명품자바프로그래밍 개정5판 5장 실습문제 풀이 p.320-330
1번

코드
class TV {
private int size;
public TV(int size) { this.size = size;}
protected int getSize() { return size; }
}
public class ColorTV extends TV {
private int color;
public ColorTV(int size, int color) {
super(size);
this.color = color;
}
public void printProperty() {
System.out.println(super.getSize() + "인치 " + color + "컬러");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorTV myTv = new ColorTV(65,65536);
myTv.printProperty();
}
}
2번

코드
// SmartTV 클래스
public class SmartTV extends ColorTV {
private String address;
public SmartTV(String address, int size, int color) {
super(size, color);
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public void printProperty() {
System.out.print("나의 SmartTV는 " + address + " 주소의 ");
super.printProperty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SmartTV smartTV = new SmartTV("192.168.0.5", 77, 20000000);
smartTV.printProperty();
}
}3번
코드
class Point {
private int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
}
public class ColorPoint extends Point {
private String color;
public ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color) {
super(x, y);
this.color = color;
}
public void setXY(int x, int y) {
move(x, y);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return color + "색의 (" + getX() + "," + getY() + ")의 점";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 5, "RED");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("BLUE");
String str = cp.toString();
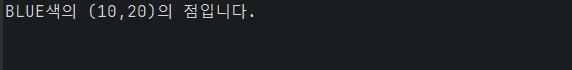
System.out.println(str + "입니다.");
}
}4번
코드
class Point {
private int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
}
public class ColorPoint2 extends Point {
private String color;
public ColorPoint2() {
super(0,0);
this.color = "WHITE";
}
public ColorPoint2(int x, int y) {
super(x,y);
this.color = "BLACK";
}
public ColorPoint2(int x, int y, String color) {
super(x,y);
this.color = color;
}
public void set(String color) {
this.color=color;
}
public void set(int x, int y) {
move(x,y);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return color + "색의 (" + getX() + "," + getY() + ")의 점";
}
public double getDistance(ColorPoint2 cp2) {
double x = Math.abs(this.getX() - cp2.getX());
double y = Math.abs(this.getY() - cp2.getY());
double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x, 2) + Math.pow(y, 2));
return distance;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint2 zeroPoint = new ColorPoint2(); // (0,0) WHITE색 점
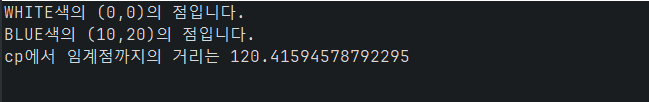
System.out.println(zeroPoint.toString() + "입니다.");
ColorPoint2 cp = new ColorPoint2(10, 10, "RED"); // (10,10) RED색 점
cp.set("BLUE");
cp.set(10,20);
System.out.println(cp.toString() + "입니다.");
ColorPoint2 thresholdPoint = new ColorPoint2(100,100); // (100,100) BLACK색 점
System.out.println("cp에서 임계점까지의 거리는 " + cp.getDistance(thresholdPoint));
}
}5번

코드
class Point {
private int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
}
public class Point3D extends Point {
private int z;
public Point3D(int x, int y, int z) {
super(x, y);
this.z = z;
}
public void moveUp(int value) { z += value; }
public void moveDown(int value) { z-= value; }
public void move(int x, int y, int z) {
super.move(x, y);
this.z = z;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return ("(" + getX() + "," + getY() + "," + z + ")의 점");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point3D p = new Point3D(3, 2, 1);
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
p.moveUp(3); // z 축으로 3 이동
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
p.moveDown(2); // z 축으로 -2 이동
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
p.move(5, 5); // x=10, y=10으로 이동
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
p.move(100, 200, 300);
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
}
}6번

코드
class Point {
private int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + x + "," + y + ")";
}
}
public class PositivePoint extends Point {
public PositivePoint(int x, int y) {
super((x > 0) ? x : 1, (y > 0) ? y : 1);
}
@Override
public void move(int x, int y) {
if (x > 0 && y > 0)
super.move(x, y);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PositivePoint p = new PositivePoint(10, 10); // (10, 10)의 점
p.move(5,5);
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
p.move(2, -2); // 점 p는 양수 공간만 이동 가능
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
PositivePoint q = new PositivePoint(-10, -10);
// 음수 점 불가. 디폴트(1,1)의 점 생성
System.out.println(q.toString() + "입니다.");
}
}7번
코드
class Point {
private int x,y;
public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
public int getX() { return x; }
public int getY() { return y; }
protected void move(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
}
public class Point3DColor extends Point {
private int z;
private String color;
public Point3DColor(int x, int y, int z, String color) {
super(x, y);
this.z = z;
this.color = color;
}
public void move(Point3DColor p) {
super.move(p.getX(), p.getY());
this.z=p.z;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + getX() + "," + getY() + "," + z + ") " + color + "점" ;
}
public boolean equals(Point3DColor p) {
if(getX() == p.getX() && getY() == p.getY() && z == p.z
&& color.equals(p.color))
return true;
else
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point3DColor p = new Point3DColor(10, 20, 30, "RED");
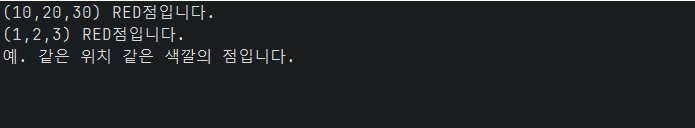
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
Point3DColor q = new Point3DColor(1, 2, 3, "BLUE");
p.move(q); // 점 p를 점 q의 위치로 이동
System.out.println(p.toString() + "입니다.");
Point3DColor r = new Point3DColor(1, 2, 3, "RED");
if(p.equals(r))
System.out.println("예. 같은 위치 같은 색깔의 점입니다.");
else
System.out.println("아니오");
}
}8번
코드
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Box{
protected int size; // 현재 박스에 들어 있는 재료의 양
public Box(int size) { // 생성자
this.size = size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0; } // 박스가 빈 경우 true 리턴
public abstract boolean consume(); // 박스에 들어있는 재료를 일정량 소비
public abstract void print(); // 박스에 들어있는 양을 "*"문자로 출력
}
class IngredientBox extends Box {
private String name;
public IngredientBox(String name, int size) { // 생성자
super(size);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean consume() {
if(isEmpty()) return false;
size--;
return true;
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.print(name + " ");
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println(size);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
IngredientBox coffee = new IngredientBox("커피", 5);
IngredientBox prim = new IngredientBox("프림", 5);
IngredientBox sugar = new IngredientBox("설탕", 5);
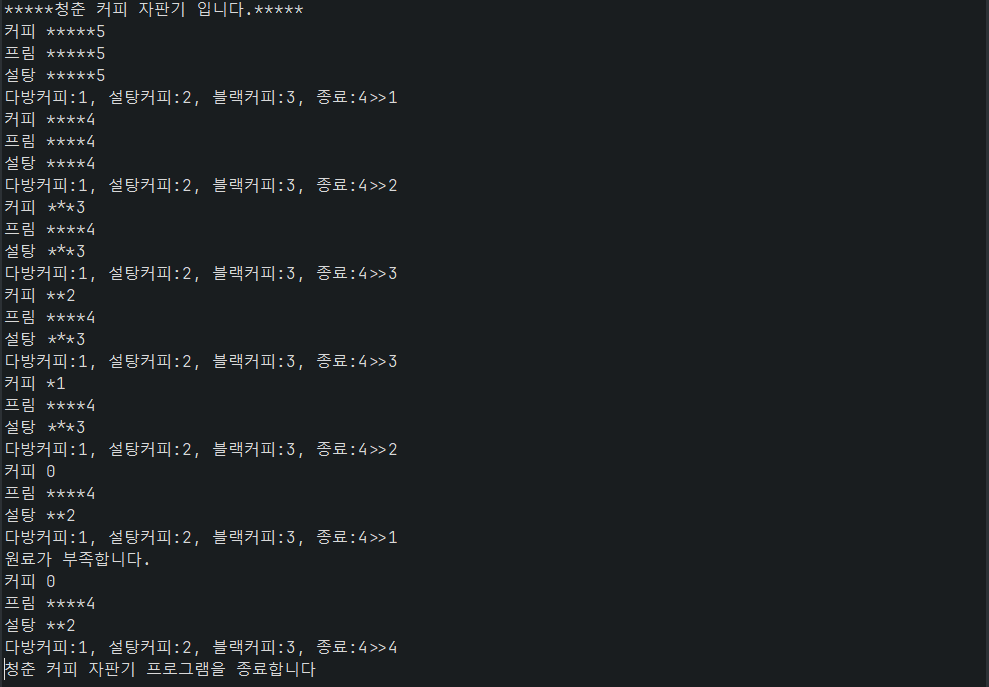
System.out.println("*****청춘 커피 자판기 입니다.*****");
coffee.print(); prim.print(); sugar.print();
while(true) {
System.out.print("다방커피:1, 설탕커피:2, 블랙커피:3, 종료:4>>");
int order = scanner.nextInt();
switch(order) {
case 1:
if( coffee.consume() && prim.consume() && sugar.consume()) {
break;
}
else {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
break;
}
case 2:
if( coffee.consume() && sugar.consume()) {
break;
}
else {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
break;
}
case 3:
if(!coffee.consume()) {
System.out.println("원료가 부족합니다.");
break;
}
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("청춘 커피 자판기 프로그램을 종료합니다");
scanner.close();
return;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다. 다시 시도해주세요.");
break;
}
coffee.print(); prim.print(); sugar.print();
}
}
}9번
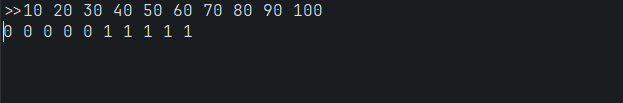
코드
import java.util.Scanner;
class BaseArray {
protected int array []; // 배열 메모리
protected int nextIndex = 0; // 다음에 삽입할 배열에 대한 인덱스
public BaseArray(int size) {
array = new int [size];
}
public int length() { return array.length; }
public void add(int n) { // 정수 n을 배열 끝에 추가
if(nextIndex == array.length) return; // 배열이 꽉찼으면 추가 안 함
array[nextIndex] = n;
nextIndex++;
}
public void print() {
for(int n : array) System.out.print(n + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public class BinaryArray extends BaseArray{
private int threshold;
public BinaryArray(int size, int threshold) {
super(size);
this.threshold= threshold;
}
@Override
public void add(int n) {
if(n > threshold)
super.add(1);
else
super.add(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int threshold = 50;
BinaryArray bArray = new BinaryArray(10, threshold);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(">>");
for(int i=0; i<bArray.length(); i++) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
bArray.add(n);
}
bArray.print();
scanner.close();
}
}10번
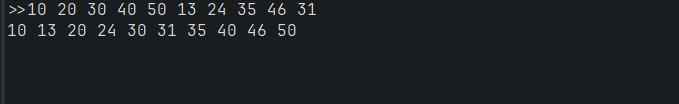
코드
import java.util.Scanner;
class BaseArray {
protected int array []; // 배열 메모리
protected int nextIndex = 0; // 다음에 삽입할 배열에 대한 인덱스
public BaseArray(int size) {
array = new int [size];
}
public int length() { return array.length; }
public void add(int n) { // 정수 n을 배열 끝에 추가
if(nextIndex == array.length) return; // 배열이 꽉찼으면 추가 안 함
array[nextIndex] = n;
nextIndex++;
}
public void print() {
for(int n : array) System.out.print(n + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public class SortedArray extends BaseArray{
public SortedArray(int size) {
super(size);
}
// 값을 큰 순서로 정렬하여 배열에 추가
@Override
public void add(int n) {
if (nextIndex == array.length) return; // 배열이 꽉 찬 경우
// 삽입할 위치 찾기
int i = nextIndex - 1;
while (i >= 0 && array[i] > n) {
array[i + 1] = array[i];
i--;
}
// 값 삽입
array[i + 1] = n;
nextIndex++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedArray sArray = new SortedArray(10);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(">>");
for(int i=0; i<sArray.length(); i++) { // sArray.length()=10
int n = scanner.nextInt();
sArray.add(n);
}
sArray.print();
scanner.close();
}
}11번

코드
(1) StringStack 클래스
interface IStack {
int capacity(); // 스택에 저장 가능한 개수 리턴
int length(); // 스택에 현재 저장된 개수 리턴
boolean push(String val); // 스택의 톱(top)에 문자열 저장하고 true 리턴.
// 꽉 차서 넣을 수 없으면 false 리턴
String pop(); // 스택의 톱(top)에 저장된 문자열 리턴. 스택이 비어 있으면 null 리턴
}
public class StringStack implements IStack{
private int top=0;
private String[] data = null;
public StringStack(int capacity) {
data = new String[capacity];
}
@Override
public int capacity() {
return data.length;
}
@Override
public int length() {
return top;
}
@Override
public boolean push(String val) {
if(top==data.length) return false;
data[top]=val;
top++;
return true;
}
@Override
public String pop() {
if(top==0) return null;
top--;
return data[top];
}
}(2) StackApp 클래스
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StackApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("스택 용량>>");
int size = scanner.nextInt();
StringStack sStack = new StringStack(size);
while(true) {
System.out.print("문자열 입력>>");
String str = scanner.next();
if(str.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
if(sStack.push(str) == false) {
System.out.println("스택이 꽉 차서 " + str + " 저장 불가");
}
}
System.out.print("스택에 저장된 문자열 팝 : ");
while(true) {
String str = sStack.pop();
if(str == null) { break; }
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
System.out.println();
scanner.close();
}
}12번

코드
(1) Dictionary 클래스
abstract class PairMap {
protected String keyArray[]; // 키 문자열을 저장하는 배열
protected String valueArray[]; // 값 문자열을 저장하는 배열
abstract public String get(String key); // key 값으로 value 검색
abstract public void put(String key, String value); // key와 value를 쌍으로 저장. key가 이미 저장되어 있으면 값을 value로 수정
abstract public String delete(String key); // key 값을 가진 아이템(value와 함께) 삭제. 삭제된 value 값 리턴
abstract public int length(); // 현재 저장된 아이템 개수 리턴
}
public class Dictionary extends PairMap {
private int size; // 현재 저장된 개수
private int capacity; // 배열 최대 크기
public Dictionary(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
this.keyArray = new String[capacity];
this.valueArray = new String[capacity];
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (keyArray[i].equals(key)) {
return valueArray[i];
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void put(String key, String value) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (keyArray[i].equals(key)) {
valueArray[i] = value; // 키가 이미 있으면 값 수정
return;
}
}
if (size < capacity) {
keyArray[size] = key;
valueArray[size] = value;
size++;
}
}
@Override
public String delete(String key) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (keyArray[i].equals(key)) {
String deletedValue = valueArray[i];
// 배열을 재구성하여 삭제 처리
for (int j = i; j < size - 1; j++) {
keyArray[j] = keyArray[j + 1];
valueArray[j] = valueArray[j + 1];
}
keyArray[size - 1] = null; // 마지막 원소 제거
valueArray[size - 1] = null;
size--;
return deletedValue; // 삭제된 값 반환
}
}
return null; // 키가 없으면 null 반환
}
@Override
public int length() {
return size;
}
}(2) DictionaryApp 클래스
public class DictionaryApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dictionary dic = new Dictionary(10);
dic.put("황기태", "자바");
dic.put("이재문", "파이썬");
dic.put("이재문", "C++"); // 값 수정
System.out.println("이재문의 값은 " + dic.get("이재문"));
System.out.println("황기태의 값은 " + dic.get("황기태"));
dic.delete("황기태");
System.out.println("황기태의 값은 " + dic.get("황기태"));
}
}13번

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Calc {
public String errorMsg;
protected int a, b;
public void setValue(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public abstract int calculate();
}
// 덧셈
class Add extends Calc {
@Override
public int calculate() {
errorMsg = null;
return a+b;
}
}
// 뺄셈
class Sub extends Calc {
@Override
public int calculate() {
errorMsg = null;
return a-b;
}
}
// 곱셈
class Mul extends Calc {
@Override
public int calculate() {
errorMsg = null;
return a*b;
}
}
// 나눗셈
class Div extends Calc {
@Override
public int calculate() {
if(b == 0) {
errorMsg = "0으로 나눌 수 없음.";
return 0;
}
else {
errorMsg = null;
return a/b;
}
}
}
public class Calculator {
public Calculator() { }
public void run() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.print("두 정수와 연산자를 입력하시오>>");
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
String operator = scanner.next();
Calc obj;
switch (operator) {
case "+": obj = new Add(); break;
case "-": obj = new Sub(); break;
case "*": obj = new Mul(); break;
case "/": obj = new Div(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 연산자입니다.");
scanner.close();
return;
}
obj.setValue(a, b);
int res = obj.calculate();
if(obj.errorMsg == null) {
System.out.println("계산 결과 " + res);
}
else {
System.out.print(obj.errorMsg);
System.out.println(" 프로그램 종료");
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator mycal = new Calculator();
mycal.run();
}
}14번
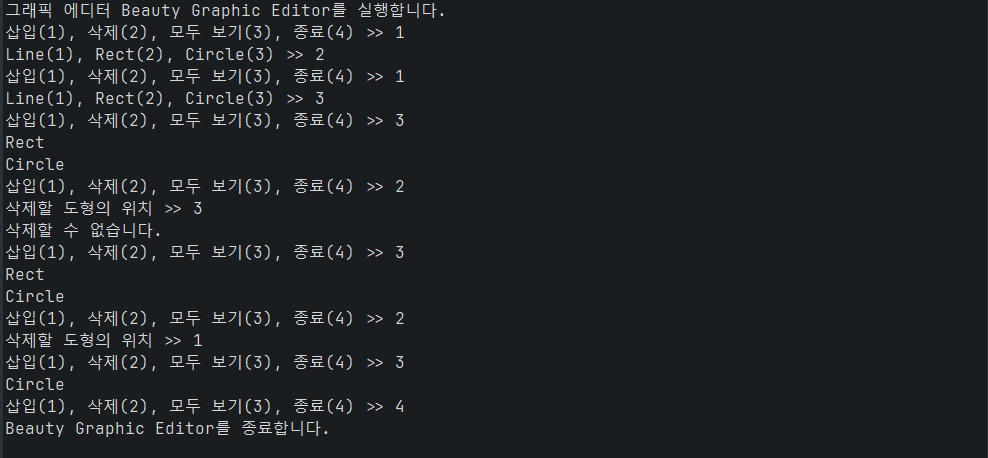
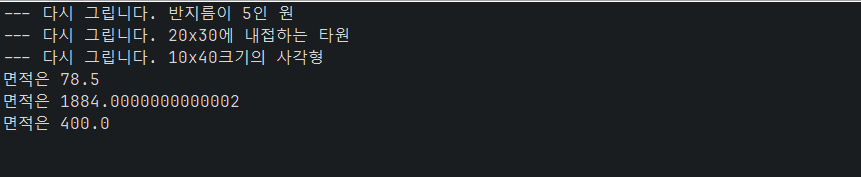
코드
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Shape {
private Shape next;
public Shape() { next = null; }
public void setNext(Shape obj) { next = obj; } // 링크 연결
public Shape getNext() { return next; }
public abstract void draw(); // 추상 메소드
}
class Line extends Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Line");
}
}
class Rect extends Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Rect");
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle");
}
}
//GraphicEditor 클래스
class GraphicEditor {
private Shape head; // 연결 리스트의 첫 번째 도형
public GraphicEditor() {
head = null;
}
// 도형 삽입
public void insert(Shape shape) {
if (head == null) {
head = shape;
} else {
Shape current = head;
while (current.getNext() != null) {
current = current.getNext();
}
current.setNext(shape);
}
}
// 저장된 모든 도형 출력
public void printAll() {
Shape current = head;
while (current != null) {
current.draw();
current = current.getNext();
}
}
// 특정 위치의 도형 삭제
public boolean delete(int position) {
if (head == null || position < 1) {
return false;
}
if (position == 1) { // 첫 번째 도형 삭제
head = head.getNext();
return true;
}
Shape current = head;
Shape previous = null;
int count = 1;
while (current != null && count < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.getNext();
count++;
}
if (current == null) {
return false; // 위치가 잘못된 경우
}
previous.setNext(current.getNext()); // 현재 위치의 도형을 삭제
return true;
}
// 프로그램 실행
public void run() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("그래픽 에디터 Beauty Graphic Editor를 실행합니다.");
while (true) {
System.out.print("삽입(1), 삭제(2), 모두 보기(3), 종료(4) >> ");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
System.out.print("Line(1), Rect(2), Circle(3) >> ");
int type = scanner.nextInt();
Shape shape = null;
if (type == 1) shape = new Line();
else if (type == 2) shape = new Rect();
else if (type == 3) shape = new Circle();
if (shape != null) {
insert(shape);
} else {
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("삭제할 도형의 위치 >> ");
int position = scanner.nextInt();
if (!delete(position)) {
System.out.println("삭제할 수 없습니다.");
}
break;
case 3:
printAll();
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Beauty Graphic Editor를 종료합니다.");
scanner.close();
return;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
break;
}
}
}
}
public class GraphicEditorApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphicEditor editor = new GraphicEditor();
editor.run();
}
}15번
코드
interface Shape {
static final double PI = 3.14;
void draw(); // 도형을 그리는 추상 메소드.
double getArea(); // 도형의 면적을 리턴하는 추상 메소드.
default public void redraw() { // 디폴트 메소드
System.out.print("--- 다시 그립니다. ");
draw();
}
}
class Circle implements Shape {
private int radius;
public Circle(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("반지름이 " + radius + "인 원");
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return PI*radius*radius;
}
}
class Oval implements Shape {
private int width, height;
public Oval(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println(width + "x" + height + "에 내접하는 타원");
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return PI*width*height;
}
}
class Rect implements Shape {
private int width, height;
public Rect(int width, int height) {
this.width = width; this.height = height;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println(width + "x" + height + "크기의 사각형");
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return width*height;
}
}
public class ShapeEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape [] list = new Shape[3]; // Shape을 상속받은 클래스 객체의 레퍼런스 배열
list[0] = new Circle(5); // 반지름이 5인 원 객체
list[1] = new Oval(20, 30); // 20x30 사각형에 내접하는 타원
list[2] = new Rect(10, 40); // 10x40 크기의 사각형
for(int i=0; i<list.length; i++) list[i].redraw();
for(int i=0; i<list.length; i++) System.out.println("면적은 " + list[i].getArea());
}
}개인 풀이이므로 틀린 부분이나 피드백이 있으면 댓글로 남겨주시면 감사하겠습니다!
