표준 내장 객체 중 Proxy를 알아보려고 한다.
Proxy는 Proxy server, Proxy Pattern 등등 개발에서 많이 등장하는 용어 중 하나이다.
Proxy?
프록시(Proxy)의 사전적인 의미는 '대리인'이라는 뜻
📌 Proxy
Proxy 객체를 사용하면 원본 Object의 행해질 동작(Method)을 가로채서 정의할 수 있다.
여기서 동작이란 수정, 확장 등의 기능을 말한다.
→ 기존 객체를 override해서 새로운 메서드를 추가할 수 있다는 말이다.
Syntax
let proxy = new Proxy(target, handler)target: 프록시할 원본 객체handler: 가로채는 작업과 가로채는 작업을 재정의하는 방법을 정의하는 객체
proxy에 작업이 가해지고 handler에 작업과 상응하는 트랩이 있으면 트랩(trap)이 실행되어 Proxy가 이 작업을 처리할 수 있다. 트랩이 없을 경우 target에 직접 작업이 수행
const target = {
message1: "hello",
message2: "everyone",
};
const handler1 = {/* 현재는 빈 값 */};
const proxy1 = new Proxy(target, handler1);트랩이 없는 예제 코드
const target = {
msg1: "hello",
msg2: "world"
};
const proxy = new Proxy(target, {}); // 빈 핸들러
console.log(proxy.msg1); // hello
console.log(proxy.msg2); // world
proxy.customMsg = "this is custom msg from user" // 새로운 프로퍼티 생성
console.log(proxy.customMsg); // this is custom msg from user
for(let key in proxy) console.log(key); // key 값
console.log(target); // { "msg1": "hello", "msg2": "world", "customMsg": "this is custom msg from user" }위 예시 Proxy는 get, set같은 트랩이 없기 때문에 proxy에 가해지는 모든 작업은 target에 전달 된다.
proxy.customMsg=를 이용해 값을 쓰면target에새로운 값이 설정proxy.customMsg를 이용해 값을 읽으면target에에서 값을 읽음proxy를 대상으로 작업(반복)을 수행하면target에에 저장된 값이 반환
트랩이 없으면 proxy는 target을 감싸는 투명한 래퍼가 된다.
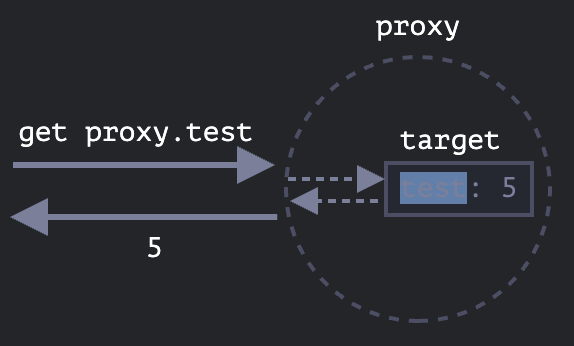
트랩 (trap)
트랩을 사용해 가로챌 수 있는 작업은 다양하게 있다.
그전에 어떻게 동작하는지부터 알아보자
객체에 어떤 작업을 수행할 때 JS 명세서에 정의된 내부 메서드가 깊숙한 곳에서 관여한다.
프로퍼티의 read 작업은 [[Get]]이라는 내부 메서드가 사용되고 write하는 작업에서는 [[Set]]이라는 내부 메서드가 사용된다.
→ 내부메서드들은 명세서에서만 정의된 메서드이기 때문에 개발자가 코드를 사용해 호출 불가하다.
Proxy의 트랩은 내부 메서드의 호출을 가로챈다.
Proxy가 가로채는 리스트는 명세서에서 확인 할 수 있다.
모든 내부 메서드엔 대응하는 트랩(핸들러 메서드)이 존재
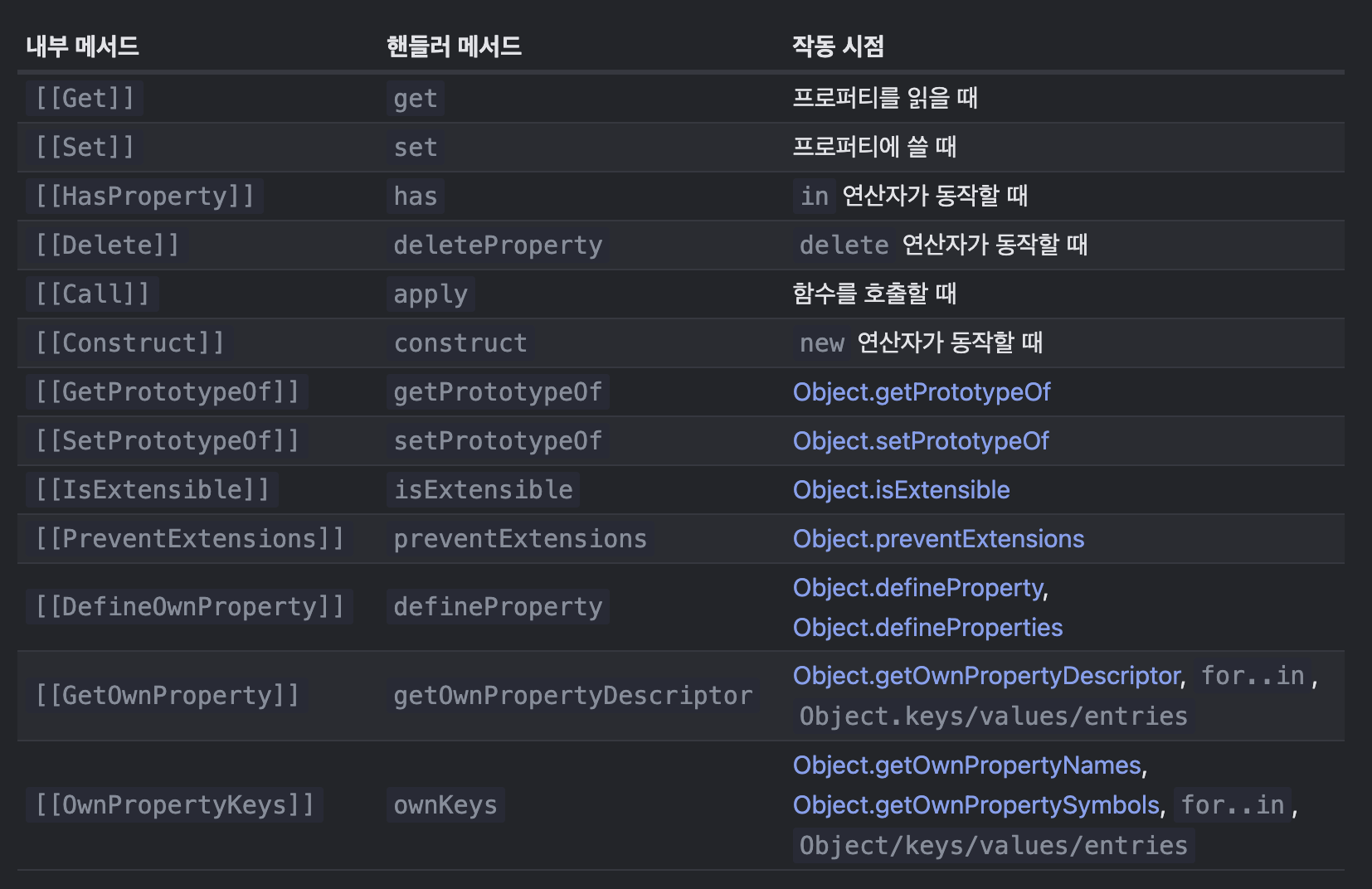
⚠️규칙
내부 메서드나 트랩을 쓸 땐 JS에서 정한 몇 가지 규칙을 반드시 따라야 한다.
대부분의 규칙은 반환 값과 관련되어 있다.
값을 쓰는 게 성공적으로 처리되었으면
[[Set]]은 반드시true를 반환해야 합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우는false를 반환해야 합니다.값을 지우는 게 성공적으로 처리되었으면
[[Delete]]는 반드시true를 반환해야 합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우는false를 반환해야 합니다.
-Proxy 객체를 대상으로[[GetPrototypeOf]]가 적용되면 Proxy 객체의 타깃 객체에[[GetPrototypeOf]]를 적용한 것과 동일한 값이 반환되어야 합니다.
→ Proxy의 프로토타입을 읽는 것은 타깃 객체의 프로토타입을 읽는 것과 동일해야 하죠.
get
-
가장 흔한 트랩
get,set
프로퍼티의 read를 가로채려면handler에get(target, property(prop), receiver메서드가 있어야 한다. -
target: 동작을 전달할 객체로new Proxy의 첫 번째 인자 -
property(prop): 프로퍼티 이름 -
receiver: 타겟 프로퍼티가 getter라면receiver는 getter가 호출될 때this
대게는proxy객체 자신이this가 됨
receiver한줄 정리
receiver를 넣으면 메서드 내의 this가 proxy를 가리키도록 보장return Reflect.get(target, prop); // receiver 빠짐 // 이 경우 get 내부의 `this`가 proxy가 아니라 원본 target이 됨.
let numbers = [0, 1, 2];
numbers = new Proxy(numbers, {
get(target, prop) {
if (prop in target) {
return target[prop];
} else {
return 0; // 기본값
}
}
});
alert( numbers[1] ); // 1
alert( numbers[123] ); // 0 (해당하는 요소가 배열에 없으므로 0이 반환됨)set
set(target, property, value, receiver)
target: 동작을 전달할 객체로new Proxy의 첫 번째 인자property– 프로퍼티 이름value– 프로퍼티 값receiver–get트랩과 유사하게 동작하는 객체로,setter프로퍼티에만 관여합니다.
다음 코드는 배열에 숫자만 저장할 수 있는 코드를 proxy를 통해 구현한 코드
set 트랩은 숫자형 값을 설정하려 할 때만 true를 그렇지 않은 경우엔(TypeError가 트리거되고) false를 반환하도록 해야 합니다.
const numbers = [];
const proxy = new Proxy(numbers, {
set(target, prop, val) { // 프로퍼티에 값을 쓰는 동작을 가로챕니다.
if (typeof val == 'number') {
target[prop] = val;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
});
proxy.push(1)
proxy.push(2)
console.log("Length is: " + numbers.length); // 2
console.log(numbers) // [1,2]
console.log("proxy", proxy) // [1,2]push나 unshift 같이 배열에 값을 추가해주는 메서드들은 내부에서 [[Set]]을 사용하고 있기 때문에 메서드를 오버라이드 하지 않아도 프락시가 동작을 가로채고 값을 검증해줍니다.
⚠️
true를 잊지 말고 반환해주세요.
set 트랩을 사용할 땐 값을 쓰는 게 성공했을 때 반드시 true를 반환해줘야 합니다.
true를 반환하지 않았거나 falsy한 값을 반환하게 되면 TypeError가 발생합니다.
📌 Reflect
Reflect는 Proxy 생성을 더 쉽게 해주는 내장 객체(built-in object)
앞서 말했듯이 [[Get]], [[Set]] 같은 내부 메서드들은 자바스크립트 명세에만 존재할 뿐 직접 호출할 수는 없다.
Reflect 객체는 이런 내부 메서드를 어느 정도 사용할 수 있게 해줍니다.
그 메서드들은 내부 메서드를 감싼 최소한의 래퍼(wrapper) 역할을 합니다.
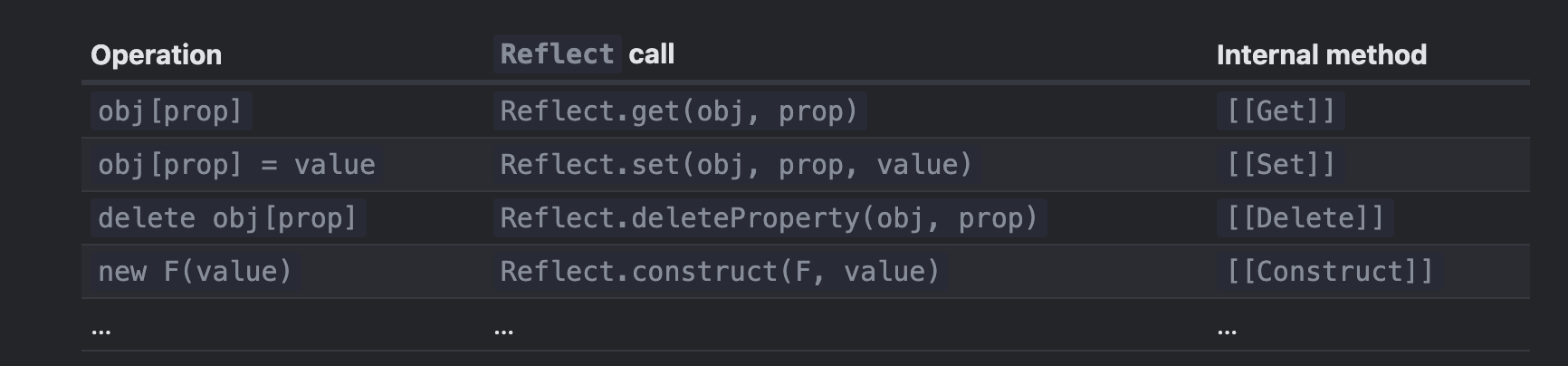
| 목적 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 기본 동작을 위임 | target[prop] = value 같은 동작을 안전하게 수행 |
| 일관된 반환값 | true/false 반환 등 규칙을 만족 |
| 예외 처리 | 잘못된 동작 시 명확한 오류를 던짐 (ex. Reflect.set 실패 시 false) |
get
const user = {
name: "Alice",
age: 30
};
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, prop, receiver) {
console.log(`Accessing property: ${prop}`);
return Reflect.get(target, prop, receiver); // 기본 동작 안전하게 위임
}
});
console.log(proxy.name); // "Accessing property: name" → "Alice"set
const user = {
name: "Bob"
};
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
set(target, prop, value, receiver) {
if (prop === "age" && typeof value !== "number") {
console.warn("Age must be a number!");
return false; // Proxy 규칙상 false 반환 시 set 실패
}
console.log(`Setting ${prop} to ${value}`);
return Reflect.set(target, prop, value, receiver);
}
});
proxy.name = "Charlie"; // Setting name to Charlie
proxy.age = "not a number"; // Age must be a number!
console.log(proxy.age); // undefineddelete
const user = {
name: "David",
role: "admin"
};
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
deleteProperty(target, prop) {
if (prop === "role") {
console.warn("You can't delete 'role'");
return false;
}
console.log(`Deleting property: ${prop}`);
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target, prop); // true or false 반환
}
});
delete proxy.name; // Deleting property: name
delete proxy.role; // You can't delete 'role'참고자료
https://ko.javascript.info/proxy#ref-567
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Proxy
