날짜 관련 함수
날짜 관련해서는 DBMS 종류 (Oracle, MySQL, Postgres 등) 에 따라 달라집니다.
회사에 따라 사용하고 있는 프로그램 언어 종류가 다르니 사실 그때그때마다 날짜 함수에 대해서는 구글링 하며 진행하는것이 좋습니다.
오늘
-- 오늘을 나타내는 기본 구문 3가지
select now()
-- yyyy-mm-dd 시간:분:초 +0900GMT
select current_date
-- yyyy-mm-dd
select current_timestamp
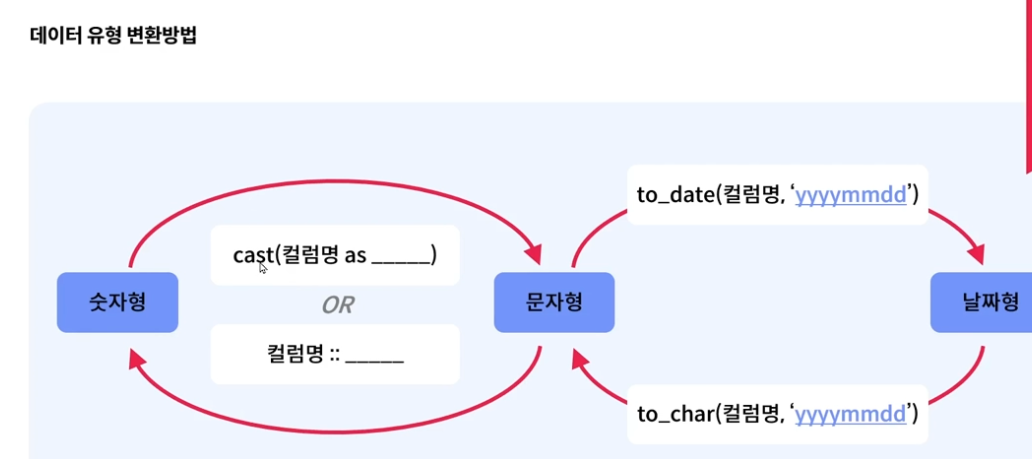
-- yyyy-mm-dd 시간:분:초 +0900GMT문자형식으로 변환 to_char()
to_char(값, '바꿀형태') : 문자형으로 변환 함수
-- 날짜형식에서 문자형식으로 변환
select to_char(now(),'yyyymmdd')
-- 변환전) yyyy-mm-dd 시간:분:초 +0900GMT
-- 변환후) yyyymmdd
select to_char(now(), 'yyyy / mm / dd')오늘 날짜 +/- interval
select now() + interval '1day'
select now() + interval '2week'
select now() + interval '3weeks'
select now() - interval '1 month'
select now() - interval '2year'
select now() - interval '30day'오늘 날짜로부터 년/월/일 추출 date_part
select date_part ('year', now())
-- 오늘이 2024년이니까 2,024가 나옵니다.
select date_part ('day', now())
-- 오늘이 1월7일이니까 7 만 나옵니다. 필요한 이유 : 최근 1년동안의 매출액 확인하거나, 오늘 기준으로 최근 60d 추이 등을 자동으로 확인할 수 있는 쿼리문을 작성할 수 있습니다.
구글링?
Postgres의 now() 함수가 mysql에서는 뭐지?
now() in mysql
now() in oracle
interval 1 month in mysql 정리
-- 날짜 함수 : SQL 언어에 따라 달라지니 사실 필요할때마다 구글링 하는 것이 좋습니다.
-- 2021년 6월 1일 하루 동안의 가상의 패션 이커머스 데이터 분석
-- 오늘을 나타내는 기본 구문 3가지
select now()
-- yyyy-mm-dd 시간:분:초 +0900GMT
select current_date
-- yyyy-mm-dd
select current_timestamp
-- yyyy-mm-dd 시간:분:초 +0900GMT
-- 날짜형식에서 문자형식으로 변환
select to_char(now(),'yyyymmdd')
-- 변환전) yyyy-mm-dd 시간:분:초 +0900GMT
-- 변환후) yyyymmdd
select to_char(now(), 'yyyy / mm / dd')
-- 오늘로부터 날짜 더하기/빼기
select now() + interval '1day'
select now() + interval '2week'
select now() + interval '3weeks'
select now() - interval '1 month'
select now() - interval '2year'
select now() - interval '30day'
-- 날짜로부터 year, month, week 추출(확인)
select date_part ('year', now())
-- 오늘이 2024년이니까 2,024가 나옵니다.
select date_part ('day', now())
-- 오늘이 1월7일이니까 7 만 나옵니다.
상품별 할인률,판매가,이익률 계산
online_order테이블에서 사칙연산을 이용해 필요한 값들을 계산해보겠습니다.
소숫점 나오게 numeric
- 할인률 = 할인액 / 매출액 = discount / gmv
- 판매가 = 매출액 - 할인액 = gmv - discount
- 이익률 = 이익액 / 매출액 = product_profit / gmv 또는 total_profit / gmv
우선 확인해보겠습니다.
-- 할인률 = 할인액 / 매출액 = discount / gmv
select
discount,
gmv ,
discount / gmv as discount_rate
from online_order oo 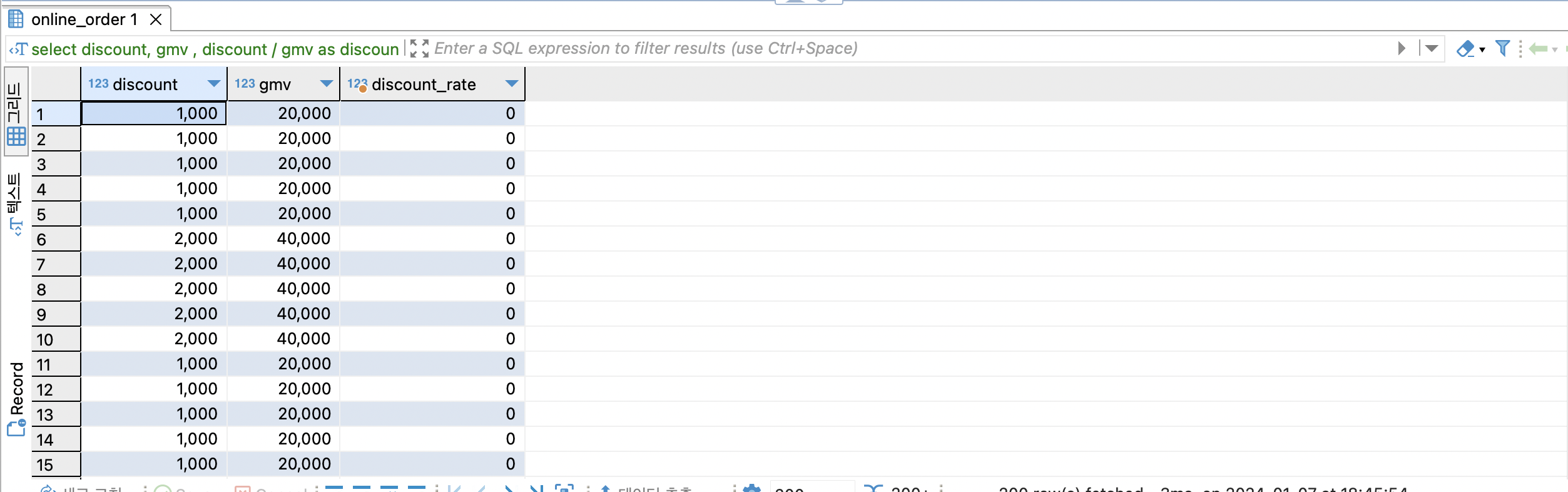
소숫점이 없는 정수 / 소숫점이 없는 정수 = 소숫점이 없는 정수 로 나와서 0이 됩니다.
소숫점이 있는 형태로 바꿔야 합니다.
형태를 바꾸는 함수 cast()로 사용합니다.
불가
-- 할인률 = 할인액 / 매출액 = discount / gmv
select
discount,
gmv ,
cast(discount / gmv as numeric ) as discount_rate
from online_order oo 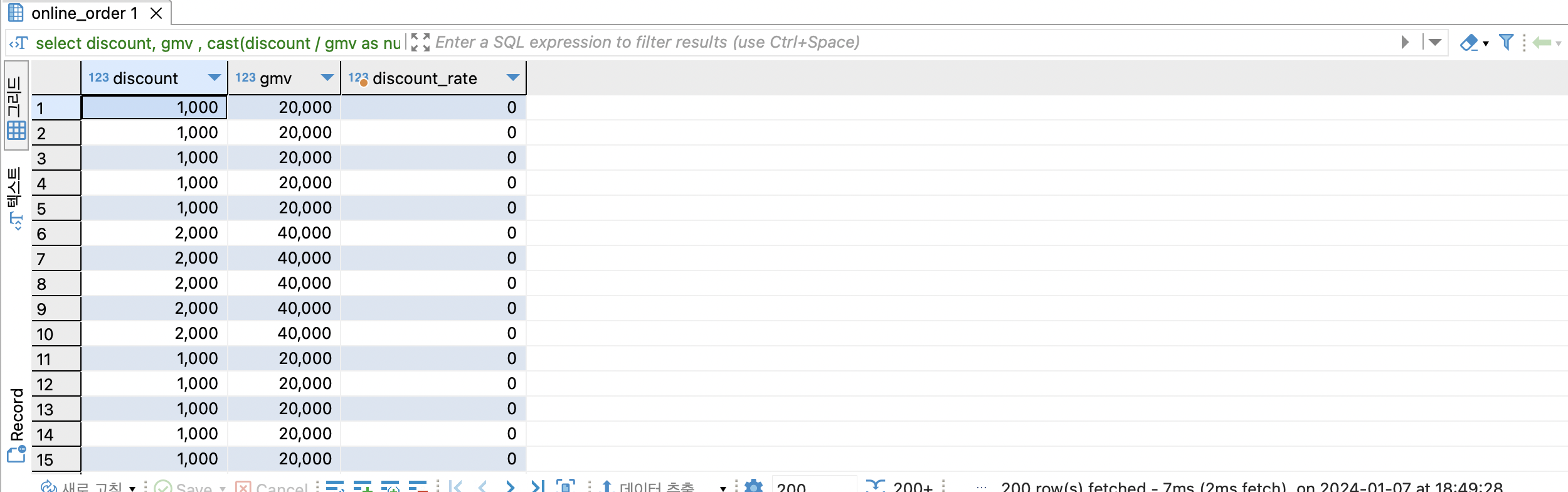
불가
-- 할인률 = 할인액 / 매출액 = discount / gmv
select
cast(discount as numeric) ,
cast(gmv as numeric) ,
cast(discount / gmv as numeric) as discount_rate
from online_order oo 정답 분자 또는 분모 둘 중 하나라도 cast () 로 numeric 변환 해주면 됩니다.
-- 할인률 = 할인액 / 매출액 = discount / gmv
select
discount,
gmv ,
cast(discount as numeric) / gmv as discount_rate
from online_order oo 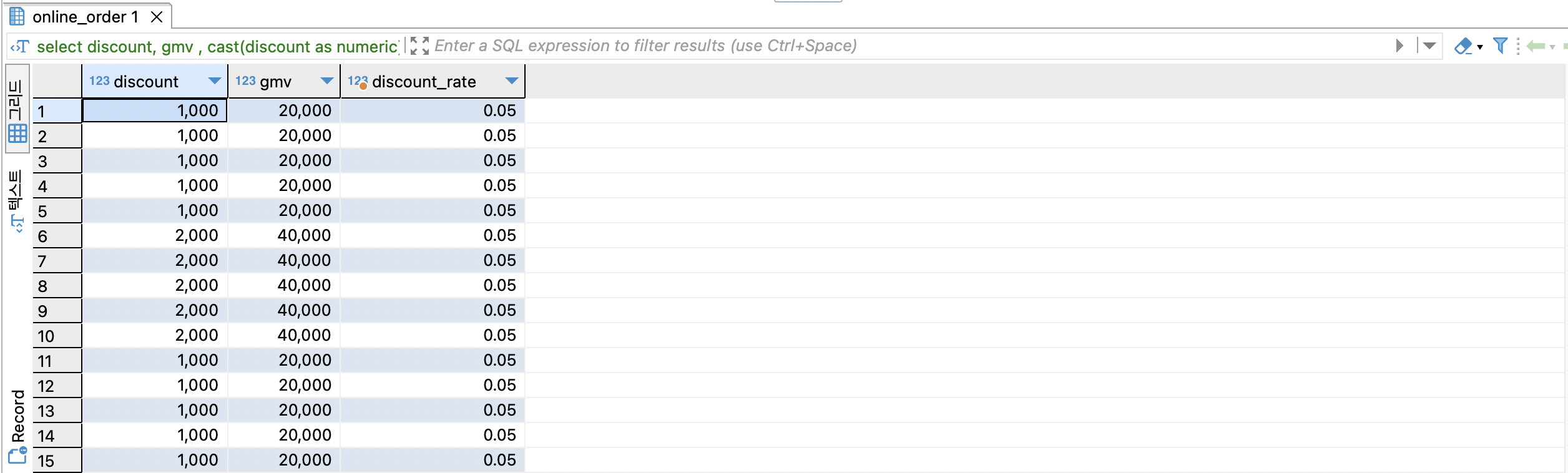
할인률
0.05 소수점 숫자를 백분률 % 퍼센트로 바꾸려면
concat(round(소숫점숫자 * 100) , '%')
-- online_order 테이블에서 할인액과 매출액을 이용한 할인률 컬럼 생성
select
discount,
gmv ,
-- 할인률 = 할인액 discount / 매출액 gmv
-- dicount / gmv 하면 정수/정수 여서 정수인 0 만 나옵니다.
-- cast(discount as numeric) / gmv 는 0.05
-- round((cast(discount as numeric) / gmv) * 100) 는 5
-- concat(round((cast(discount as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') 는 5%
concat(round((cast(discount as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as discount_rate
from online_order oo 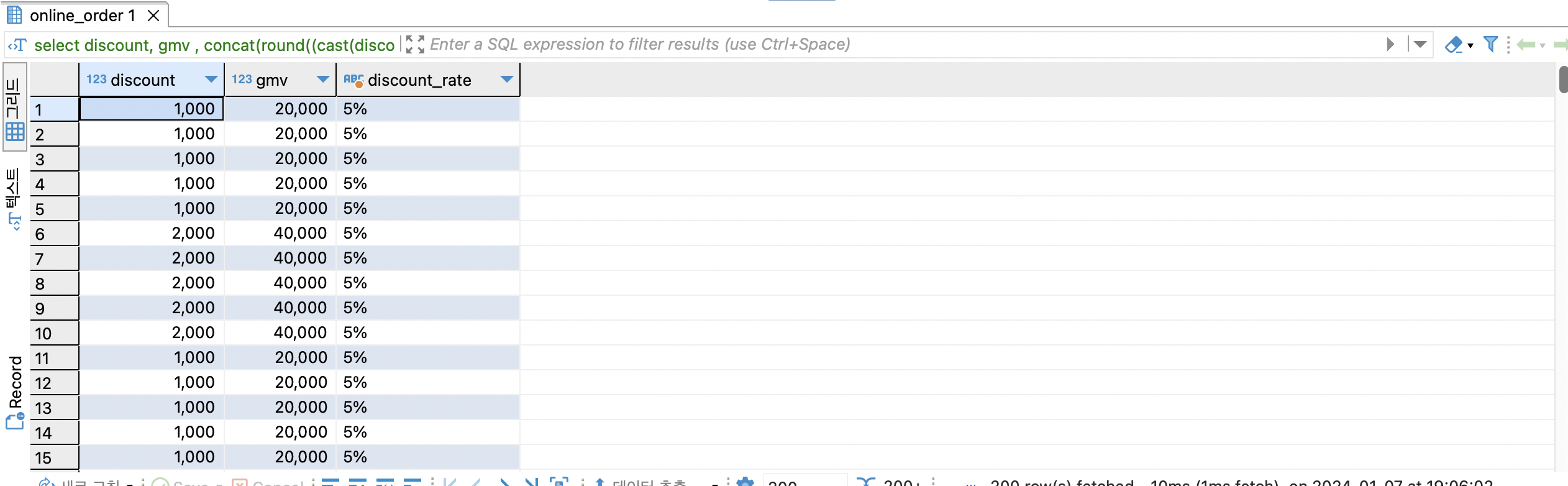
할인률, 판매가, 이익률 계산
-- online_order 테이블에서 할인률, 판매가, 이익률 컬럼 생성
-- 할인률 = 할인액 / 매출액 = discount / gmv
-- 판매가 = 매출액 - 할인액 = gmv - discount
-- 상품이익률 = 이익액 / 매출액 = product_profit / gmv
-- 종합이익률 = 이익액 / 매출액 = total_profit / gmv
-- 0.05 소수점 숫자를 백분률 % 퍼센트로 바꾸려면 = concat(round(소숫점숫자 * 100) , '%')
select
discount,
gmv ,
concat(round((cast(discount as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as discount_rate , --할인률
gmv - discount as paid_amount , --판매가
concat(round((cast(product_profit as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as product_magin, -- 상품마진률
concat(round((cast(total_profit as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as total_magin
from online_order oo 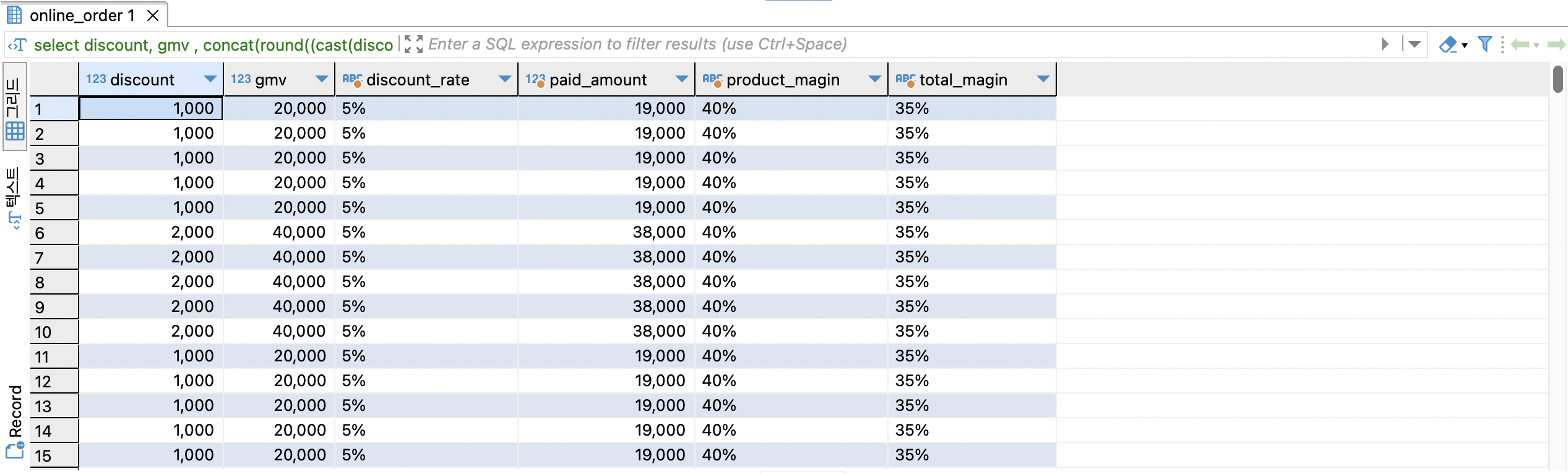
카테고리별 집계 (join과 sum())
위에 만든 할인률, 판매가, 이익률을 상품(category테이블의 cate1)별 로 집계해보겠습니다.
- online_order 테이블의 itemid = item 테이블의 id
- item테이블의 category_id = category테이블의 id
이렇게 세 테이블을 연결 연결!
select
c.cate1,
concat(round((cast(discount as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as discount_rate , --할인률
gmv - discount as paid_amount , --판매가
concat(round((cast(product_profit as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as product_magin, -- 상품마진률
concat(round((cast(total_profit as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as total_magin --종합이익률
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
join category c on i.category_id = c.id 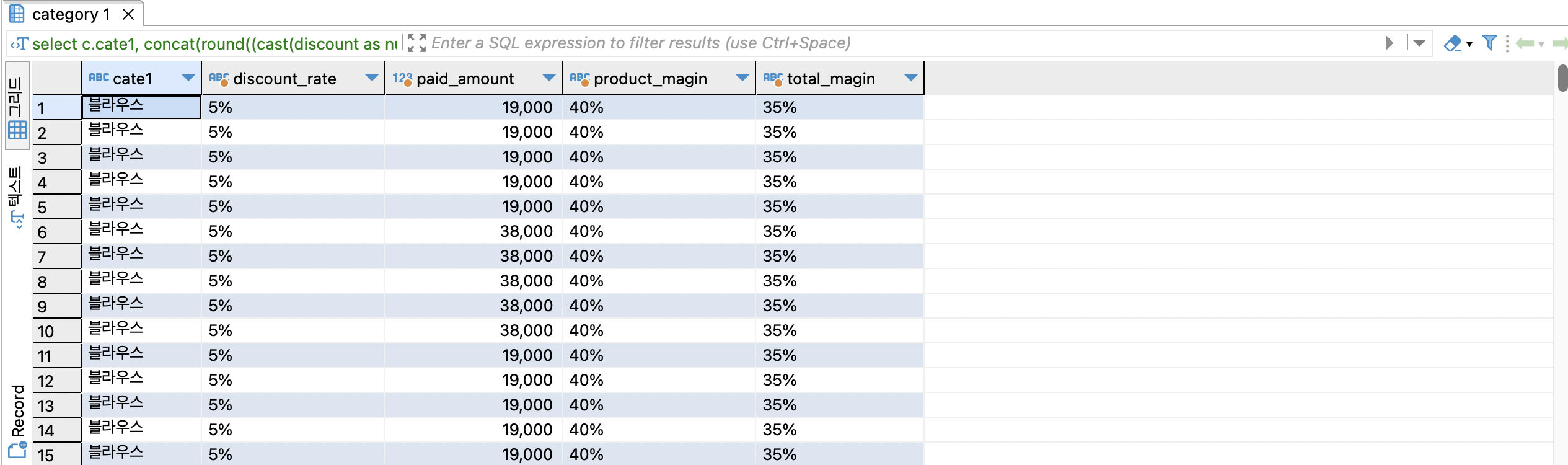
역시나 Group by 를 통해 상품별 집계를 해주겠습니다.
에러 : 그냥 Group by 1 만 추가했더니 에러가 나왔습니다.
select
c.cate1,
concat(round((cast(discount as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as discount_rate , --할인률
gmv - discount as paid_amount , --판매가
concat(round((cast(product_profit as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as product_magin, -- 상품마진률
concat(round((cast(total_profit as numeric) / gmv) * 100), '%') as total_magin --종합이익률
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
join category c on i.category_id = c.id
group by 1 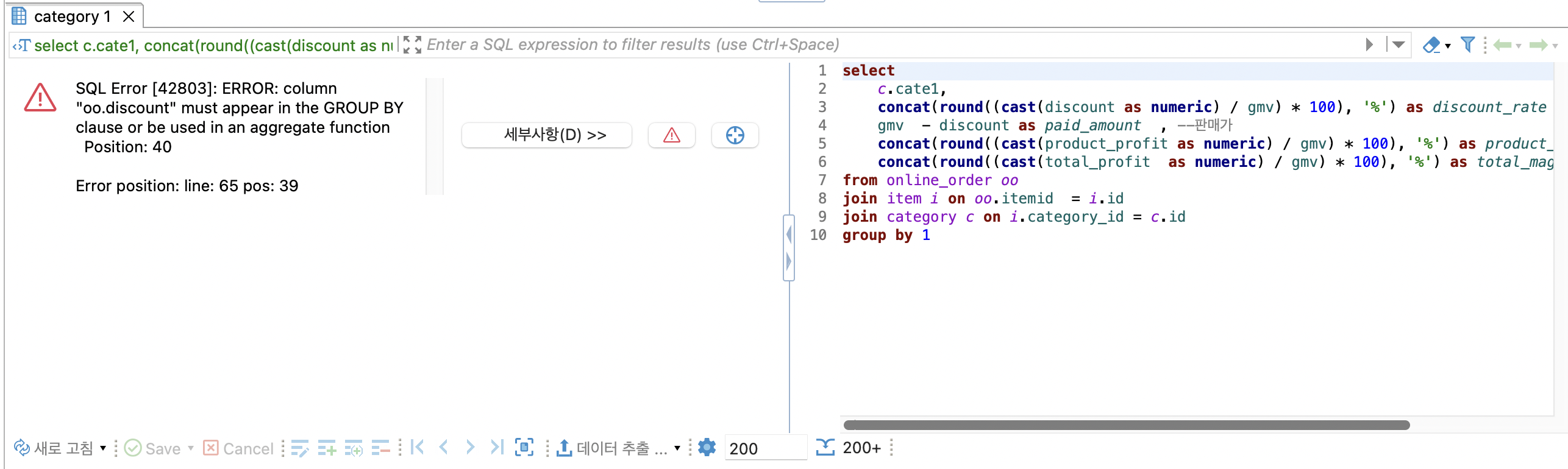
에러가 나온 이유는 cate1 각 값에 따라 여러개의 row가 있기 때문에 sum() 으로 묶어 줘야 합니다.
쉽게 말하자면 cate1가 블라우스 일 때, 여러개의 rows가 있어서 이걸 합쳐줘야 하니깐요
집계 함수가 있을 때, group by를 해주려면 각각의 분모와 분자에 sum()으로 묶어줘야 합니다.
더 정확한 수치를 확인하기 위해 백분율 함수 등을 제거하겠습니다.
select
c.cate1,
sum(cast(discount as numeric)) / sum(gmv) as discount_rate,
sum(gmv) - sum(discount) as paid_mount,
sum(cast(product_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv) as product_magin,
sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv) as total_margin
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
join category c on i.category_id = c.id
group by 1
order by 3 desc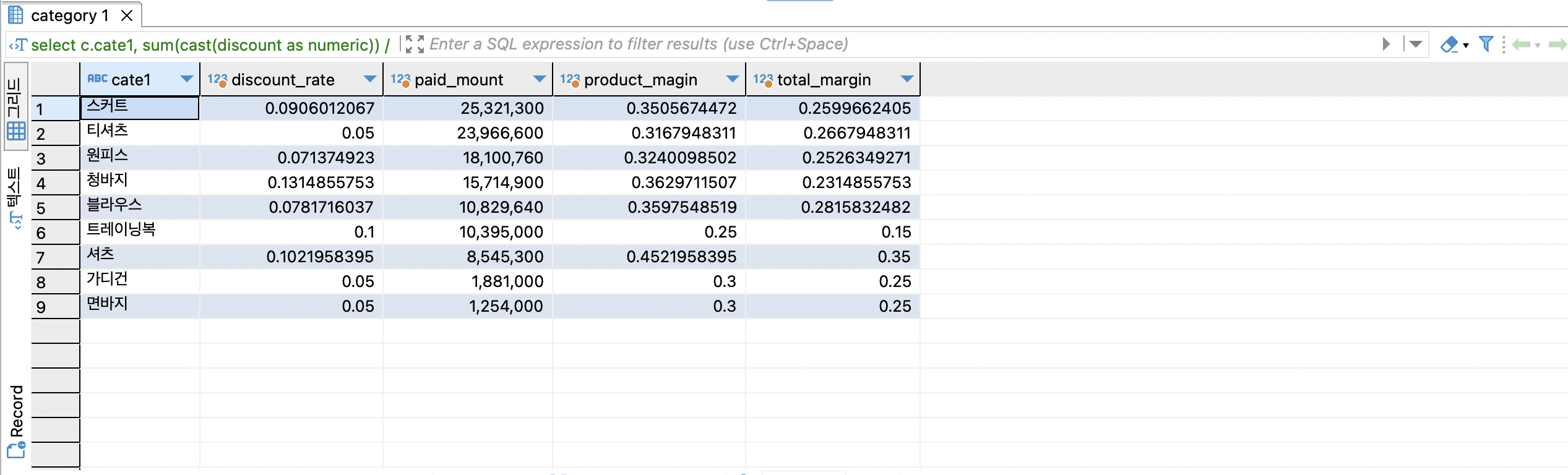
소숫점 2번째 자리까지 표시되게끔 round(값, 2)
select
c.cate1,
round(sum(cast(discount as numeric)) / sum(gmv),2) as discount_rate,
sum(gmv) - sum(discount) as paid_mount,
round(sum(cast(product_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv),2) as product_magin,
round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv),2) as total_margin
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
join category c on i.category_id = c.id
group by 1
order by 3 desc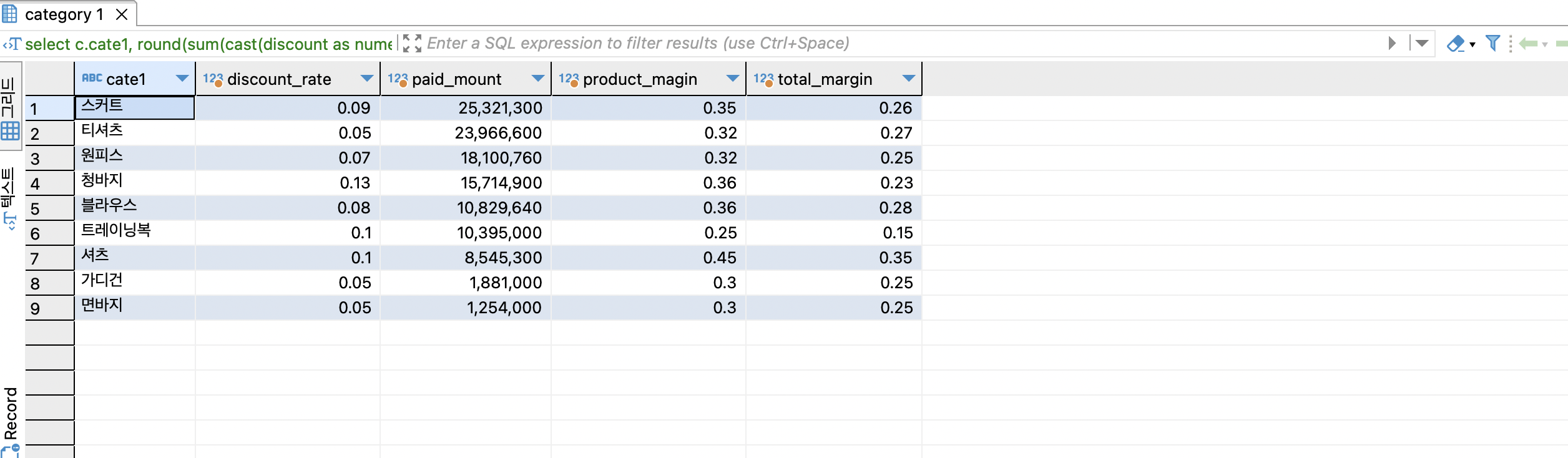
백분율로 다시 변환되게 * 100
select
c.cate1,
round(sum(cast(discount as numeric)) / sum(gmv),2) * 100 as discount_rate,
sum(gmv) - sum(discount) as paid_mount,
round(sum(cast(product_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv),2) *100 as product_magin,
round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv),2) * 100 as total_margin
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
join category c on i.category_id = c.id
group by 1
order by 3 desc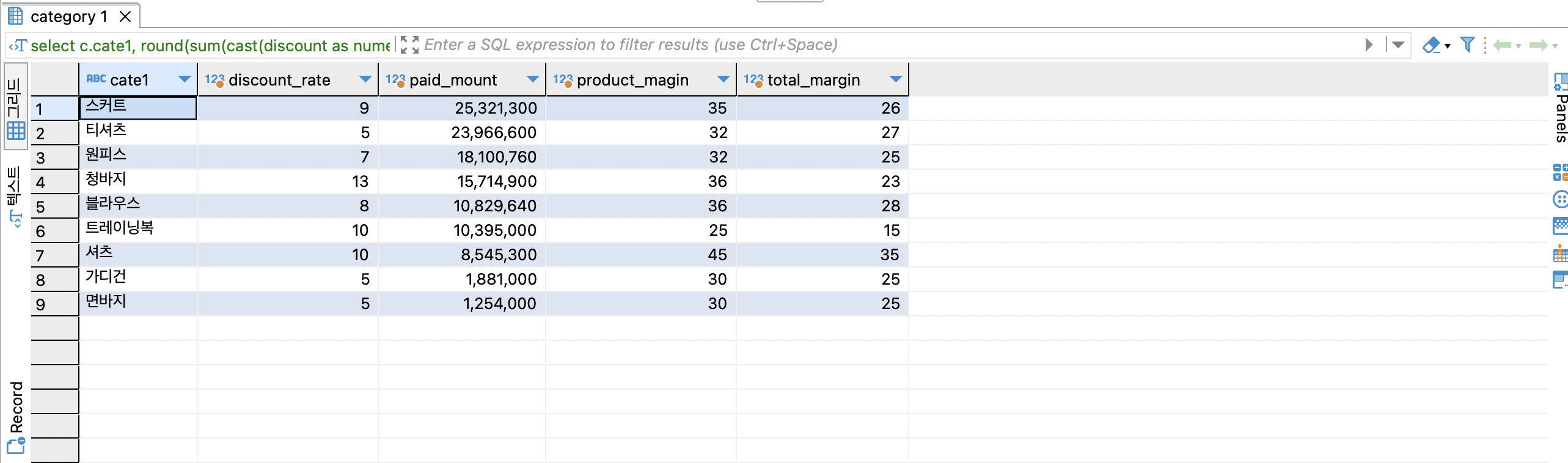
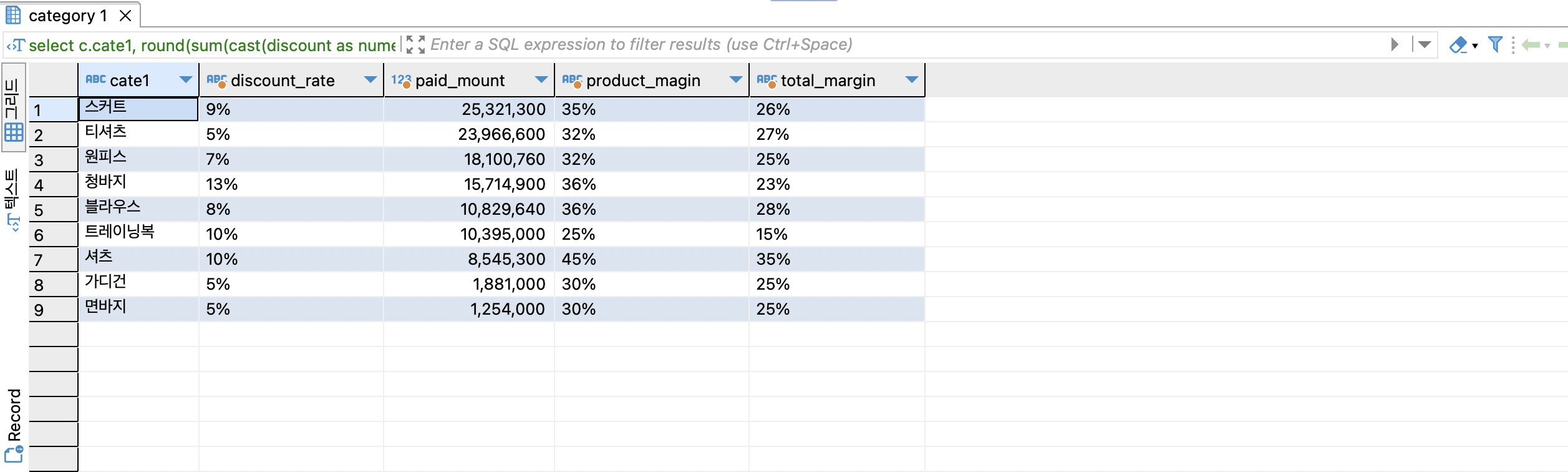
숫자열+문자열은 ||'%'
여기에 문자열 '%' 추가하려면 concat보다는 || 가 더 간단합니다.
postgres에는 가능하지만 다른 sql에서는 안 될 수 있습니다.
select
c.cate1,
round(sum(cast(discount as numeric)) / sum(gmv)* 100) || '%' as discount_rate,
sum(gmv) - sum(discount) as paid_mount,
round(sum(cast(product_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv)* 100) || '%' as product_magin,
--round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv), 2) * 100 || '%' as total_margin 하게되면 26.00%
--round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv) * 100) || '%' as total_margin 하게되면 26%
round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv) * 100) || '%' as total_margin
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
join category c on i.category_id = c.id
group by 1
order by 3 desc
숫자열+문자열은 cast(값 as varchar)
다른 sql언어에서 안되는경우
round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv) * 100) || '%' as total_margin
가 안되는 경우,
cast(round(sum(cast(total_profit as numeric)) / sum(gmv) * 100) as varchar) || '%' as total_margin
로 해줍니다. 고객 관점 분석
- 고객관점에서의 분석 (1인당 평균 구매수량과 1인당 평균 구매금액)
- 100명의 고객이 구매했을 때, 총 판매수량이 200개라고 가정한다.
- 1인당 평균 구매수량 = 총 판매수량 / 총 고객 수
- 1인당 평균 구매금액 = 총 구매금액 / 총 고객 수
1인당 구매수량이 높은 상품
-- 1인당 구매수량이 높은 상품 확인 = 상품별 판매수량/고객수
-- 상품확인은 item테이블의 item_name + 구매수량(판매수량)은 order테이블의 unitsold + 중복값제거된 고객수는 userid의 고유값 셈
select
i.item_name , -- 상품별
sum(unitsold) as unitsold , -- 판매수량의 합계
count (distinct userid) as user_count, -- 고유 유저수
sum(unitsold) / count(distinct userid) as avg_unitsold_per_customer
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
group by 1 
역시나 나누기 했을때는 정수/정수 = 정수 로 표현됩니다.
cast( 값 as numeric) 으로 분자나 분모 둘 중 하나만 해줍니다.
select
i.item_name , -- 상품별
sum(unitsold) as unitsold , -- 판매수량의 합계
count (distinct userid) as user_count, -- 고유 유저수
sum(cast(unitsold as numeric)) / count(distinct userid) as avg_unitsold_per_customer
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
group by 1 
소숫점 두 자리까지 나오도록 하겠습니다.
round(값, 2)
select
i.item_name , -- 상품별
sum(unitsold) as unitsold , -- 판매수량의 합계
count (distinct userid) as user_count, -- 고유 유저수
round(sum(cast(unitsold as numeric)) / count(distinct userid),2) as avg_unitsold_per_customer
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
group by 1 
이제 order by 로 내림차순 정렬 하겠습니다.
select
i.item_name , -- 상품별
sum(unitsold) as unitsold , -- 판매수량의 합계
count (distinct userid) as user_count, -- 고유 유저수
round(sum(cast(unitsold as numeric)) / count(distinct userid),2) as avg_unitsold_per_customer
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
group by 1
order by 4 desc
-- 커플룩 > 기본필수 라운드티 > 여름필수 브이넥 등 여러벌 구매할수 있는 제품의 구매수량이 높습니다. 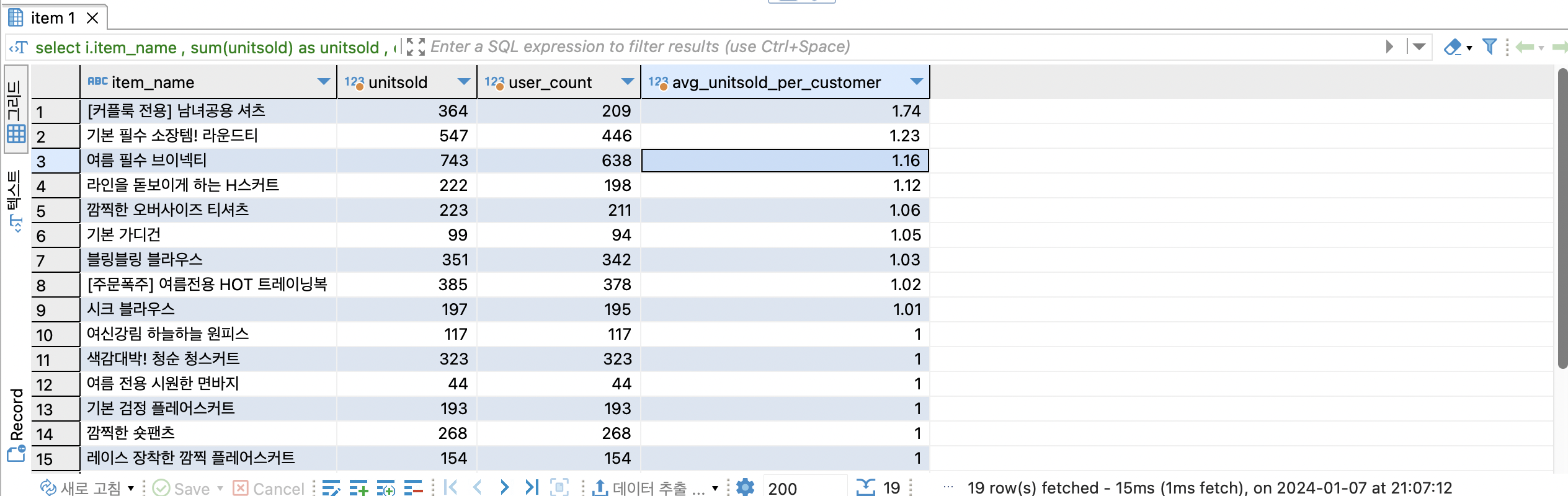
1인당 구매금액이 높은 상품
-- 1인당 평균 구매금액은 위에 unitsold대신 gmv로 대체해줍니다.
select
i.item_name , -- 상품별
sum(unitsold) as unitsold , -- 판매수량의 합계
count (distinct userid) as user_count, -- 고유 유저수
round(sum(cast(unitsold as numeric)) / count(distinct userid),2) as avg_unitsold_per_customer,
round(sum(cast(gmv as numeric)) / count(distinct userid)) as avg_gmv_per_customer
from online_order oo
join item i on oo.itemid = i.id
group by 1
order by 5 desc 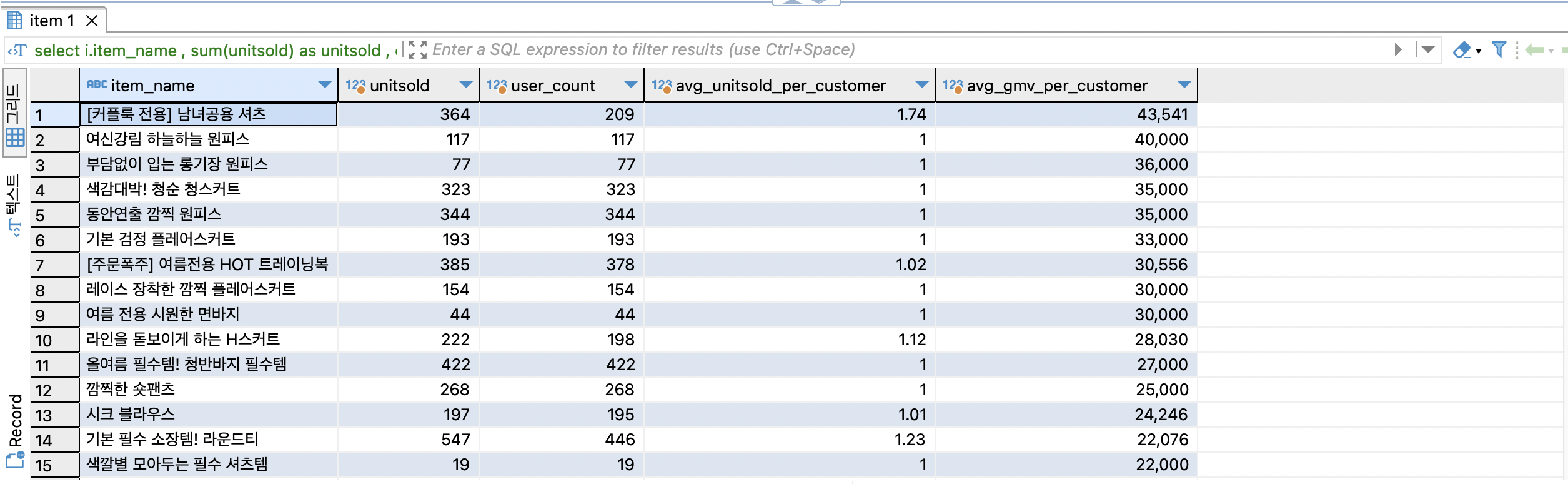
1인당 구매금액이 높은 성별/연령대
-- 1인당 구매금액이 높은 성별/연령대 확인
-- online_order 테이블의 userid = user_info테이블의 userid
-- 성별(user테이블), 연령(user테이블), 구매액sum(order테이블), 유저수count+distinct(order테이블)
select
gender
, age_band
, sum(gmv) as gmv
, count(distinct oo.userid) as user_count
from online_order oo
join user_info ui on oo.userid = ui.userid
group by 1,2 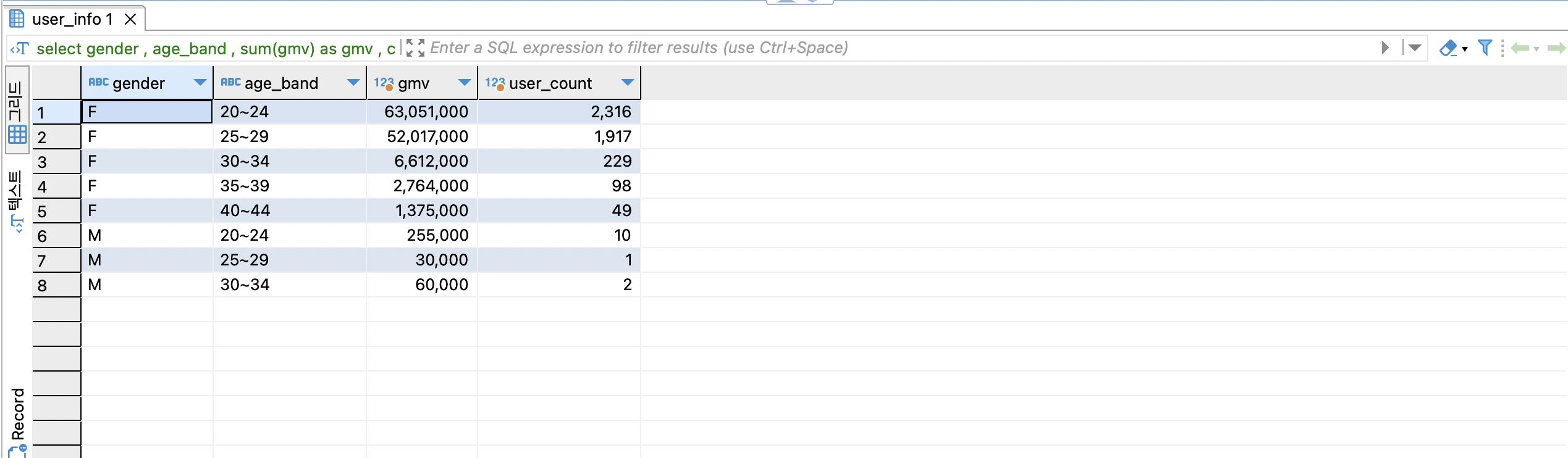
1인당 구매금액 = 구매액 합계 / 고유 유저수
-- 1인당 구매금액이 높은 성별/연령대 확인
-- online_order 테이블의 userid = user_info테이블의 userid
-- 성별(user테이블), 연령(user테이블), 구매액sum(order테이블), 유저수count+distinct(order테이블)
select
gender
, age_band
, sum(gmv) as gmv
, count(distinct oo.userid) as user_count
, sum(gmv) / count(distinct oo.userid) as avg_gmv_per_customer
from online_order oo
join user_info ui on oo.userid = ui.userid
group by 1,2
order by 5 desc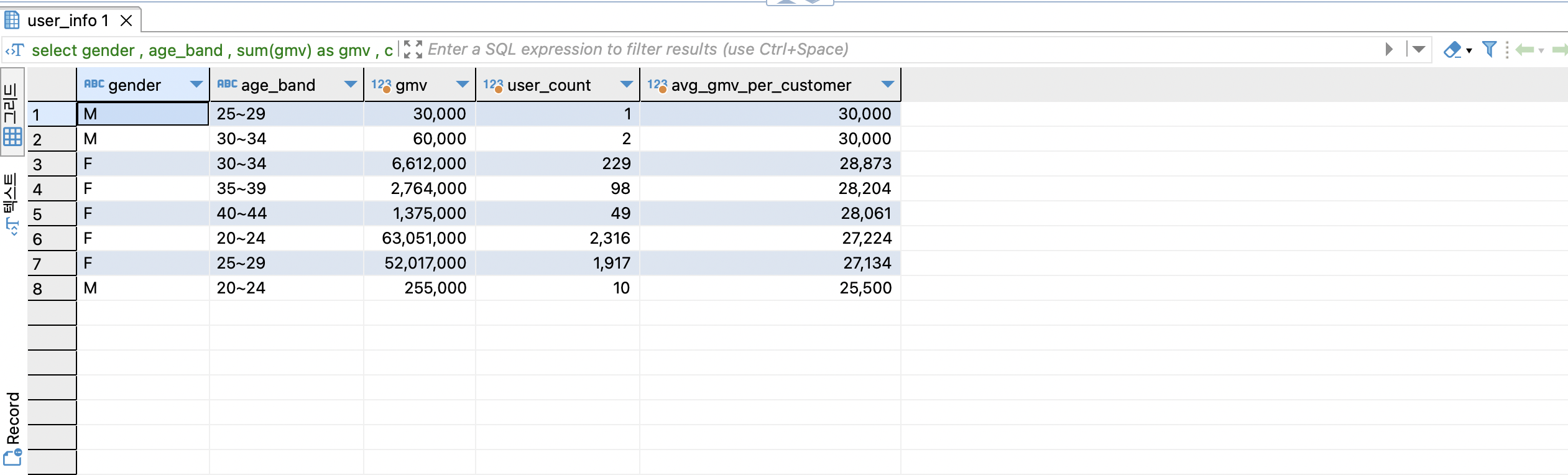
1인당 구매금액은 25~34세 남성들이 많은걸로 확인됩니다.
하지만 유저 수(모수) 가 합쳐도 고작 3명...! 너무 작습니다.
이것만 봐서 남성들의 구매파워가 강하다! 라고 말하긴 좀 그렇습니다...;;
이 3명을 제외하면 30-34세의 여성들의 파워가 가장 강한 것 같습니다!
이론 되짚어보기
sql은 한 가지 기능에 따라 여러가지 함수가 있습니다.
물론 sql 언어에 따라 달라질 수도 있습니다!
데이터 유형

- int 정수 (소숫점 없음)
- bigint 큰 정수 (숫자가 많을 때 사용)
- numeric 소숫점 있는 수
cast(정수 as numeric ) 으로 소숫점 있는 숫자로 변환
정수 :: numeric 으로도 변환 가능합니다. - date 시, 분, 초
- timestamp 년, 월, 일
데이터 변환
기존컬럼 :: 바꿀 형태로 간단하게 바꿀 수도 있습니다.
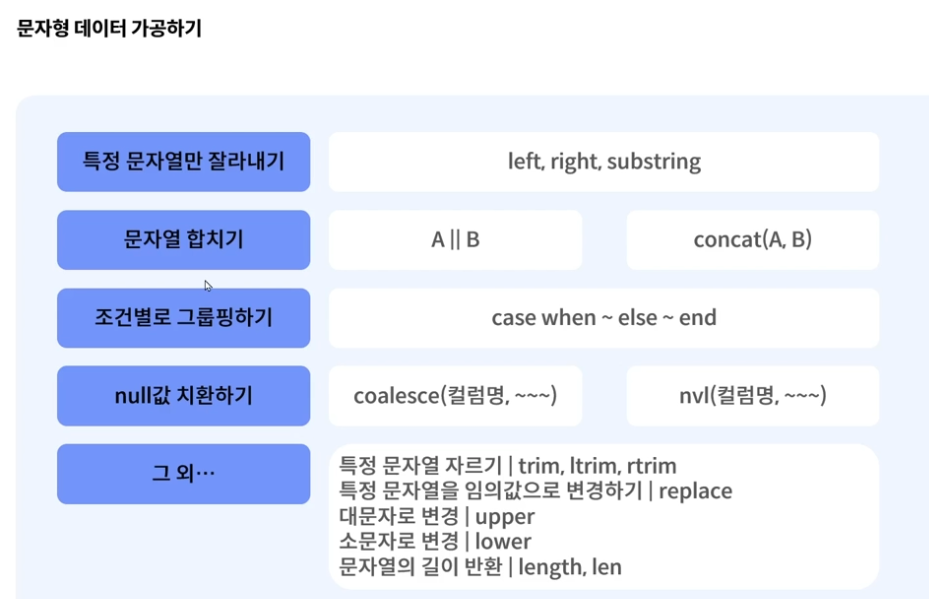
데이터 가공(문자)
문자열 추출 : left , right, substring
문자열 자르기 : trim, ltrim, rtrim
문자열 길이 반환 : len, length
문자열 병합 : || , concat()
문자열 변경 : replace
대문자 변경 : upper
소문자 변경 : lower
조건문 : case when ~ else ~ end
Null값 : coalesce() , nvl()
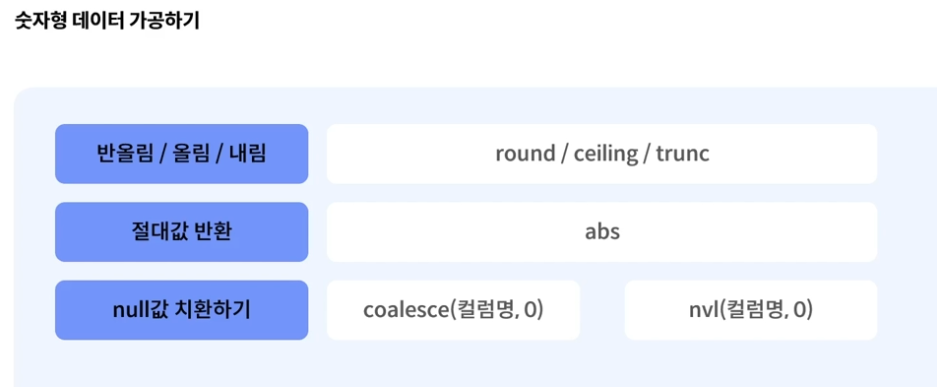
데이터 가공(숫자)
반올림 : round
올림 : ceiling
내림 : trunc
절대값 반환 : abs
Null값 : coalesce , nvl
데이터 가공(날짜)
날짜 더하기 : - interval '더할날짜', dateadd()
날짜 빼주기 : datediff()
날짜 추출 : date_part(), to_char()
현재 날짜의 월1일 : date_trunc('month', now())
현재 날짜의 분기1일 : date_trunc('quarter', now())
현재 날짜의 주 시작일 추출 : date_truc('week', now())

배운 내용 확인

성장률, 구매비중 , 랭킹 등에 대해서는 sql로는 복잡해지니 Python, Tableau 같은 프로그램에서 진행하는 것이 더 좋습니다.
SQL은 단순하게! 빠르게! 원하는 데이터를 필터링을 걸어 추출하는 목적입니다.
과거 데이터 기반 시각적 요소나 예측 등에 대해서는 다른 프로그램으로 진행합니다!
