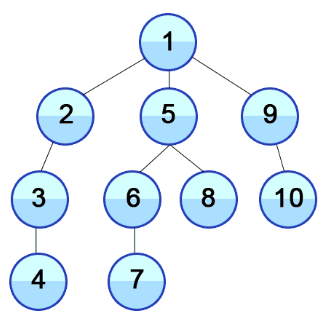
DFS : 깊이 우선 탐색
- 그래프에서 깊은 부분을 우선적으로 탐색하는 알고리즘
- Brute Force(완전 탐색) 알고리즘
- 스택 or 재귀를 이용해 구현
- 임의 노드에서 다음 브랜치로 넘어가기 전에 해당 브랜치를 모두 탐색하는 방법
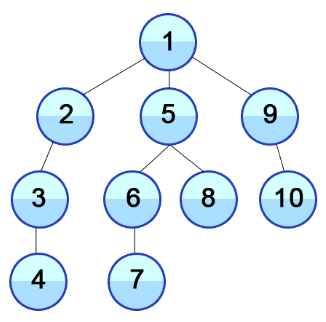
DFS의 효용성
- 일반적인 상황에서 DFS는 BFS의 기능으로 모두 대체 가능
- 일반적인 상황에서 트리의 높이를 리턴하는 BFS의 특성상 BFS가 DFS보다 유용하다.
- 단, 그래프와 트리에서 DFS가 유용해진다.
DFS <-> BFS
- 다차원 배열에서 DFS가 스택으로 구현된 경우 적용 가능
- 스택을 큐로 바꾸면 BFS가 된다.
- DFS 구현 방법
- 탐색 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입하고 방문 처리
- 스택 상단 노드에 방문하지 않은 인접 노드가 있으면, 그 노드를 스택에 넣고 방문 처리
- 방문하지 않은 인접 도느가 없다면, 스택에서 최 상단 노드를 꺼냄
- 2번 과정을 더이상 수행할 수 없을 때까지 반복
DFS 사용 예제
1. 그래프 DFS 사용 예제
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool visited[9];
vector<int> graph[9];
void dfs(int start) {
visited[start] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[start].size(); i++) {
int x = graph[start][i];
if (!visited[x])
dfs(x);
}
}
int main(void) {
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[1].push_back(3);
graph[1].push_back(8);
graph[2].push_back(1);
graph[2].push_back(7);
graph[3].push_back(1);
graph[3].push_back(4);
graph[3].push_back(5);
graph[4].push_back(3);
graph[4].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(3);
graph[5].push_back(4);
graph[6].push_back(7);
graph[7].push_back(2);
graph[7].push_back(6);
graph[7].push_back(8);
graph[8].push_back(1);
graph[8].push_back(7);
dfs(1);
}
2. 재귀 DFS 사용 예제
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 20
int dist[100001] = {0};
bool visited[100001];
bool arr[MAX][MAX];
vector<int> list[MAX];
vector<pair<int, int>> edges;
void dfs(int x, int n){
visited[x] = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if(arr[x][i] == true && visited[i] == false)
dfs(i, n);
}
3. 스택 DFS 사용 예제
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define X first
#define Y second
int board[502][502] =
{{1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0} };
bool visited[502][502];
int n = 7, m = 10;
int dx[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
int dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
stack<pair<int,int>> Q;
visited[0][0] = 1;
Q.push({0,0});
while(!Q.empty()){
pair<int,int> cur = Q.front();
Q.pop();
cout << '(' << cur.X << ", " << cur.Y << ") -> ";
for(int dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++){
int nx = cur.X + dx[dir];
int ny = cur.Y + dy[dir];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
if(visited[nx][ny] || board[nx][ny] != 1) continue;
visited[nx][ny] = 1;
Q.push({nx,ny});
}
}
}