] = bfs(i, j);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
std::sort(arr, arr+p);
for (int i = 0; i < p; ++i) printf("%d ", arr[i]);
return 0;
}배울 점
- bfs로 푸셨다. bfs로 풀면 시간을 줄일 수 있을 것이다.
