array와 arrayList의 공통점은?
1. add and get method
Array와 ArrayList는 요소를 추가하거나 가져올 때의 성능은 비슷하다. 두 작업 모두 일정한 시간에 실행된다.
2. Duplicate elements
둘 다 중복되는 요소를 저장할 수 있다.
3. Null Values
Null 값을 저장할 수 있고 index를 사용하여 값을 참조할 수 있다.
4. 순서
순서가 지정되지 않음.
array와 arrayList의 차이점은?
Array와 ArrayList은 모든 것이 비슷합니다. 가장 큰 차이점은 길이를 조정할 수 있는가? 없는가? 입니다.
Java의 Array는 고정 길이 입니다. 따라서, 정해진 길이의 배열을 모두 채우면, 새로운 데이터를 추가하고 싶을 경우 새로운 배열을 만들어주어야 합니다.
Java의 ArrayList는 가변 길이입니다. 하지만 내부적으론 배열로 구성되어 있습니다. ArrayList는 Default로 10개의 공간을 가진 배열로 시작합니다. 하지만 최적화(지연 초기화)로 인해 막 생성하면 0개의 사이즈로 시작됩니다. 다만, 편리함의 대가로 살짝 Array보다 느리니 Array로 충분히 처리 가능하다거나 코딩 테스트나 알고리즘을 풀 때에는 Array를 활용해주는 것이 좋을 것 같습니다.
1. Resizable
- Array : Array는 static하다(길이 고정). Array 객체를 생성한 후에는 Array의 길이를 마음대로 변경할 수 없다.
- ArrayList : ArrayList는 사이즈가 dynamic하다. 각각의 ArrayList Object는 ArrayList의 size를 나타내는 capacity 인스턴스 변수를 가지고 있다. ArrayList에 요소들이 더해지면 ArrayList의 capacity 또한 자동적으로 늘어난다. 만약 설정한 capacity를 넘어서 더 많은 객체가 들어오면, 배열 크기를 1.5배 증가시킨다.
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //기존 용량 + 기존 용량 /2 (우측 shift 연산)
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}다시 한번 정리하자면, element를 add하려고 할때, capacity가 배열의 길이와 같아지면 일반적으로 기존의 용량 + 기존 용량/2 만큼 크기가 늘어난 배열에 기존의 배열을 copy해준다.
- Q. ArrayList는 저장용량을 지정해주지 않지 않나요? Default 저장용량은 10이다.
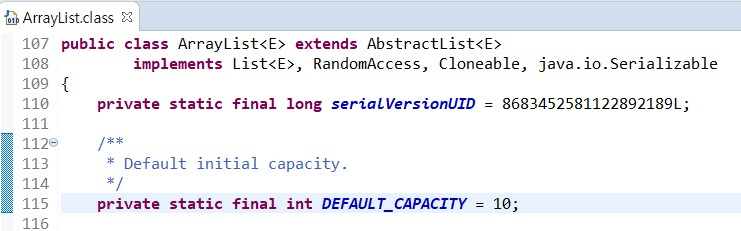
// DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10
// 기본 저장용량 10으로 리스트 생성
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 저장 용량을 100으로 설정해 ArrayList 생성
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(100);2. Performance
-
Array와 ArrayList의 성능은 수행되는 작업에 따라 달라진다.
-
resize() operation : ArrayList의 자동 크기 조정은 임시 배열을 사용하여 이전 배열의 요소를 새 배열로 복사하기 때문에 성능이 저하된다.
ArrayList의 자동 resize는 성능을 낮출 것이다(old array에서 new array로 요소들을 옮길 때 임시 array를 사용하기 때문에). ArrayList는 resizing하는 동안 내부적으로 Array의 지원을 받는다.(내부적으로 native method인 System.arrayCopy(...)를 사용하기 때문에)
-
add() or get() operation : Array나 ArrayList로 부터 요소를 얻거나 추가할 때는 거의 비슷한 성능을 보인다.
3. Primitives
- Array : primitive type, Object
- ArrayList : ArrayList는 primitive data types(int, float, double etc)을 가질 수 없다. 오직 Object만을 가질 수 있다.
- 사람들은 ArrayList가 primitive type을 저장할 수 있다는 오해를 종종 한다. 하지만 그렇지 않다.
ArrayList<int> arrList//x
ArrayList<Integer> arrList//O
ArrayList arraylisttoobject = new ArrayList();
arraylisttoobject.add(23); // try to add 23(primitive)
- JVM은 Autoboxing(내부적으로 primitive type을 타입에 상응하는 object로 변환해주는 것, int => Integer)을 통해 ArrayList에 Object만 저장되도록 한다. 따라서, 위의 코드는 내부적으로 아래와 같이 수행된다.
arraylisttoobject.add(new Integer(23));
// Converted int primitive to Integer object and added to arraylistobject
4. Iterating the values
- Array : for loop 아니면 for each loop를 통해 array를 순회할 수 있다.
- ArrayList : iterator를 사용해 ArrayList를 순회할 수 있다.
5. Type-Safety
- Array : Array는 동종(homogeneous) data structure이다. 따라서 Array는 특정 데이터 타입의 primitives나 특정 클래스의 objects만을 저장할 수 있다. 만약 명시된 타입이 아닌 다른 데이터 유형을 Array에 저장할 경우 ArrayStoreException이 발생한다.
String temp[] = new String[2]; // creates a string array of size 2
temp[0] = new Integer(12); // throws ArrayStoreException,
- ArrayList : Generics(제네릭스)를 통해 Type-Safety를 보장한다.
6. Length
- Array : Array의 길이를 반환하는 length 변수
int arrayobject[] = new int[3];
int arraylength = arrayobject.length;- ArrayList : size() 메소드
int len = arraylist.size(); // uses arraylistobject size method7. Adding elements
- Array : Assign operator(=)를 사용하여 요소를 추가한다.
- ArrayList : add() 메소드를 사용하여 요소를 추가한다.
8. Multi-dimensional
- Array : 다차원이 가능하다.
int addarrayobject[][] = new int[3][2];- ArrayList : 항상 단일 차원이다.
요약
| array | arrayList | |
|---|---|---|
| 사이즈 | 초기화시 고정 | 초기화시 사이즈를 표시하지 않음. 사이즈가 동적이다. |
| 속도 | 초기화 시 메모리에 할당되어 속도 빠름 | 추가시 메모리를 재할당하여 속도가 느림 |
| 변경 | 사이즈 변경 불가 | 추가,삭제 가능 |
| 다차원 | 가능 | 불가능 |
| 타입 | primitive type(int,byte, char etc), object | object elemnet만 가능 |
| 제네릭 | 사용 불가능 | 사용 가능(타입 안정성 보장) |
| 길이 | length 변수 | size() 메서드 |
| 변수 추가 | assignment 연산자 사용 | add() 메소드 사용 |
출처 1. https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-an-array-and-an-array-list#:~:targetText=First%20and%20Major%20difference%20between%20Array%20and%20ArrayList%20in%20Java,primitives%20and%20Objects%20in%20Java.
2. https://javahungry.blogspot.com/2015/03/difference-between-array-and-arraylist-in-java-example.html
3. https://velog.io/@adam2/Array%EC%99%80-List%EA%B7%B8%EB%A6%AC%EA%B3%A0-Java-List#java-list-collection 4. https://zorba91.tistory.com/287
5. https://zorba91.tistory.com/287


잘보고갑니다 ^^