
📖Review (21.04.09)
OOP (Object Oriented Programming)
객체지향 프로그래밍
- 관계성있는 객체들의 집합이라는 관점으로 접근하는 소프트웨어 디자인
- 객체지향 프로그래밍은 보다 유연하고 유지보수하기 쉬우며 확장성 측면에서도 유리한 프로그래밍을 하도록 의도되었고, 대규모 소프트웨어 개발에 널리 쓰인다.
클래스 기반 vs 프로토타입 기반
클래스 기반 언어
클래스 기반 언어(Java, C++, C#, Python, Ruby,,,)는 클래스로 객체의 자료구조와 기능을 정의하고 생성자(constructor)를 통해 인스턴스를 생성한다.
모든 인스턴스는 오직 클래스에서 정의된 범위 내에서만 작동하며 런타임에 그 구조를 변경할 수 없다.
프로토타입 기반 언어
자바스크립트는 멀티-패러다임 언어로 명령형(imperative), 함수형(functional), 프로토타입 기반(prototype-based) 객체지향 언어다.
클래스 정의 (Class Definition)
ES6 클래스는 class 키워드를 사용하여 정의한다.
// 클래스 선언문
class Person {
// constructor(생성자)
constructor(name) {
this._name = name;
}
sayHi() {
console.log(`Hi! ${this._name}`);
}
}
// 인스턴스 생성
const me = new Person('Lee');
me.sayHi(); // Hi! Lee
console.log(me instanceof Person); // true클래스는 클래스 선언문 이전에 참조할 수 없다.
console.log(Foo);
// ReferenceError: Cannot access 'Foo' before initialization
class Foo {}일반적이지는 않지만, 표현식으로도 클래스를 정의할 수 있다. 함수와 마찬가지로 클래스는 이름을 가질 수도 갖지 않을 수도 있다. 이때 클래스가 할당된 변수를 사용해 클래스를 생성하지 않고 기명 클래스의 클래스 이름을 사용해 클래스를 생성하면 에러가 발생한다. 이는 함수와 마찬가지로 클래스 표현식에서 사용한 클래스 이름은 외부 코드에서 접근 불가능하기 때문이다.
// 클래스명 MyClass는 함수 표현식과 동일하게 클래스 몸체 내부에서만 유효한 식별자이다.
const Foo = class MyClass {};
const foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo); // MyClass {}
new MyClass(); // ReferenceError: MyClass is not defined인스턴스 생성
생성자 함수와 같이 new 연산자와 함께 클래스 이름을 호출하면 클래스의 인스턴스가 생성된다.
class Foo {}
const foo = new Foo();위 코드에서 new 연산자와 함께 호출한 Foo는 클래스의 이름이 아니라 constructor(생성자)이다.
// Foo는 사실 생성자 함수(constructor)이다.
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(foo).constructor === Foo); // truenew 연산자를 사용하지 않고 constructor를 호출하면 타입 에러(TypeError)가 발생한다. constructor는 new 연산자 없이 호출할 수 없다.
constructor
constructor는 인스턴스를 생성하고 클래스 필드를 초기화하기 위한 특수한 메소드이다.
클래스 필드(class field)
클래스 내부의 캡슐화된 변수를 말한다. 데이터 멤버 또는 멤버 변수라고도 부른다. 클래스 필드는 인스턴스의 프로퍼티 또는 정적 프로퍼티가 될 수 있다. 쉽게 말해, 자바스크립트의 생성자 함수에서 this에 추가한 프로퍼티를 클래스 기반 객체지향 언어에서는 클래스 필드라고 부른다.
// 클래스 선언문
class Person {
// constructor(생성자). 이름을 바꿀 수 없다.
constructor(name) {
// this는 클래스가 생성할 인스턴스를 가리킨다.
// _name은 클래스 필드이다.
this._name = name;
}
}
// 인스턴스 생성
const me = new Person('Lee');
console.log(me); // Person {_name: "Lee"}constructor는 생략할 수 있다. constructor를 생략하면 클래스에 constructor() {}를 포함한 것과 동일하게 동작한다. 즉, 빈 객체를 생성한다. 따라서 인스턴스에 프로퍼티를 추가하려면 인스턴스를 생성한 이후, 프로퍼티를 동적으로 추가해야 한다.
class Foo { }
const foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo); // Foo {}
// 프로퍼티 동적 할당 및 초기화
foo.num = 1;
console.log(foo); // Foo { num: 1 }constructor는 인스턴스의 생성과 동시에 클래스 필드의 생성과 초기화를 실행한다.
class Foo {
// constructor는 인스턴스의 생성과 동시에 클래스 필드의 생성과 초기화를 실행한다.
constructor(num) {
this.num = num;
}
}
const foo = new Foo(1);
console.log(foo); // Foo { num: 1 }클래스 필드
클래스 몸체(class body)에는 메소드만 선언할 수 있다. 클래스 바디에 클래스 필드(멤버 변수)를 선언하면 문법 에러(SyntaxError)가 발생한다. 클래스 필드의 선언과 초기화는 반드시 constructor 내부에서 실시한다.
class Foo {
name = ''; // SyntaxError
constructor() {}
}정적 메소드
클래스의 정적(static) 메소드를 정의할 때 static 키워드를 사용한다. 정적 메소드는 클래스의 인스턴스가 아닌 클래스 이름으로 호출한다. 따라서 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있다.
class Foo {
constructor(prop) {
this.prop = prop;
}
static staticMethod() {
/*
정적 메소드는 this를 사용할 수 없다.
정적 메소드 내부에서 this는 클래스의 인스턴스가 아닌 클래스 자신을 가리킨다.
*/
return 'staticMethod';
}
prototypeMethod() {
return this.prop;
}
}
// 정적 메소드는 클래스 이름으로 호출한다.
console.log(Foo.staticMethod());
const foo = new Foo(123);
// 정적 메소드는 인스턴스로 호출할 수 없다.
console.log(foo.staticMethod()); // Uncaught TypeError: foo.staticMethod is not a function위 예제를 ES5로 표현해보면
var Foo = (function () {
// 생성자 함수
function Foo(prop) {
this.prop = prop;
}
Foo.staticMethod = function () {
return 'staticMethod';
};
Foo.prototype.prototypeMethod = function () {
return this.prop;
};
return Foo;
}());
var foo = new Foo(123);
console.log(foo.prototypeMethod()); // 123
console.log(Foo.staticMethod()); // staticMethod
console.log(foo.staticMethod()); // Uncaught TypeError: foo.staticMethod is not a function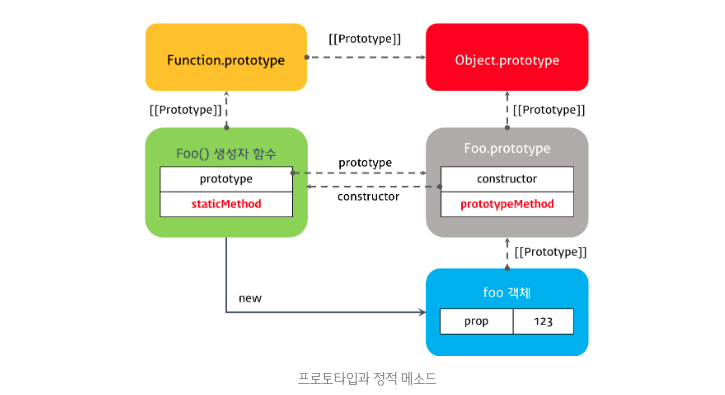
클래스 상속 (class inheritance)
클래스 상속(Class Inheritance)은 코드 재사용 관점에서 매우 유용하다
extends 키워드
extends 키워드는 부모 클래스(base class)를 상속받는 자식 클래스(sub class)를 정의할 때 사용한다.
// 부모 클래스
class Circle {
constructor(radius) {
this.radius = radius; // 반지름
}
// 원의 지름
getDiameter() {
return 2 * this.radius;
}
// 원의 둘레
getPerimeter() {
return 2 * Math.PI * this.radius;
}
// 원의 넓이
getArea() {
return Math.PI * Math.pow(this.radius, 2);
}
}
// 자식 클래스
class Cylinder extends Circle {
constructor(radius, height) {
super(radius);
this.height = height;
}
// 원통의 넓이: 부모 클래스의 getArea 메소드를 오버라이딩하였다.
getArea() {
// (원통의 높이 * 원의 둘레) + (2 * 원의 넓이)
return (this.height * super.getPerimeter()) + (2 * super.getArea());
}
// 원통의 부피
getVolume() {
return super.getArea() * this.height;
}
}
// 반지름이 2, 높이가 10인 원통
const cylinder = new Cylinder(2, 10);
// 원의 지름
console.log(cylinder.getDiameter()); // 4
// 원의 둘레
console.log(cylinder.getPerimeter()); // 12.566370614359172
// 원통의 넓이
console.log(cylinder.getArea()); // 150.79644737231007
// 원통의 부피
console.log(cylinder.getVolume()); // 125.66370614359172
// cylinder는 Cylinder 클래스의 인스턴스이다.
console.log(cylinder instanceof Cylinder); // true
// cylinder는 Circle 클래스의 인스턴스이다.
console.log(cylinder instanceof Circle); // trueconsole.log(cylinder.__proto__ === Cylinder.prototype); // true
console.log(Cylinder.prototype.__proto__ === Circle.prototype); // true
console.log(Circle.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__ === null); // truesuper 키워드
super 키워드는 부모 클래스를 참조(Reference)할 때 또는 부모 클래스의 constructor를 호출할 때 사용한다.
