Props란
props는 부모 컴포넌트가 자식 컴포넌트의 JSX 태그에 전달하는 정보이다.
React components use props to communicate with each other. Every parent component can pass some information to its child components by giving them props. Props might remind you of HTML attributes, but you can pass any JavaScript value through them, including objects, arrays, and functions.
React 컴포넌트들은 props를 사용하여 서로 커뮤니케이션한다. 모든 부모 컴포넌트는 props를 자식 컴포넌트에게 줌으로써 정보를 자식 컴포넌트에게 전달할 수 있다. Props는 HTML 속성을 떠오르게 할 수도 있지만, 객체, 배열, 함수를 포함한 모든 Js 값을 전달할 수 있다.
props 사용
props를 통해 부모 컴포넌트와 자식 컴포넌트를 독립적으로 생각할 수 있다.
- Hello.jsx
const Hello = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>Hello {props.name}</p>
</div>
)
};
export default Hello;- App.jsx
import Hello from './components/Hello.jsx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Hello name={"bbongchill"}/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;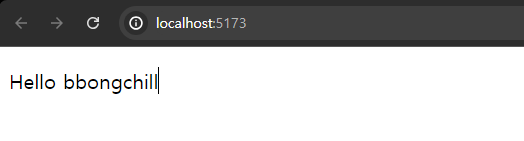
위 코드에서는 Hello 컴포넌트가 매개변수로 props 객체를 받고, <p>태그 안에 {props.name}을 선언하여 name을 받아온다. name을 받아오기 위해 App.jsx에서 <Hello />태그 안에서 name="bbongchill"을 선언하여 name을 할당한다.
이처럼 Hello 컴포넌트가 name을 어떻게 사용하는지 생각할 필요없이 수정할 수 있다.
여러 개를 받아오는 것도 가능하다.
- Hello.jsx
const Hello = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>Hello {props.name}</p>
<p>My age is {props.age}</p>
</div>
)
};
export default Hello;- App.jsx
import Hello from './components/Hello.jsx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Hello name={"bbongchill"} age={20}/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;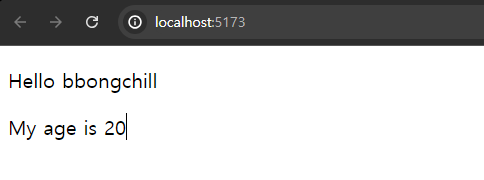
다른 형태로 props 사용
props로 전달된 값이 많아지면, 객체의 점 표기법을 사용해야하는 것이 많이 번거롭게 느껴진다. 이를 해결하기 위해 props도 객체이므로 구조 분해 할당을 활용하여 컴포넌트의 매개변수를 표현할 수 있다.
- Hello.jsx
const Hello = ({name, age}) => {
return (
<div>
<p>Hello {name}</p>
<p>My age is {age}</p>
</div>
)
};
export default Hello;- App.jsx
import Hello from './components/Hello.jsx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Hello name={"gongchill"} age={22}/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;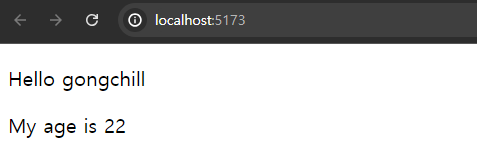
props 기본값 지정
Hello 컴포넌트의 매개변수를 작성할 때 기본값을 지정할 수 있다.
- Hello.jsx
const Hello = ({name, age = 20}) => {
return (
<div>
<p>Hello {name}</p>
<p>My age is {age}</p>
</div>
)
};
export default Hello;- App.jsx
import Hello from './components/Hello.jsx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Hello name={"gongchill"}/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;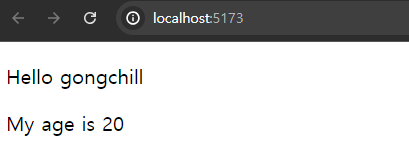
spread 연산자로 여러 개의 값 전달
부모 컴포넌트에서 props로 전달할 값이 많으면, 값을 하나하나 지정해줘야하고, 가독성이 떨어지게 된다. 이 때 spread 연산자를 사용하면 간결하게 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
- Hello.jsx
const Hello = ({name, age, country, gender}) => {
return (
<div>
<p>Hello {name}</p>
<p>My age is {age}</p>
<p>I am from {country}</p>
<p>I am {gender}</p>
</div>
)
};
export default Hello;- App.jsx (변경 전)
import Hello from './components/Hello.jsx'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Hello
name={"gongchill"}
age={20}
country={"Korea"}
gender={"male"}
/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;- App.jsx (변경 후)
import Hello from './components/Hello.jsx'
function App() {
const bodyProps = {
name:"gongchill",
age:20,
country:"Korea",
gender:"male"
}
return (
<div>
<Hello {...bodyProps}/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;자식을 JSX로 전달
JSX 태그 내에 컨텐츠를 중첩하면, 부모 컴포넌트는 해당 컨텐츠를 childern이라는 props 객체의 요소로 받는다.
- Hello.jsx
const Hello = ({name, age, country, gender, childern}) => {
return (
<div>
<p>Hello {name}</p>
<p>My age is {age}</p>
<p>I am from {country}</p>
<p>I am {gender}</p>
{childern}
</div>
)
};
export default Hello;- App.jsx
import Hello from "./components/Hello.jsx"
function App() {
const bodyProps = {
name:"gongchill",
age:20,
country:"Korea",
gender:"male"
};
return (
<div>
<Hello {...bodyProps} />
안녕하세요<br/>
저의 20살<br/>
저는 한국에서 왔습니다.<br/>
저는 남자입니다.<br/>
</div>
)
}
export default App;<Hello /> 이후의 코드들이 childern prop의 내용이 되고, 이것을 <div> 태그로 렌더링한다.
