AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming)
관점지향 프로그램
스프링 어플리케이션은 대부분 특별한 경우를 제외하고 MVC 웹 어플리케이션에서는 WebLayer, BusinessLayer, DataLayer로 정의한다.
1. Web Layer
REST API를 제공하며, Client 중심의 로직 적용
2. Business Layer
내부 정책에 따른 로직을 개발하며, 주로 해당 부분 개발
3. Data Layer
데이터베이스 및 외부와의 연동 처리
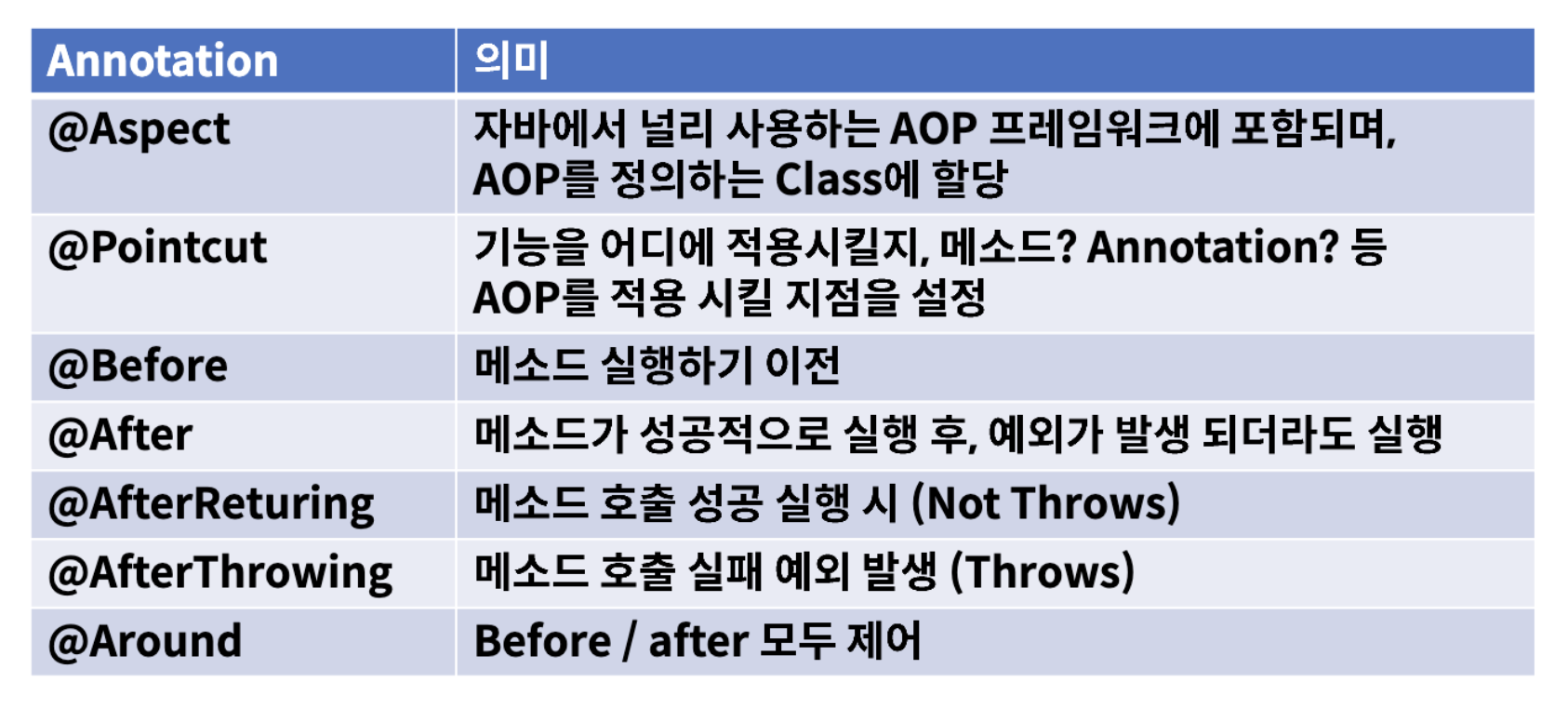
주요 @Annotation
실습
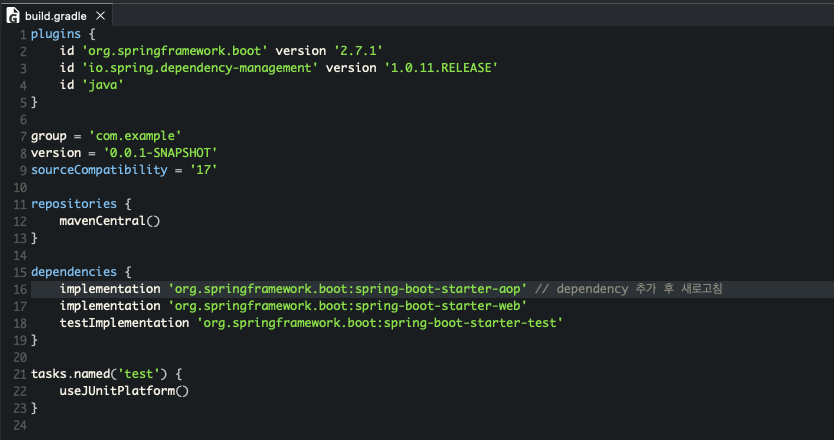
AOP를 사용하기 위해 Dependency 를 추가해야함
// 주석으로 된 코드는 기본 RestApi 실습
package com.example.aop.controller
RestApiController.java
package com.example.aop.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.aop.dto.User;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class RestApiController {
/*
RequestParam과 PathVariable 차이
** RequestParam
http://192.168.0.1:8080?aaa=bbb&ccc=ddd
** PathVariable
http://192.168.0.1:8080/bbb/ddd
*/
// URL: http://localhost:9091/api/get/100?name=ila
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
// public void get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name ) {
// System.out.println("get method");
// System.out.println("get method : " + id);
// System.out.println("get method : " + name);
// }
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name ) {
//System.out.println("get method");
//System.out.println("get method : " + id);
//System.out.println("get method : " + name);
return id + " " + name;
}
@PostMapping("/post")
// public void post(@RequestBody User user) {
// System.out.println("post method : " + user);
//
// }
public User post(@RequestBody User user) {
//System.out.println("post method : " + user);
return user;
}
}package com.example.aop.dto User.java
package com.example.aop.dto;
public class User {
private String id;
private String pw;
private String email;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPw() {
return pw;
}
public void setPw(String pw) {
this.pw = pw;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", pw=" + pw + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}package com.example.aop.aop
ParameterAop.java
// Aop 관리하기 위해 (여러개의 api endpoint 설정할때 좋다)
package com.example.aop.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect // 클래스가 aop로 동작하기 위해 사용
@Component //스프링에서 관리 하기 위해 필요
public class ParameterAop {
// Aop 범위 설정
@Pointcut("execution (* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut() {}
// 메소드가 실행되기 전 넘어가는 Argument 확인
@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 메소드 이름 출력
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
System.out.println(method.getName());
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args) {
System.out.println("type : " + obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value : " + obj);
}
}
// return이 됬을때 반환값 확인
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj) {
System.out.println("return obj");
System.out.println(returnObj);
}
}console
url : http://localhost:9091/api/post
post
type : User
value : User [id=ila, pw=1234, email=hyerihello@gmail.com]
return obj
User [id=ila, pw=1234, email=hyerihello@gmail.com]
url : http://localhost:9091/api/get/100?name=ila
get
type : Long
value : 100
type : String
value : ila
return obj
100 ilaTimer Aop
본래 아래와 같이 timer를 보고싶을때 로직을 짠다.
일관된 로직을 get, post, delete 모든것에 넣기보다는
aop에 만들어서 일괄 적용하면 쉽다!
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name ) {
StopWatch stopwatch = new StopWatch();
stopwatch.start();
//TODO
stopwatch.stop();
System.out.println("total :" + stopwatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
return id + " " + name;
}
package com.example.aop.aop
TimerAop.java
package com.example.aop.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
/* @Bean과, @Component 차이 !
* @Bean 은 class에 붙일 수 없음 (메소드에서 사용)
* @Component 를 통해 class 단위로 Bean에 올릴 수 있다!
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimerAop {
// Aop 범위 설정
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop.annotation.Timer)")
private void enableTimer(){}
@Around("cut() && enableTimer()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
stopWatch.stop();
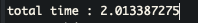
System.out.println("total time : "+stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
}package com.example.aop.annotation
(interface)Timer.java
package com.example.aop.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Timer {
}RestApiControll.java 에 메서드추가
@Timer
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public void delete() throws InterruptedException {
//db logic
Thread.sleep(1000*2);
}
Decode
package com.example.aop.annotation
(interface)Decode.java
package com.example.aop.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Decode {
}
}RestApiControll.java 에 메서드추가
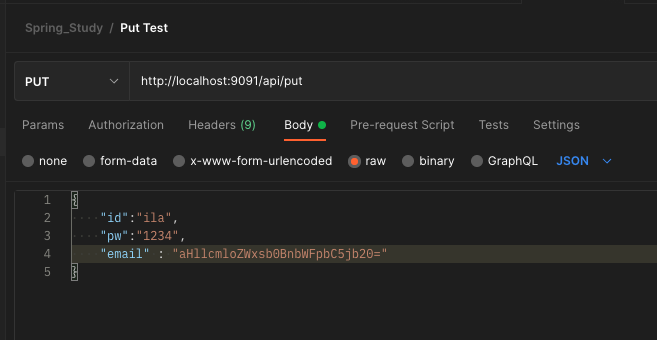
@Decode
@PutMapping("/put")
public User put(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("put");
System.out.println(user);
return user;
}package com.example.aop.aop
DecodeAop.java
package com.example.aop.aop;
import com.example.aop.dto.User;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Base64;
@Aspect
@Component
public class DecodeAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut(){}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop.annotation.Decode)")
private void enableDecode(){}
// 디코딩
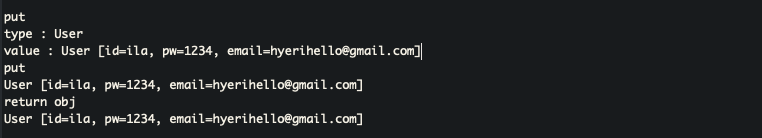
@Before("cut() && enableDecode()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object arg : args){
if(arg instanceof User){
User user = User.class.cast(arg);
String base64Email = user.getEmail();
String email = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Email),"UTF-8");
user.setEmail(email);
}
}
}
//인코딩
@AfterReturning(value = "cut() && enableDecode()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj){
if(returnObj instanceof User){
User user = User.class.cast(returnObj);
String email = user.getEmail();
String base64Email = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(email.getBytes());
user.setEmail(base64Email);
}
}
}