명품 자바 프로그래밍(개정5판) 2장 실습문제 풀이 p.110-114
1번
코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class scanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
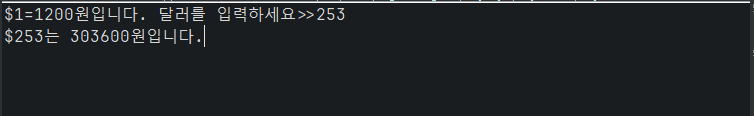
System.out.print("$1=1200원입니다. 달러를 입력하세요>>");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int dollar = s.nextInt();
int won = dollar * 1200;
System.out.print("$" + dollar + "는 " + won + "원입니다.");
s.close();
}
}2번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class birth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("생일 입력 하세요>>");
int birth = s.nextInt();
int year = birth / 10000;
int month = birth % 10000 / 100;
int day = birth % 100;
System.out.println(year + "년 " + month + "월 " + day + "일");
s.close();
}
}3번
코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class snackFood {
public static void main(String[] args) {
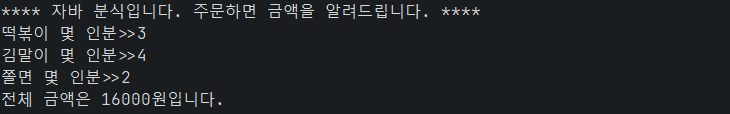
System.out.println("**** 자바 분식입니다. 주문하면 금액을 알려드립니다. ****");
System.out.print("떡볶이 몇 인분>>");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int tteokbokki = s.nextInt();
System.out.print("김말이 몇 인분>>");
int seaweed = s.nextInt();
System.out.print("쫄면 몇 인분>>");
int jjolmyeon = s.nextInt();
int price = tteokbokki * 2000 + seaweed * 1000 + jjolmyeon * 3000;
System.out.println("전체 금액은 " + price + "원입니다.");
s.close();
}
}4번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TravelCost {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("여행지>>");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
String area = s.nextLine();
System.out.print("인원수>>");
int people = s.nextInt();
int rooms = people / 2 + people % 2;
System.out.print("숙박일>>");
int sleep = s.nextInt();
int days = sleep + 1;
System.out.print("1인당 항공료>>");
int airfare = s.nextInt();
System.out.print("1방 숙박비>>");
int accommodation = s.nextInt();
int cost = airfare * people + accommodation * rooms * sleep;
System.out.print(people + "명의 " + area + " " + sleep + "박 " + days +
"일 여행에는 방이 " + rooms + "개 필요하며 경비는 " + cost + "원입니다.");
s.close();
}
}5번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Attendance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("학생1>>");
String student1 = s.next();
int a = s.nextInt();
int b = s.nextInt();
int deduction1 = a * 3 + b * 8;
int score1 = 100 - deduction1;
System.out.print("학생2>>");
String student2 = s.next();
int x = s.nextInt();
int y = s.nextInt();
int deduction2 = x * 3 + y * 8;
int score2 = 100 - deduction2;
System.out.println(student1 + "의 감점은 " + deduction1 + ", " + student2 + "의 감점은 " + deduction2);
if (score1 > score2) {
System.out.println(student1 + "의 출석 점수가 더 높음. " + student1 + "출석 점수는 " + score1);
}
else if (score1 < score2) {
System.out.println(student2 + "의 출석 점수가 더 높음. " + student2 + "출석 점수는 " + score2);
}
else {
System.out.println("점수 동일");
}
s.close();
}
}6번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Candle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("나이를 입력하세요>>");
int age = s.nextInt();
if (age <= 0) {
System.out.println("나이는 양수로만 입력하세요.");
System.exit(0); // 프로그램 종료
}
int red = age / 10;
int blue = age % 10 / 5;
int yellow = age % 5;
int sum = red + blue + yellow;
System.out.print("빨간 초 " + red + "개, 파란 초 " + blue + "개, 노란 초 " + yellow + "개. ");
System.out.println("총 " + sum + "개가 필요합니다.");
s.close();
}
}
7번

7-1 (if-else 문) 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Season {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("월을 입력하세요(1~12)>>");
int month = s.nextInt();
if(month >=3 && month <=5)
System.out.println("따뜻한 봄");
else if(month >=6 && month <=8)
System.out.println("바다가 즐거운 여름");
else if(month >=9 && month <=11)
System.out.println("낙엽이 지는 아름다운 가을");
else if(month == 12 || month <=2)
System.out.println("눈 내리는 하얀 겨울");
else
System.out.println("1~12만 입력하세요.");
s.close();
}
}7-2 (switch 문) 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Season {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("월을 입력하세요(1~12)>>");
int month = s.nextInt();
switch(month) {
case 3: case 4: case 5:
System.out.println("따뜻한 봄");
break;
case 6: case 7: case 8:
System.out.println("바다가 즐거운 여름");
break;
case 9: case 10: case 11:
System.out.println("낙엽이 지는 아름다운 가을");
break;
case 12: case 1: case 2:
System.out.println("눈 내리는 하얀 겨울");
break;
default:
System.out.println("1~12만 입력하세요.");
}
s.close();
}
}8번

8-1 (if-else 문) 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class OperationIf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("연산 입력>>");
double x = s.nextDouble();
String op = s.next();
double y = s.nextDouble();
double result;
if(op.equals("더하기"))
result = x+y;
else if(op.equals("빼기"))
result = x-y;
else if(op.equals("곱하기"))
result = x*y;
else if(op.equals("나누기"))
result = x/y;
else {
System.out.println("사칙연산이 아닙니다.");
s.close();
return;
}
System.out.println(x + " " + op + " " + y + "의 계산 결과는 " + result);
s.close();
}
}8-2 (switch 문) 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class OperationSwitch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("연산 입력>>");
double x = s.nextDouble();
String op = s.next();
double y = s.nextDouble();
double result;
switch(op) {
case "더하기" :
result = x+y;
break;
case "빼기" :
result = x-y;
break;
case "곱하기" :
result = x*y;
break;
case "나누기" :
result = x/y;
break;
default:
System.out.println("사칙연산이 아닙니다.");
s.close();
return;
}
System.out.println(x + " " + op + " " + y + "의 계산 결과는 " + result);
s.close();
}
}switch문 내부에서 String을 비교할 때는 equals()를 사용한 것과 동일하게 동작하며, 비교는 equals()로 처리됨
9번



코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Rect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("점 (x,y)의 좌표 입력>>");
int x = s.nextInt();
int y = s.nextInt();
if ((x == 10 || x == 200) && (y >= 10 && y <= 300)
|| (y == 10 || y == 300) && (x >= 10 && x <= 200)) {
System.out.println("("+ x + "," + y + ")는 사각형 선 상에 있습니다.");
}
else if (x>10 && x<200 && y>10 && y<300) {
System.out.println("("+ x + "," + y + ")는 사각형 안에 있습니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("("+ x + "," + y + ")는 사각형 밖에 있습니다.");
}
s.close();
}
}10번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Rect2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("(x1, y1), (x2, y2)의 좌표 입력>>");
// (x1, y1)이 왼쪽 아래, (x2, y2)가 오른쪽 위 좌표라고 가정
int x1 = s.nextInt();
int y1 = s.nextInt();
int x2 = s.nextInt();
int y2 = s.nextInt();
System.out.print("(" + x1 + ", " + y1 + ") (" + x2 + "," + y2 + ") ");
if(x1>=10 && y1>=10 && x2<=200 && y2<=300)
System.out.println("사각형은 (10,10) (200,300) 사각형에 포함된다.");
else
System.out.println("사각형은 (10,10) (200,300) 사각형에 포함되지 않는다.");
s.close();
}
}
11번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Embedded {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
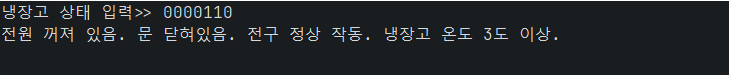
System.out.print("냉장고 상태 입력>> ");
String str = s.next();
byte status = Byte.parseByte(str, 2);
// 비트 0
if ((status & 0b00000001) != 0) System.out.print("전원 켜져 있음. ");
else System.out.print("전원 꺼져 있음. ");
// 비트 1
if ((status & 0b00000010) != 0) System.out.print("문 닫혀있음. ");
else System.out.print("문 열려 있음. ");
// 비트 2
if ((status & 0b00000100) != 0) System.out.print("전구 정상 작동. ");
else System.out.print("전구 손상됨. ");
// 비트 3
if ((status & 0b00001000) != 0) System.out.print("냉장고 온도 3도 미만.");
else System.out.print("냉장고 온도 3도 이상.");
s.close();
}
}
12번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CarStatus {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
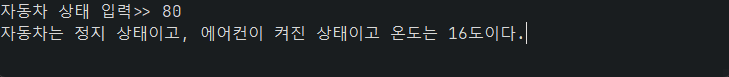
System.out.print("자동차 상태 입력>> ");
int status = s.nextInt();
// 비트 7
if ((status & 0b10000000) != 0) System.out.print("자동차는 달리는 상태이고, ");
else System.out.print("자동차는 정지 상태이고, ");
// 비트 6
if ((status & 0b01000000) != 0) System.out.print("에어컨이 켜진 상태이고 ");
else System.out.print("에어컨이 꺼진 상태이며 ");
// 비트 0~5
int temperature = status & 0b00111111; // 비트 AND 연산
System.out.println("온도는 " + temperature + "도이다.");
s.close();
}
}
개인 풀이이므로 틀린 부분이나 피드백이 있으면 댓글로 남겨주시면 감사하겠습니다!
