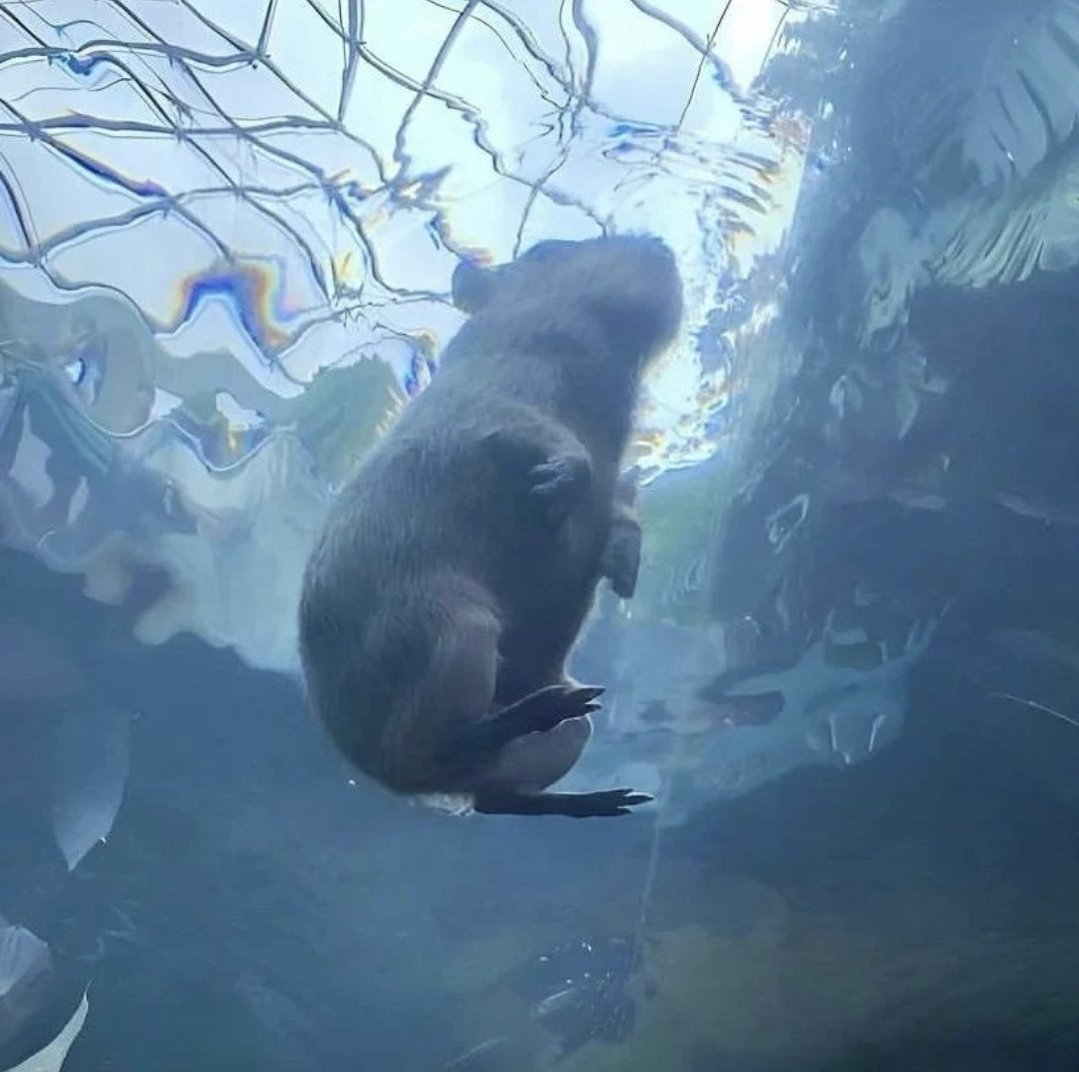
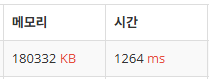
0. 메모리 및 실행시간
1. 제출 코드
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int T = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // T분 동안 음식 먹음
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 음식 종류
int D = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 다이어트 효과 유지 시간
int K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 몇 잔?
int[] time = new int[N];
int[] next = new int[N];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
time[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
Arrays.sort(time);
int[] cnt = new int[N];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
while (j < N && time[j] <= time[i] + D - 1) j++;
cnt[i] = j - i;
next[i] = j - 1;
}
int[][] dp = new int[K+1][N+1];
for (int r = 1; r <= K; r++) {
for (int c = N-1; c >= 0; c--) {
int no = dp[r][c+1];
int yes = cnt[c] + dp[r-1][next[c]+1];
dp[r][c] = Math.max(no, yes);
}
}
System.out.println(dp[K][0]);
br.close();
}
}
2. 풀이과정 및 리뷰
- 시간복잡도:
- 풀이과정
- 처음 접근 (실패)
- 정답과 같은 방식으로 DP 배열 계산 but T 길이의 카운팅 정렬 이용 → 메모리초과
time배열 : 음식 먹는 타이밍 저장 후 정렬cnt배열 : 해당 타이밍에 차를 마시는 경우 영향을 받는 음식의 수next배열 : 해당 타이밍에 차를 마시는 경우, 차의 영향이 끝나는 인덱스 + 1dp배열 :퇴사 문제처럼뒤쪽 인덱스부터 시작해서- 안 마시는 경우 : 바로 다음 인덱스의 값 그대로 가져오기
- 마시는 경우 : 지금 마실 때 영향을 받는 음식 수 from
cnt배열 + 그 다음 인덱스에서 한 잔 덜 마실 때의 dp값
- 처음 접근 (실패)
3. 개선점
🔹 (1) DP 1차원 배열로 압축
dp[r][c]는 dp[r-1][...]만 참조하므로,
이전 행만 저장하면 충분합니다.
int[] prev = new int[N+1];
int[] curr = new int[N+1];
for (int r = 1; r <= K; r++) {
for (int c = N-1; c >= 0; c--) {
int no = curr[c+1];
int yes = cnt[c] + prev[next[c]+1];
curr[c] = Math.max(no, yes);
}
int[] tmp = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
System.out.println(prev[0]);➡️ 메모리: O(N)
➡️ 시간: 여전히 O(KN) (단, 캐시 효율↑, 실행속도 개선)
🔹 (2) 누적 최대값(prefix max) 최적화 (가능할 경우)
다음 상태가 항상 next[c]+1로 점프하므로,
dp[r-1]에 대해 미리 suffix max 배열을 만들어 두면 O(1)로 접근 가능.
for (int r = 1; r <= K; r++) {
int[] suffix = new int[N+2];
for (int c = N-1; c >= 0; c--) {
suffix[c] = Math.max(suffix[c+1], prev[c]);
}
for (int c = N-1; c >= 0; c--) {
int no = curr[c+1];
int yes = cnt[c] + suffix[next[c]+1];
curr[c] = Math.max(no, yes);
}
int[] tmp = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = tmp;
}suffix계산은 O(N)- 내부 루프도 O(N)
- 따라서 한 라운드(
r)당 O(N) - 전체 O(KN)이지만 실제 상수항이 매우 작아져서 체감 속도 크게 향상
🔹 (3) 근본적인 속도 개선: K가 크다면 완전 DP로는 불가
K가 최대 수천이라면 DP는 이미 한계.- 이 문제의 구조(간격 기반 + 최댓값)는 그리디 또는 구간 선택 문제 형태로 변환 가능.
- 예를 들어, 각 구간
[time[i], time[i]+D-1]를 “간격(interval)”로 보고 서로 겹치지 않게 K개를 고르는 최대 카운트 문제로 바꾸면,
→ 이분탐색 + DP + 누적합 형태로 O(N log N + K log N)까지 최적화 가능.
