
해당 문제를 처음 읽었을 때 소수를 판별하기 위한 로직을 짜야 하는 건가라고 생각했지만, 시간 복잡도 차원에서 보면 O(N)의 복잡도의 알고리즘을 사용해야 한다.
일부 필요 없는 조건을 가지치기 한 뒤, DFS로 구현하여 문제를 해결하면 된다.
⌛ 시간 복잡도
- 2초 : 2억
- 제한 조건 : 최대 99,999,999(9천 9백만)
- O(n) 이하 사용 가능
📜 로직
- 일의 자리인 소수 2,3,5,7을 분기로 dfs 수행
- 십의 자리 수부터는 뒤의 숫자를 붙일 때, 짝수는 2의 약수가 무조건 들어가기 때문에 '가지치기' 해준다.(따라서 홀수만 뒤에 숫자로 붙여준다)
ex)
- 2 + '홀수' : 소수일수도 아닐수도 있다.
- 2 + '짝수' : 약수에 2가 무조건 포함되어 소수가 아니다.
- 값을 붙여준 뒤, 해당 값이 소수인지 판별해준다.
- 소수가 맞으면, 값을 붙여준 뒤 자릿수를 1자리 올려준다.
- 소수 판별 시, 에라토스테네스 체 의 원리를 이용한다.
- 2 ~ √n 까지의 수만 판별해준다.('가지치기')
- 자릿수가 일치하면 소수여부 판별 후 출력한다.
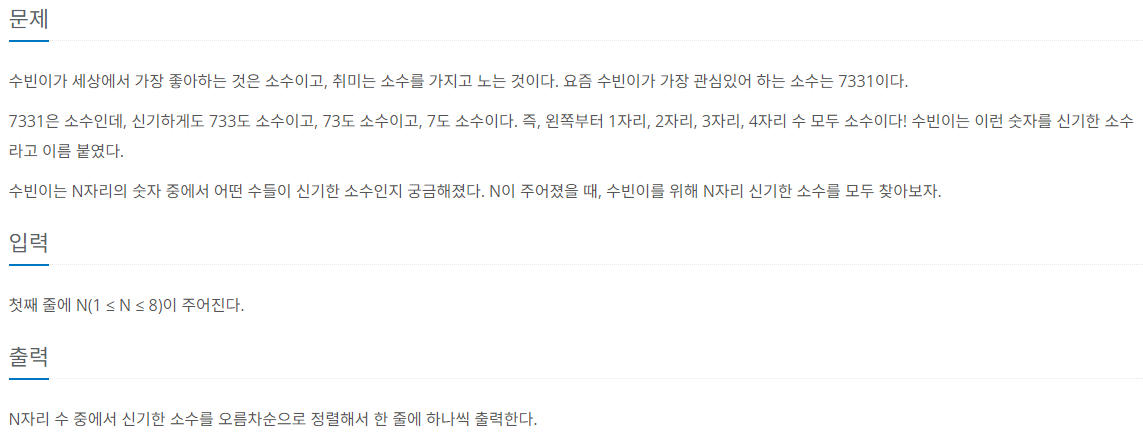
위의 로직에서 에라토스테네스 체를 사용하지 않았을 때와 사용했을 때의 시간차이는 무려 600ms나 차이난다.
😀 성공
적용 전
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N;
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
br.close();
dfs(2,1);
dfs(3,1);
dfs(5,1);
dfs(7,1);
}
static void dfs(int n, int digit){
if(N == digit){
if(isPrime(n)){
System.out.println(n);
}
return;
}
for(int i=1; i<10; i+=2){
if(isPrime(n*10+i)){
dfs(n*10+i,digit+1);
}
}
}
static boolean isPrime(int n){
for(int i=2; i <= n/2; i++){
if(n%i==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}적용 후
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N;
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
br.close();
dfs(2,1);
dfs(3,1);
dfs(5,1);
dfs(7,1);
}
static void dfs(int n, int digit){
if(N == digit){
if(isPrime(n)){
System.out.println(n);
}
return;
}
for(int i=1; i<10; i+=2){
if(isPrime(n*10+i)){
dfs(n*10+i,digit+1);
}
}
}
static boolean isPrime(int n){
for(int i=2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++){
if(n%i==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}