풀이 방법:
DFS, BFS 알고리즘 공부를 위한 문제이므로 DFS, BFS 알고리즘 개념 공부 후 풀었습니다
접근 방법:
DFS, BFS 알고리즘을 각각 구현하면 되며, 문제에서 정점 번호가 여러 개인 경우에는 정점 번호가 작은 것을 먼저 방문하라 했으므로, 그냥 정점 별로 간선 연결할 때 정렬해주면된다.
변수 선언:
-
int N = 정점의 개수
-
int M = 간선의 개수
-
int V = 시작할 정점의 번호
-
LinkedList와 크기를 가지고 있을 Graph 클래스
Graph 클래스 필드:
-
int V = 정점의 크기
-
LinkedList adj[] = 인접한 정점들을 이을 배열
-
Graph 생성자(int v)
-
Graph 메소드:
-
addEdge(간선간 연결) 메소드
-
DFSUtill 메소드 = DFS 메소드가 사용
-
DFS 메소드: DFS를 위한 메소드
-
BFS 메소드: BFS를 위한 메소드
풀이 과정:
-
- 입력받은대로 Graph의 정점간 연결을 생성한다
-
- 정점간 연결을 하는 addEdge를 진행할 때, 단일 연결 리스트가 아닌 다중 연결 리스트로 이어줘야 한다. 정렬도 작은 수가 우선순위를 가지므로 두 방향 모두 오름차순 정렬을 한다
-
3-1. DFS 방식을 진행하는데 이때 스택, 재귀함수 방식 중 재귀함수 방식을 사용했다
-
3-2 방문했는지를 체크해주는 boolean 타입의 visited 배열을 클래스에 있는 정점의 개수 크기로 생성한다.
-
3-3. DFSUtill을 재귀함수로 실행하는데 일단 정점의 방문을 체크하고 출력하며, 인접한 노드를 방문하여 해당 노드가 방문하지 않았다면 방문으로 바꿔주고 다시 재귀함수의 과정을 진행한다.
-
3-4. 방문했다면 재귀함수가 실행되지 않고 그냥 넘어갈 것이다.
-
4-1. BFS 방식을 진행하는데 큐 방식을 사용했다.
-
4-2. 정점은 큐에 저장하며, 정점을 출력한다. 인접한 노드들을 방문하지 않았다면 모두 큐에 넣는다.
-
4-3. 다시 반복되어 큐에 있는 값을 모두 출력하고 다시 인접한 노드가 있는지 확인하며 있으먼 큐에 넣는다
-
4-4. DFS와 다르게 정점 노드와 연결되어 있는 것들이 먼저 큐에 저장되고 그다음에 각각에 연결되어 있는 것들을 다 보면서 큐에 저장하기 때문에 DFS 방식과는 다르게 동작함을 확인할 수 있다
작성 코드:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Graph{
private int V;
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[];
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
Graph(int v){
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for(int i=0; i<v; i++){
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
}
void addEdge(int v, int w){
adj[v].add(w);
adj[w].add(v);
Collections.sort(adj[v]);
Collections.sort(adj[w]);
}
void DFSUtill(int v, boolean visited[]) throws IOException {
visited[v] = true;
bw.write(v+" ");
Iterator<Integer> i = adj[v].listIterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
int n = i.next();
if(!visited[n]){
DFSUtill(n, visited);
}
}
}
void DFS(int v) throws IOException {
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
DFSUtill(v, visited);
}
void BFS(int s) throws IOException {
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited[s] = true;
queue.add(s);
bw.write("\n");
while(queue.size() != 0 ){
s = queue.poll();
bw.write(s+" ");
Iterator<Integer> i = adj[s].listIterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
int n = i.next();
if(!visited[n]){
visited[n] = true;
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
bw.close();
}
/* void Stack_DFS(int s) throws IOException {
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
visited[s] = true;
stack.push(s);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Collections.sort(stack,Collections.reverseOrder());
s = stack.pop();
bw.write(s+" ");
for(int j=0; j<adj[s].size(); j++){
int chk = adj[s].get(j);
//System.out.println(chk + "\n");
if(!visited[chk]){
visited[chk] = true;
stack.push(chk);
}
}
}
bw.close();
}*/
}
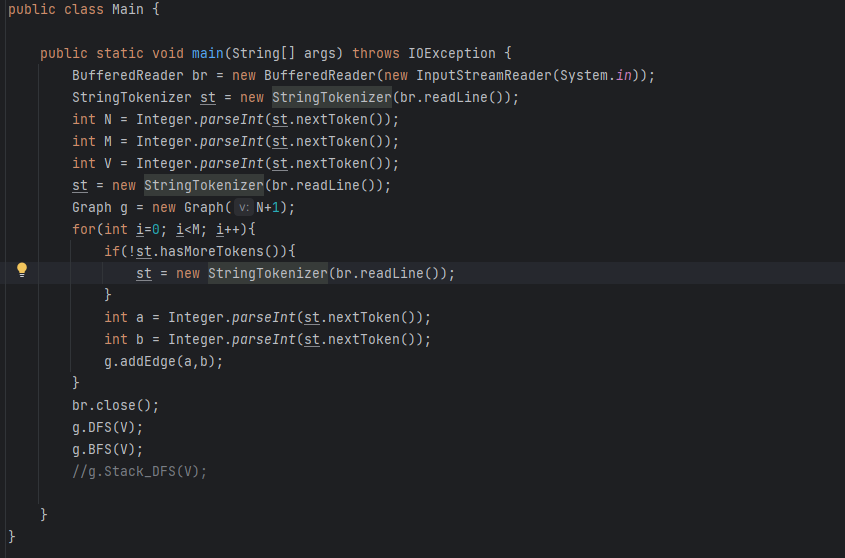
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
Graph g = new Graph(N+1);
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
if(!st.hasMoreTokens()){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
}
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
g.addEdge(a,b);
}
br.close();
g.DFS(V);
g.BFS(V);
//g.Stack_DFS(V);
}
}결과:

예제 코드가 잘 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
