서론
이전 게시물에서 API Gateway를 구현했습니다.
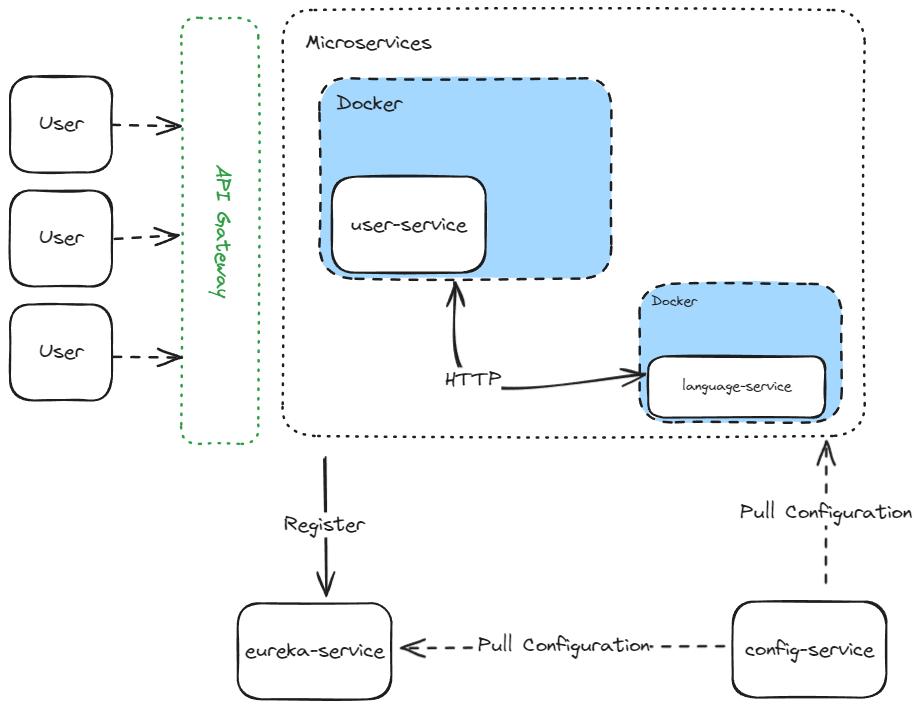
현재까지 구현 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
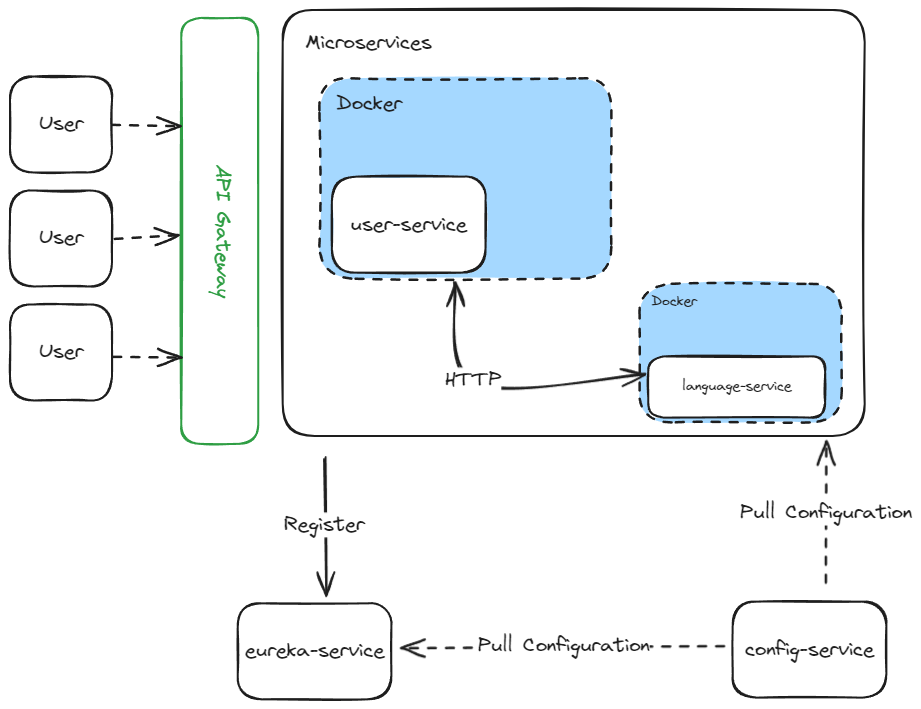
여기서 점선은 아직 구현되지 않은 부분을 의미합니다.
이번 게시물에서 구현할 내용은 설정 파일을 관리 중앙화 입니다.
본론
설정 파일 관리의 중앙화
MSA에서 각 서비스의 설정 파일 관리는 중요한 과제 입니다.
설정 파일을 마이크로서비스 내부에서 관리하면 다음과 같은 문제가 발생합니다.
- 성능 테스트
서버 성능 테스트를 위해 설정 파일의 특정 수치를 조절해야할 때, 설정 파일이 서버 내에 있다면, 수치를 변경할 때마다 애플리케이션을 새로 빌드하고 배포해야 합니다.
단순한 설정 변경에도 불구하고 전체 애플리케이션 재배포라는 불필요한 과정을 거치 됩니다. - 공통 설정 변경
여러 마이크로서비스에 공통으로 적용되는 설정 값을 변경해야 할 때, ㄱ삭 서비스의 설정 파일을 개별적으로 수정해야 하므로, 시간 소모적이며 휴먼에러가 발생할 수 있습니다.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 설정 파일을 서버 외부 중앙 위치에 관리하는 방식이 제안되고 있습니다.
- 빠른 설정 변경 : 애플리케이션 재배포 없이 설정을 즉시 변경할 수 있습니다.
- 일관성 유지 : 여러 서비스에 걸친 공통 설정의 일관성을 유지합니다.
- 버전 관리 : 설정 변경 이력을 추적하고 관리하기 용이 합니다.
- 보안 강화 : 중앙화된 위치에서 설정 접근 권한을 더 엄격히 제한할 수 있습니다.
Spring Cloud Config
Spring Cloud Config는 이러한 중앙화된 설정 관리를 위한 라이브러리 입니다.
- 분산 시스템에서 외부화된 구성을 위한 서버 및 클라이언트 제공
- Config Server 사용 시, 모든 환경에서 애플리케이션의 외부 속성을 관리할 수 있는 중앙 집중식 장소 생성
- 저장소의 기본 구현은 git을 사용하므로 버전 관리 및 쉽게 접근 가능
Spring Cloud Config를 구현하면 설정 파일들을 하나의 서버에서 관리할 수 있으며
설정 파일이 변경되어도 서버의 재빌드 & 재배포 없이 운영할 수 있습니다.
Spring Cloud Config 적용하기
Spring Cloud Config Server 구현
의존성 추가
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-config-server'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator'
}Github Repository에 설정 파일 추가
Spring Cloud Config Server가 올바르게 파일을 인식하고 제공할 수 있도록 파일 이름을 특정 형식에 맞춰야 합니다.Spring Cloud Config Server가 인식할 수 있는 파일 이름 형식은 다음과 같습니다:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]{application}-{profile}.yml/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml{application}-{profile}.properties/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
여기서 {application}은 애플리케이션 이름, {profile}은 환경(예: dev, prod), {label}은 Git 브랜치나 커밋 ID를 나타냅니다.이러한 명명 규칙을 따라 설정 파일을 생성하고 GitHub Repository에 추가하면, Spring Cloud Config Server가 정확하게 설정을 제공할 수 있습니다.
다음과 같이 2번째 형식으로 configuration 폴더 안에 설정 파일을 생성합니다.
.
├── config-server
│ ├── build
│ ├── build.gradle
│ ├── gradle
│ ├── gradlew
│ ├── gradlew.bat
│ ├── HELP.md
│ ├── settings.gradle
│ └── src
├── **configuration**
│ ├── language-service
│ │ ├── language-service-local.yml
│ └── user-service
│ │ ├── language-service-local.yml
├── eureka-service
│ ├── build
│ ├── build.gradle
│ ├── gradle
│ ├── gradlew
│ ├── gradlew.bat
│ ├── HELP.md
│ ├── settings.gradle
│ └── src
├── gateway
│ ├── build
│ ├── build.gradle
│ ├── gradle
│ ├── gradlew
│ ├── gradlew.bat
│ ├── HELP.md
│ ├── settings.gradle
│ └── src
├── language-service
│ ├── build
│ ├── build.gradle
│ ├── gradle
│ ├── gradlew
│ ├── gradlew.bat
│ ├── settings.gradle
│ └── src
└── user-service
├── build
├── build.gradle
├── gradle
├── gradlew
├── gradlew.bat
├── HELP.md
├── settings.gradle
└── src
Spring Cloud Config Server application.yml 설정 파일 추가
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: config-server
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/{username}/myMSA # 레포지토리 주소
username: # 레포지토리가 private일 때 인증
password: # private Key
search-paths: configuration/**
default-label: dev/config
ignoreLocalSshSettings: true레포지토리가 private가 아닌 public 일 때는
deploy key 설정을 할 수 있습니다.
spring:
application:
name: config-server
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/{username}/myMSA # 레포지토리 주소
username: # 레포지토리가 private일 때 인증
password: # private Key
search-paths: configuration/**
default-label: dev/config
ignoreLocalSshSettings: true
hostKey: hostKey # hostKey를 base64 인코딩한 값
hostKeyAlgorithm: # ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 //
privateKey:
-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY-----
-----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----
passphrase: passphrase # 비대칭키 생성 시 입력한 값-
hostKey 생성
``` ssh-keygen -m PEM -t ecdsa -b 256 ``` -
hostKey 조회
``` ssh-keyscan -t ecdsa github.com ``` -
privateKey 조회
``` cat {key 저장 경로}/id_ecdsa ```
Spirng Cloud Config Server 활성화
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}설정 파일 내용 갱신
Spring Cloud Config는 설정 파일 내용이 변경 되었을 때 3가지 구현을 통해 갱신합니다.
- 변경한 설정을 갱신할 Spring Cloud Config Client(각 마이크로 서비스)들의 actuator API 호출하기
- spring-cloud-bus를 통해 변경을 감지하여 갱신 이벤트 전파하기
- Watcher를 통해 지속적으로 변경 여부를 질의하여 갱신하기
1번째 방법으로 설정 파일을 갱신하기 위해
각 마이크로서비스의 application.yml에 다음과 같이 acutator API를 활성화 합니다.
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"이제 {각 서비스 URL}/actuator/refresh를 보내면 설정 갱신이 이루어집니다.
결론
이번 게시물에서는 Spring Cloud Config를 활용하여 MSA에서 설정 파일 관리의 중앙화를 구현하는 방법에 대해 살펴보았습니다. 중앙화된 설정 관리의 필요성과 그 이점은 다음과 같습니다:
- 신속한 설정 변경: 설정 파일을 중앙에서 관리함으로써, 애플리케이션을 재배포하지 않고도 즉시 설정을 변경할 수 있습니다. 이는 개발 및 운영 효율성을 크게 향상시킵니다.
- 일관된 설정 유지: 여러 마이크로서비스에 걸쳐 공통으로 적용되는 설정을 중앙에서 관리함으로써, 일관성을 유지하고 휴먼 에러를 줄일 수 있습니다.
- 효율적인 버전 관리: Git을 기반으로 한 저장소를 통해 설정 변경 이력을 쉽게 관리하고 추적할 수 있어, 필요 시 이전 버전으로의 롤백이 용이합니다.
- 강화된 보안: 중앙화된 위치에서 설정 파일에 대한 접근 권한을 보다 엄격하게 설정함으로써, 보안성을 높일 수 있습니다.
Spring Cloud Config Server의 구현을 통해 설정 파일을 효과적으로 관리하고, 각 마이크로서비스가 필요할 때마다 최신 설정을 손쉽게 가져올 수 있는 환경을 구축할 수 있습니다.