자바스크립트에서는 비동기 처리를 다룰 수 있는 방법으로
callback , promise , async/await 가 있습니다.
이 중에서도 가장 자주 사용되는 promise , async/await 두 가지를 살펴보겠습니다!
Promise
프로미스를 사용하게 되면 마치 동기 메서드처럼 값을 반환할 수 있습니다.
- 대기 (pending) : 이행하지도, 거부하지도 않은 초기 상태
- 이행 (fullfilled) : 연산이 성공적으로 완료됨
- 거부 (rejected) : 연산이 실패함.
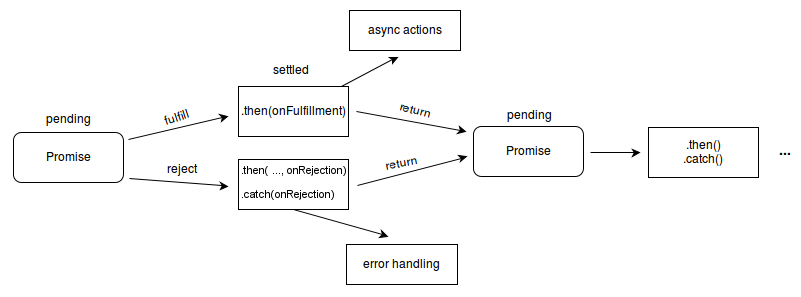
대기 중인 프로미스는 값과 함께 이행할 수도, 어떤 이유(오류)로 인해 거부될 수도 있습니다.
이행이나 거부의 경우 then 메서드에 의해 대기열(큐) 에 추가된 처리기들이 호출됩니다.
fullfilled) .then(onFullfillment)
reject) .then(...onRejection), .catch(onRejection)
연결
Promise.prototype.then(),Promise.prototype.catch(),Promise.prototype.finally() 메서드는 추가 작업을 연결하는데 사용됩니다.
.then()
최대 두 개의 인수를 받습니다.
- 이행된 경우에 대한 콜백 함수
- 거부된 경우에 대한 콜백 함수
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("foo");
}, 300);
});
myPromise
.then(handleFulfilledA, handleRejectedA)
.then(handleFulfilledB, handleRejectedB)
.then(handleFulfilledC, handleRejectedC);.then()에 프로미스 객체를 반환하는 콜백 함수가 없는 경우에도 처리는 체인의 다음 링크까지 계속됩니다.
화살표 함수를 사용한 예제
myPromise
.then((value) => `${value} and bar`)
.then((value) => `${value} and bar again`)
.then((value) => `${value} and again`)
.then((value) => `${value} and again`)
.then((value) => {
console.log(value);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
.then 은 연쇄적으로 일어나는데, 이때 여기서 오류가 발생하거나 프로미스가 reject되면 바로 .catch로 이동합니다.
async / await
callback과 promise 의 단점을 최소화하고자 나왔습니다.
await를 이용해 promise 반환값을 받아 올 수 있습니다.
function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
const result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
// Expected output: "resolved"
}
asyncCall();async 함수에는 await 식이 포함될 수 있습니다.
이 식은 async 함수의 실행을 일시 중지하고 전달된 Promise의 해결을 기다린 다음 async 함수의 실행을 다시 시작하고 완료 후 값을 반환합니다.
async 함수는 항상 promise를 반환합니다.
차이점
에러 헨들링
Promise를 활용할 시에는.catch()문을 통해 에러 핸들링이 가능하지만,async/await는 에러 핸들링을 할 수 있는 기능이 없어try-catch()문을 활용해야 합니다.
코드 가독성
Promise의.then()지옥의 가능성이 있습니다.- 코드가 길어지면 길어질수록,
async/await를 활용한 코드가 가독성이 더 좋습니다, 고로 에러를 쉽게 잡을 수 있습니다. async/await은 비동기 코드가 동기 코드처럼 읽히게 해줍니다.
추가 내용
.then 혹은 await 가 없다면 어떻게 될까?
function setTimeoutPromise(delay) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
async function startAsync() {
setTimeoutPromise(1000);
setTimeoutPromise(1500);
setTimeoutPromise(2000); // 프로그래머는 뭔가 기다리겠다는 의도를 비쳤습니다.
}
console.log("시작입니다.");
const promise = startAsync();
promise.then(() => {
console.log("끝났습니다?");
process.exit(0); // 프로그래머는 이 때에 모든 작업이 완료되었다고 생각합니다.
});출력결과
시작입니다.
끝났습니다?await를 걸지 않았으므로, 해당 비동기 작업 이후의 작업을 정의하지 않겠다는 의미입니다.
따라서, Promise에 await을 바로 걸지는 않아도 되지만 무조건, 언젠가 빠짐없이 걸기는 해야합니다.
.then 혹은 await 을 동시에 실행한다면?
function setTimeoutPromise(delay) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
async function startAsync() {
await setTimeoutPromise(1000).then(() => {
console.log("1초 지났습니다.");
});
}
console.log("시작입니다.");
startAsync();위 코드는 문법적으로는 전혀 틀리지 않았습니다.
의도가 불분명하므로 개발자에게 혼돈을 줍니다.
.then 에 async 함수를 넣는다면?
function setTimeoutPromise(delay) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
async function startAsync() {
await setTimeoutPromise(1000).then(async () => {
await setTimeoutPromise(1000);
console.log("A");
});
console.log("B");
}
startAsync();출력은 A,B 순차적으로 나와, 우리의 의도에 부합하지만, 코드가 매우 난잡하게 됩니다.
function setTimeoutPromise(delay) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
async function startAsync() {
await setTimeoutPromise(1000);
await setTimeoutPromise(1000);
console.log("A");
console.log("B");
}
startAsync();혹은
function setTimeoutPromise(delay) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
function startAsync() {
setTimeoutPromise(1000)
.then(() => setTimeoutPromise(1000))
.then(() => console.log("A"))
.then(() => console.log("B"));
}
startAsync();이렇게 작성하는 편이 좋습니다.
출처블로그
Promise
async function
Promise와 async/await 차이점
8. Async/Await와 Promise의 차이에 대해 설명해주세요.
[Javascript] 비동기, Promise, async, await 확실하게 이해하기
