

1. If Statements & Boolean Operators
(1) If Statements
<!--If condition A is true, return B-->
if(A) {
return B;
}
<!--IF condition A is true, return a.
If condition B is true, return B.
If neither one is true, return C.-->
if(A) {
return a;
} else if (B) {
return b;
} else {
return c;
}(2) Boolean Operators
Boolean operators are important for conditional code, 'cause it returns either true or false.
- ==: check for value equality
- !==: check for value inequality
- === and !==: check for value AND type (in)equality
- > and <: check for value being greater/smaller
- >= and <=: check for value being greater or equal
- !: check if NOT true
(3) The Logical AND and OR operators
AND and OR operators are meant to combine 2 or more conditions.
- &&(and): evaluated together(yields true if each condition yields true)
- ||(or): evaluated as an alternative
(4) ToBoolean Result
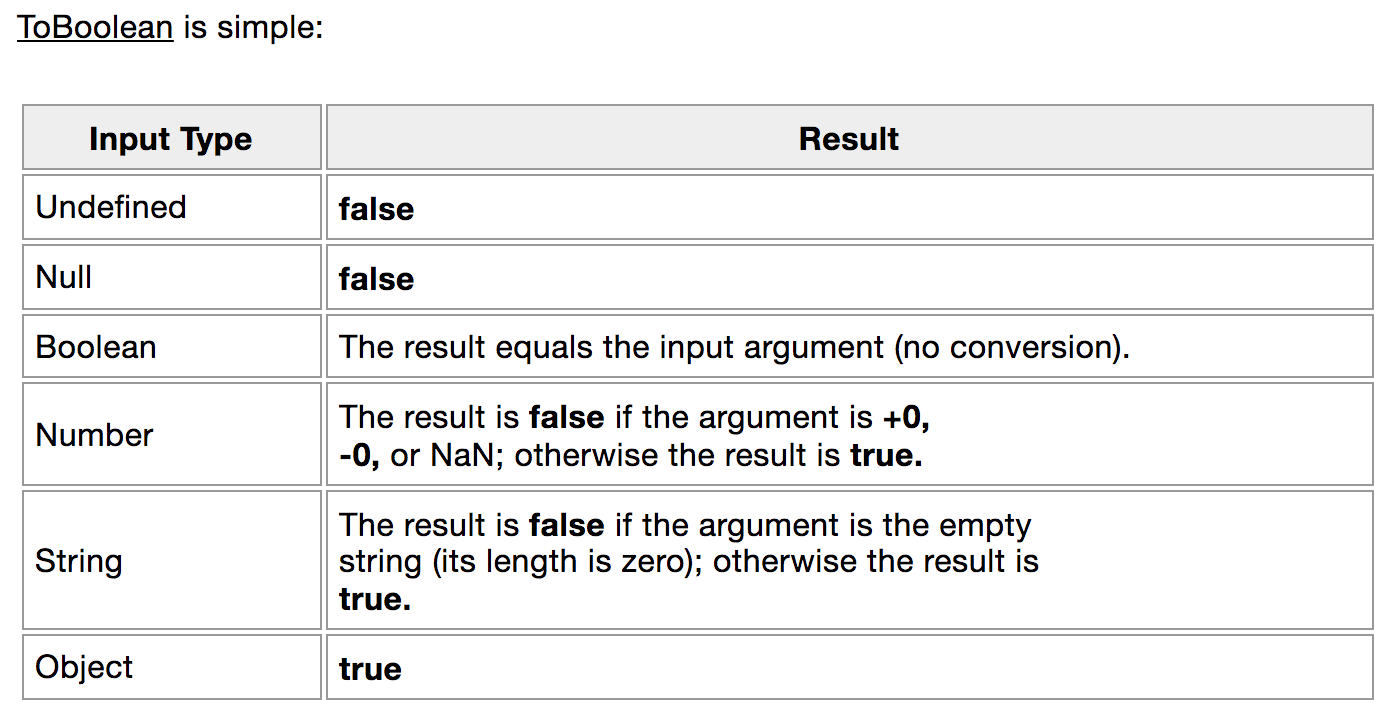
const nameInput = 'Nina'
if(nameInput) {
...
}This code works fine eventhough nameInput itself is not a condition. JS treis to coerce values to a boolean value if a boolean is required(it is a string which is not empty, so it returns true).
(5) Ternary Operator
const userName = isLogin ? 'Nina' : nullIf isLogin(condition) is true, return 'Nina'. If not, return null.
(6) Switch-case Statement
<!--if statement-->
if(date === 1) {
console.log('Monday');
} else if(date ===2) {
console.log('Tuesday');
} else if(date ===3) {
console.log('Wednesday');
} else if(date ===4) {
console.log('Thursday');
} else if(date ===5) {
console.log('Friday');
} else if(date ===6) {
console.log('Saturday');
} else if(date ===7) {
console.log('Sunday');
}
<!--switch-case statement-->
Switch (date) {
case 1:
console.log('Monday')
break;
case 2:
console.log('Tuesday')
break;
case 3:
console.log('Wednesday')
break;
case 4:
console.log('Thursday')
break;
case 5:
console.log('Friday')
break;
case 6:
console.log('Saturday')
break;
case 7:
console.log('Sunday')
break;
}2. Loops
"Loops are handy, if you want to run the same code over and over again, each time with a different value."
(1) Kinds of Loops
for loop
'for loop' executes code a certain amount of times
for(let i = 0; i < 3; i++){
console.log(i);
}for-of loop
'for-of loop' executes for every element in an array
for(const el of array){
console.log(el);
}for-in loop
'for-in loop' executes for every key in an object
for(const key in obj){
console.log(key);
console.log(obj[key]);
}while loop
'while loop' executes code as long as the condition is true
while(isLoggedIn){..} while loop: checks the condition first
do-while loop: executes the condition first and then checks the condition
(2) Controlling Loop
Break
"The break statement can also be used to jump out of a loop.
The break statement breaks the loop and continues executing the code after the loop (if any):"
You can use "break" inside of the loop to stop the execution.
Continue
"The continue statement breaks one iteration (in the loop), if a specified condition occurs, and continues with the next iteration in the loop."
"continue" stops current execution, but doesn't stop the entire loop.
