웹을 구성하는 3요소 HTML, CSS, JS
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
웹 페이지의 구조를 정의하는 표준 Markup 언어
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
HTML 요소의 스타일을 지정하는 언어
JavaScript
웹 페이지에 동적인 기능을 추가하는 프로그래밍 언어
html 구성 요소
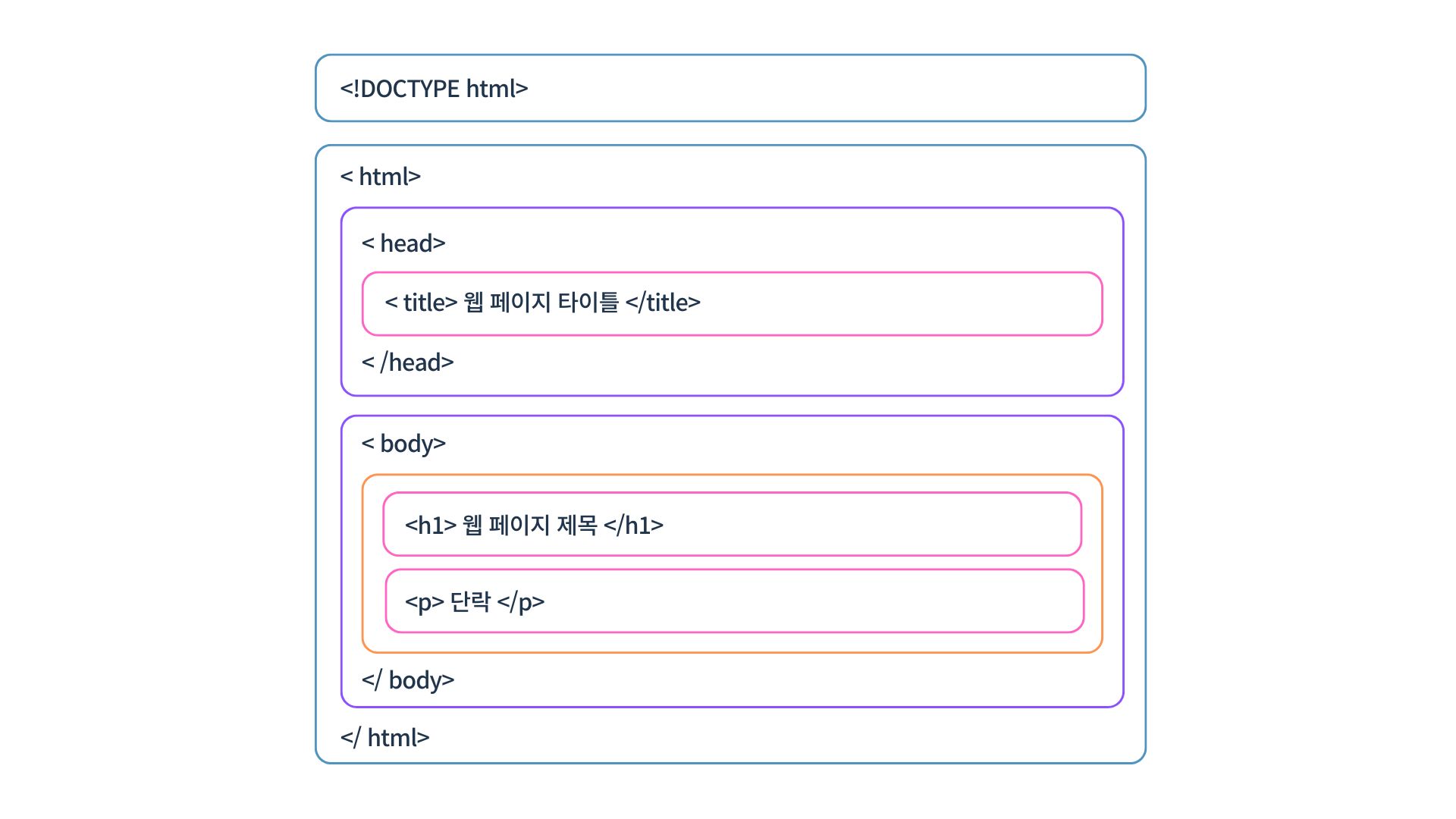
<!DOCTYPE html> <!-- html 선언문 -->
<html lang="en">
<head> <!-- html 문서 정보 -->
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>웹 페이지 타이틀</title>
</head>
<body> <!-- html 문서의 본문 -->
<h1>웹 페이지 제목</h1>
<p>단락</p>
<a href="https://velog.io/@hyejiining/posts">링크</a>
</body>
</html>CSS 구성 요소
CSS는 선택자(selector)와 선언(declaration)으로 구성
선언은 속성(property)과 값(value)으로 구성
선택자 {
속성 : 값;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS 예제</title>
<style>
/* 배경 */
.background-example {
background-color: lightblue; /* 배경색 */
background-image: url('example.jpg'); /* 배경 이미지 */
background-size: cover; /* 배경 이미지 크기 */
}
/* 사이즈 */
.size-example {
width: 300px; /* 너비 */
height: 200px; /* 높이 */
}
/* 폰트 */
.font-example {
font-size: 20pt; /* 글자 크기 */
font-weight: bold; /* 글자 굵기 */
font-family: "돋움체"; /* 글꼴 */
color: green; /* 글자 색상 */
}
/* 간격 */
.spacing-example {
margin: 20px; /* 외부 여백 */
padding: 15px; /* 내부 여백 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="background-example size-example spacing-example font-example">
<h1>CSS 속성 예제</h1>
<p>다양한 CSS 속성</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>JavaScript 구성 요소
변수 (Variables)
데이터를 저장할 수 있는 공간을 선언 var, let, const 키워드를 사용
데이터 타입 (Data Types)
문자열(String), 숫자(Number), 불리언(Boolean), 널(Null),
정의되지 않음(Undefined), 객체(Object), 심볼(Symbol)
연산자 (Operators)
산술 연산자, 할당 연산자, 비교 연산자, 논리 연산자
조건문 (Conditional Statements)
조건에 따라 코드의 실행을 제어 if, else if, else 문이 사용
반복문 (Loops)
특정 코드를 반복적으로 실행
for, while, do...while
함수 (Functions)
특정 작업을 수행하는 코드 블록으로 재사용성을 높이고, 구조화된 프로그래밍 가능
객체 (Objects)
속성(property)과 메서드(method)를 포함하는 데이터 구조
객체는 키-값 쌍으로 구성
배열 (Arrays)
여러 값을 하나의 변수에 저장할 수 있는 데이터 구조
배열은 인덱스를 사용하여 값에 접근
이벤트 (Events)
사용자 동작이나 브라우저 상의 특정 상황에 반응하는 코드
클릭 이벤트, 마우스 오버 이벤트, 키보드 입력 이벤트 등
<!-- 변수 -->
<section>
<header>변수 (Variables)</header>
<script>
// 변수 선언
var name = "hyejin"; // var 변수명 = 값
name = "test"; // 변수 값 변경
var age = 30;
// 출력
document.write("이름: " + name + "<br>");
document.write("나이: " + age + "살<br>");
</script>
</section>
<!-- let, const, var의 차이 -->
<section>
<header>let, const, var의 차이</header>
<script>
var foo = 123;
document.write("var foo: " + foo + "<br>");
{
var foo = 456; // 중복 선언 가능
}
document.write("블록 외부에서 var foo: " + foo + "<br>");
let foo2 = 789;
document.write("let foo2: " + foo2 + "<br>");
{
let foo2 = 456; // 중복 선언 불가
document.write("블록 내부에서 let foo2: " + foo2 + "<br>");
}
document.write("블록 외부에서 let foo2: " + foo2 + "<br>");
const TOO = 123;
document.write("const TOO: " + TOO + "<br>");
{
const BAR = 456;
document.write("블록 내부에서 const BAR: " + BAR + "<br>");
}
</script>
</section>
<!-- 연산자 -->
<section>
<header>연산자 (Operators)</header>
<script>
let res = 20 + 30;
document.write("20 + 30 = " + res + "<br>");
res = 20 - 30;
document.write("20 - 30 = " + res + "<br>");
res = 20 * 30;
document.write("20 * 30 = " + res + "<br>");
res = 20 / 30;
document.write("20 / 30 = " + res + "<br>");
let a = 5, b = 10;
let c = a > b;
document.write("a > b: " + c + "<br>");
</script>
</section>
<!-- 함수 -->
<section>
<header>함수 (Functions)</header>
<script>
// 매개변수 없음, 반환값 없음
function print1() {
document.write("단순하고 반복적인 일을 주로 담당<br>");
}
// 매개변수 있음, 반환값 없음
let print2 = function(su) {
document.write("입력받은 값: " + su + "<br>");
};
// 매개변수 있음, 반환값 있음
function print4(su, su2) {
let result = su + su2;
return result;
}
// 함수 호출
print1();
print2(30);
document.write("print4(10, 20) = " + print4(10, 20) + "<br>");
</script>
</section>
<!-- 이벤트 -->
<section>
<header>이벤트 (Events)</header>
<input type="button" value="함수 호출1" onclick="alert('함수 호출됨')">
<input type="button" value="함수 호출2" onclick="print1()">
<a href="#" onclick="alert('매개변수 전달')">함수 호출 유형 연습</a>
<a href="#" onclick="print2(25)">함수 호출 유형 연습</a>
</section>
