참조형 변수를 사용할 때, 데이터 위치를 명시해 주어야 한다.
아니면 다음과 같은 오류를 만날 수 있다. 그렇다면, 어떨 때 어떤 위치를 명시해 주어야 할까?

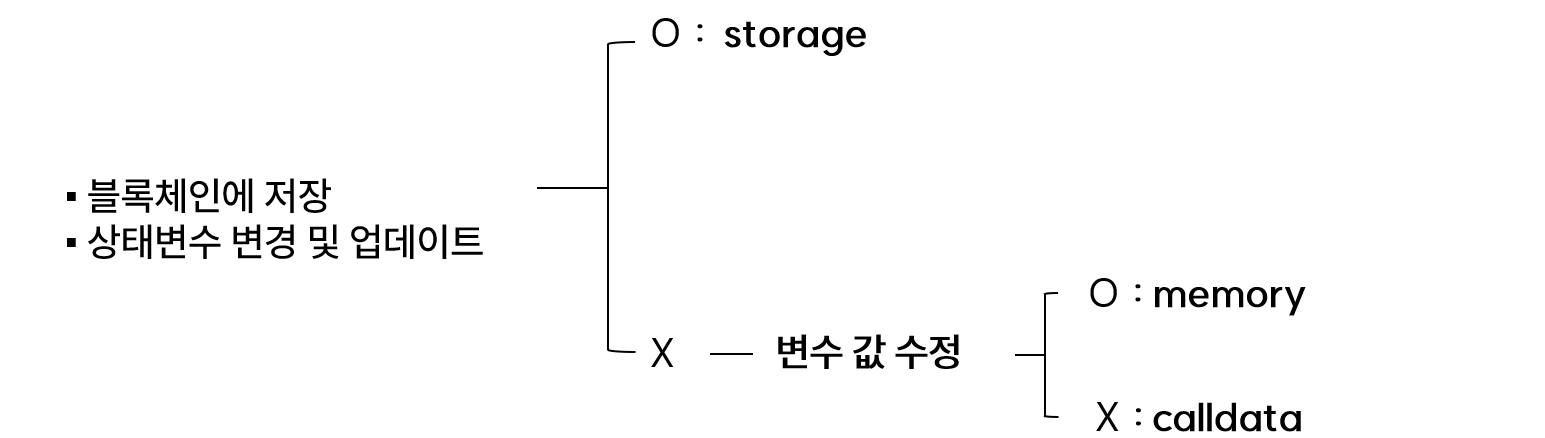
- 참조형 변수 : struct, mapping, array(string, bytes)
- 데이터 위치 : storage, calldata, memory
📝 데이터의 위치(data location)
1. storage
- 상태변수(State variable)가 저장되는 공간
- 블록 체인에 저장되는 데이터
2. calldata
- 함수 호출시 인자로 포함된 데이터들이 위치하는 공간
- 불러온 데이터 원본
- 수정 불가
3. memory
- 함수 호출 시에만 존재하는 휘발성 데이터가 위치하는 공간
- calldata의 복사본
- 수정 가능
- calldata보다 더 많은 가스비 소요
아래 코드를 통해 데이터 위치에 따른 값의 변경을 자세히 살펴볼 수 있다.
contract DataLocations {
// Data locations of state variables are storage
struct MyStruct {
uint num;
string text;
}
mapping(address => MyStruct) public myStructs;
//myStruct값을 받아서 storage에 저장할 경우 상태변수의 값이 변경됨
function setStorage(address _addr, string calldata _text) external {
MyStruct storage myStruct = myStructs[_addr];
myStruct.text = _text;
}
//memory에서 값을 변경할 경우, 상태변수로 저장된 myStructs에 영향을 주지 않음
function setMemory(address _addr, string calldata _text) external view {
MyStruct memory myStruct = myStructs[_addr];
myStruct.text = _text;
}
string public a;
//_text값을 상태변수 a에 저장
function storageA (string calldata _text) external {
a = _text;
}
//_text값 memory값에 저장 ; 상태변수 a값은 변경되지 않음
function memory1 (string calldata _text) external pure {
string memory a = _text;
// _text = "impossible"; //calldata로 받아와서 변경 불가
}
//_text값 변경 후, 상태변수 a에 저장
function memory2 (string memory _text) external {
_text = "possible";
a = _text;
}
}- 참고자료
: https://wnjoon.github.io/2022/10/21/blockchain-eth_data_location/
: https://medium.com/@aiden.p/solidity-%EC%94%A8-%EB%A6%AC%EC%A6%88-%EC%9D%80%EA%B7%BC-%ED%97%B7%EA%B0%88%EB%A6%AC%EB%8A%94-data-location-2690cefb72db
: https://medium.com/coinmonks/solidity-storage-vs-memory-vs-calldata-8c7e8c38bce