문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2307
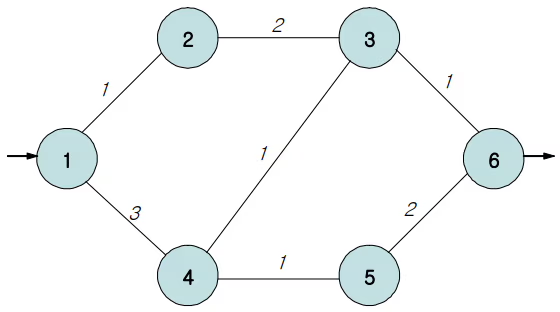
입력
- 지점의 수를 나타내는 정수 N, 도로의 수 M
- M개의 각 줄에는 도로(a, b)와 그 통과시간 t가 a b t 로 표시된다.
출력
- 경찰이 하나의 도로를 막음으로써 지연시킬 수 있는 최대 시간을 정수로 출력한다. (단, 그 지연시간이 무한대이면 -1을 출력해야 한다.)
풀이
제한조건
- N(6 ≤ N ≤ 1000)
- M(6 ≤ M ≤ 5000)
- a < b 이고 1 ≤ t ≤ 10000
접근방법
다익스트라 응용
문제의 추가설명 4번을 유심히 보자
용의자는 검문을 피해서 가장 빨리 도시를 빠져나가고자 하고, 경찰은 적절한 도로를 선택하여 이 용의자들의 탈출시간을 최대한 지연시키고자 한다.
이 문구를 통해서 용의자는 경찰이 배치되지 않은 경로로 항상 최단거리로 이동한다. 라는 것을 알 수 있다.
경찰은 적절한 도로를 선택하여 이 용의자들의 탈출시간을 최대한 지연시키고자 한다.
라는 말은 조금 생각해보면, 적절한 도로를 선택하여 탈출 시간을 지연시키기 위해서는
당연히 용의자가 최단경로로 이동했던 길 중 하나를 선택하여 막아야 지연이 발생한다는 것을 알 수 있다.
따라서 기본 아이디어를 정리하자면 아래와 같다.
1. 다익스트라를 통해 1->N 까지 최단거리 탐색
a. 최단거리 탐색과정에서의 경로 기록 필요
2. 최단 거리의 이동 경로를 바탕으로 경찰이 막을 도로 선정
3. 다익스트라를 통해 1->N 까지 최단거리 탐색
4. 지연된 시간 비교이 문제의 핵심은
당신은 다익스트라를 구현할 수 있습니까? 가 아니라
당신은 다익스트라의 경로를 추출할 수 있습니까? 를 묻는 것이다.
다익스트라의 경로를 찾으려면 어떻게 할 수 있을지 생각해보자.
private static void dijkstra(int start, int end) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[start] = 0;
pq.add(new Node(1, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = pq.poll();
if (cur.to == end) // 목적지 도달
break;
for (Node next : graph[cur.to]) {
if (dist[next.to] > dist[cur.to] + next.weight) {
dist[next.to] = dist[cur.to] + next.weight; // 비용 갱신
pq.add(new Node(next.to, dist[next.to]));
}
}
}
}일반적으로 다익스크라 구현을 했다면 위와 같은식으로 구현이 된다.
여기서 아이디어를 생각해보자면,
다음 목적지로의 비용을 갱신하는 과정에서 이전에 어디서 왔는지를 기록하면 된다.
private static void dijkstra(int start, int end, int[] disable) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[start] = 0;
pq.add(new Node(1, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = pq.poll();
if (cur.to == end) // 목적지 도달
break;
for (Node next : graph[cur.to]) {
// 현재 위치에서 다음 위치로 가는길에 검문이 있다. -> 지나갈 수 없음
if (cur.to == disable[0] && next.to == disable[1])
continue;
if (dist[next.to] > dist[cur.to] + next.weight) {
dist[next.to] = dist[cur.to] + next.weight; // 비용 갱신
prev[next.to] = cur.to; // 경로 기록
pq.add(new Node(next.to, dist[next.to]));
}
}
}
}위와 같은 식으로 기록을 했다면, N번 노드로 가기위해 바로 직전 방문했던 노드가 prev[N]번 노드임을 알 수 있다.
이제 어떤 경로로 이동했는지 파악이 가능하므로, 각 경로를 하나씩 막으면서 다시 다익스트라 알고리즘을 수행하며 거리를 파악하자.
새롭게 산출된 값과 기존의 값을 비교하며 얼마나 지연시킬 수 있는지 확인한다면 끝이다.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Main {
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int to;
int weight;
Node(int to, int weight) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
}
static List<Node>[] graph;
static int N, M;
static int[] dist, prev;
static int INF = 987654321;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader((System.in)));
String[] inputs = in.readLine().split(" ");
N = stoi(inputs[0]);
M = stoi(inputs[1]);
graph = new List[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; ++i)
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
inputs = in.readLine().split(" ");
int p1 = stoi(inputs[0]);
int p2 = stoi(inputs[1]);
int cost = stoi(inputs[2]);
graph[p1].add(new Node(p2, cost));
graph[p2].add(new Node(p1, cost));
}
dist = new int[N + 1];
prev = new int[N + 1];
dijkstra(1, N, new int[] {0, 0});
// 지나왔던 경로를 바탕으로, 이동할 수 없는 도로를 생성.
List<int[]> pathList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = N; prev[i] != 0; i = prev[i])
pathList.add(new int[] {prev[i], i});
int max = 0;
int orgTime = dist[N];
for (int[] path : pathList) {
dijkstra(1, N, path);
int fixTime = dist[N];
// 도시를 빠져나가지 못하게 만들 수 있는 경우
if (fixTime == INF) {
max = -1;
break;
}
max = Math.max(max, fixTime - orgTime);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
private static void dijkstra(int start, int end, int[] disable) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[start] = 0;
pq.add(new Node(1, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = pq.poll();
if (cur.to == end) // 목적지 도달
break;
for (Node next : graph[cur.to]) {
// 현재 위치에서 다음 위치로 가는길에 검문이 있다. -> 지나갈 수 없음
if (cur.to == disable[0] && next.to == disable[1])
continue;
if (dist[next.to] > dist[cur.to] + next.weight) {
dist[next.to] = dist[cur.to] + next.weight; // 비용 갱신
prev[next.to] = cur.to; // 경로 기록
pq.add(new Node(next.to, dist[next.to]));
}
}
}
}
private static int stoi(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}