2.1 What is sort?
std::sort는 C++의 표준 템플릿 라이브러리에서 제공하는 강력한 정렬 함수이다.
2.2 sort 사용법
2.2.1 함수 기본 형식
std::sort(시작 반복자, 끝 반복자, 비교 함수);- 시작 반복자(begin): 정렬을 시작할 위치
- 끝 반복자(end): 정렬을 종료할 위치
- 비교 함수(comparison function): 두 요소를 비교하여 true 또는 false를 반환하는 함수 또는 함수 객체
2.2.2 기본 사용법
std::sort는 주어진 범위의 요소들을 오름차순으로 정렬한다. 다음은 간단한 예제이다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
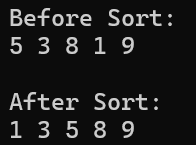
vector<int> numbers = { 5, 3, 8, 1, 9 };
// Before sort
cout << "Before Sort: " << endl;
for (int number : numbers)
cout << number << " ";
cout << endl << endl;
// sort
sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// After sort
cout << "After Sort: " << endl;
for (int number : numbers)
cout << number << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2.3 사용자 정의 비교 함수 활용
특정 기준으로 정렬해야 할 때, 사용자 정의 비교 함수를 사용할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 문자열의 길이에 따라 정렬하려면 다음과 같이 작성할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
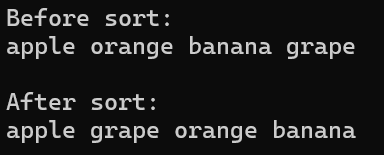
vector<string> words = { "apple", "orange", "banana", "grape" };
// Before sort
cout << "Before sort: " << endl;
for (const string& word : words)
cout << word << " ";
cout << endl << endl;
// customized sort
sort(words.begin(), words.end(), [](const string& a, const string& b) {
return a.size() < b.size();
});
// After sort
cout << "After sort:" << endl;
for (const string& word : words)
cout << word << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2.4 std::greater를 활용한 내림차순 정렬
기본적으로 std::sort는 오름차순으로 정렬되지만, std::greater를 사용하면 내림차순 정렬이 가능하다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
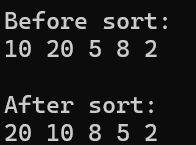
vector<int> numbers = { 10, 20, 5, 8, 2 };
// Before sort
cout << "Before sort: " << endl;
for (int number : numbers)
cout << number << " ";
cout << endl << endl;
// descending sort
sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), greater<int>());
// after sort
cout << "After sort: " << endl;
for (int number : numbers)
cout << number << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2.5 pair 활용하기
※ pair란?
std::pair는 C++ 표준 라이브러리에서 제공하는 클래스 템플릿으로, 두 개의 값(요소)을 하나의 객체로 묶어주는 데이터 구조이다. 두 요소는 서로 다른 타입일 수도 있으며, first와 second라는 멤버로 접근할 수 있다.
※ pair의 특징
1. 정의 및 초기화
- std::pair<Type1, Type2> 형식으로 정의한다.
- 생성 시, 두 값을 초기화할 수 있다.
pair<int, string> p1 = {1, "apple"};
pair<int, double> p2(2, 3.14);2. 요소 접근
- p.first: 첫 번째 값
- p.second: 두 번째 값
cout << p1.first << " " << p1.second << endl; // 출력: 1 apple다음은 pair을 활용하여 정렬 기준을 커스터마이징하는 예제이다.
문제:
학생들의 성적(점수)과 이름이 주어질 때, 점수를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬하고, 점수가 같다면 이름을 사전 순으로 정렬하세요.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 점수 기준으로 오름차순, 점수가 같으면 이름 기준으로 정렬
bool compare(const pair<int, string>& a, const pair<int, string>& b)
{
if (a.first == b.first) // 점수가 같다면 이름 사전 순
return a.second < b.second;
return a.first < b.first; // 점수 기준 오름차순
}
int main()
{
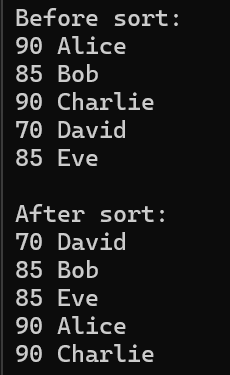
vector<pair<int, string>> students = {
{90, "Alice"},
{85, "Bob"},
{90, "Charlie"},
{70, "David"},
{85, "Eve"}
};
// Before sort
cout << "Before sort:" << endl;
for (const auto& student : students)
cout << student.first << " " << student.second << endl;
cout << endl;
// sort
sort(students.begin(), students.end(), compare);
// After sort
cout << "After sort: " << endl;
for (const auto& student : students)
cout << student.first << " " << student.second << endl;
return 0;
}
2.3 sort의 시간 복잡도
std::sort는 평균적으로 의 시간 복잡도를 가지며, 대부분의 경우 매우 빠르게 동작한다. 이는 내부적으로 Quick Sort, Heap Sort, Insertion Sort을 조합한 하이브리드 알고리즘을 사용하기 때문이다.
