힙
"힙(heap)"은 이진 트리를 기반으로 한 특수한 트리 기반 데이터 구조다. 데이터에서 최댓값과 최솟값을 빠르게 찾기 위해 고안된 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)이며, 힙에는 두 가지 주요한 속성이 있다.
- 최대 힙 (Max Heap): 각 노드의 값이 그 자식 노드들의 값보다 크거나 같은 완전 이진 트리다. 즉, 최대 힙의 루트(root)는 힙 내의 최대값을 가진다.
- 최소 힙 (Min Heap): 각 노드의 값이 그 자식 노드들의 값보다 작거나 같은 완전 이진 트리다. 최소 힙의 루트는 힙 내의 최소값을 가진다.
힙은 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 데 사용되며, 우선순위 큐는 여러 곳에서 사용된다. 예를 들어, CPU 스케줄링, 그래프 알고리즘(다익스트라 알고리즘, 프림 알고리즘 등), 데이터 압축 알고리즘 등에서 사용된다.
배열에 데이터를 넣고, 최댓값과 최솟값을 찾으려면 O(n)이 걸리지만, 힙의 삽입 및 삭제 연산은 대략적으로 O()의 시간 복잡도를 가진다. 이는 모든 레벨에서 요소를 삽입하거나 제거하는 경우를 기준으로 한다. 이러한 특성 때문에 힙은 효율적인 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 데 매우 유용하다.
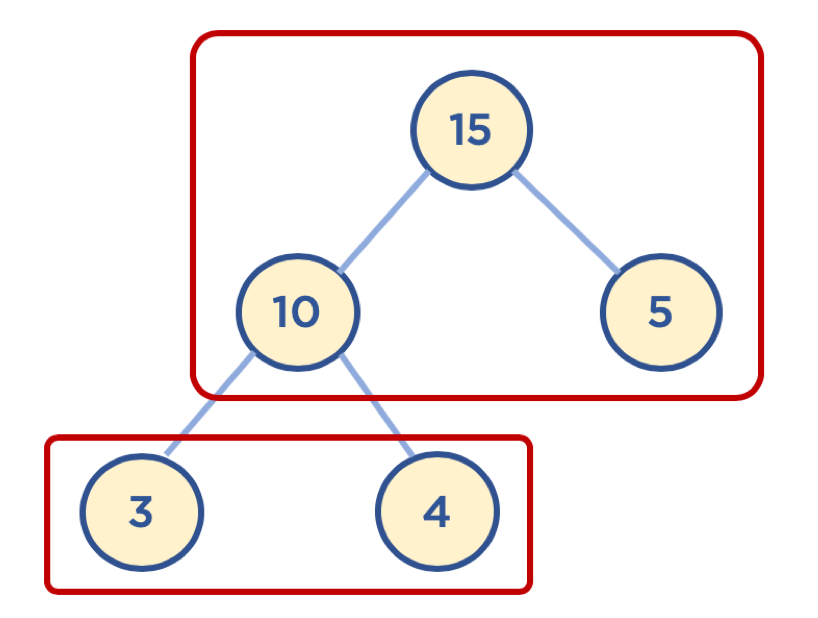
힙 (Heap) 구조
- 힙은 최대값을 구하기 위한 구조 (최대 힙, Max Heap) 와, 최소값을 구하기 위한 구조 (최소 힙, Min Heap) 로 분류할 수 있음
- 힙은 다음과 같이 두 가지 조건을 가지고 있는 자료구조임
- 각 노드의 값은 해당 노드의 자식 노드가 가진 값보다 크거나 같다. (최대 힙의 경우)
- 최소 힙의 경우는 각 노드의 값은 해당 노드의 자식 노드가 가진 값보다 크거나 작음
- 완전 이진 트리 형태를 가짐
- 각 노드의 값은 해당 노드의 자식 노드가 가진 값보다 크거나 같다. (최대 힙의 경우)
- 힙의 구현 : 힙은 일반적으로 배열로 구현한다. 이진 트리의 특성을 이용하면, 배열을 사용하여 힙의 노드를 쉽게 찾을 수 있다. 루트 노드가 배열의 인덱스 0에 위치한다면, 각 인덱스에 대해 인덱스 i의 왼쪽 자식 노드는 2i + 1에, 오른쪽 자식 노드는 2i + 2에 위치하고, 부모 노드는 (i - 1) / 2 (정수 나누기)에 위치한다.
- 힙의 용도 : 힙은 우선순위 큐와 같은 추상적인 데이터 유형을 구현하는 데 사용될 수 있다. 이외에도 힙은 그래프 알고리즘에서 최소 비용을 찾는 데 사용되며(다익스트라 알고리즘 등), 'K번째 최소/최대 원소 찾기' 같은 문제를 효율적으로 해결하는 데에도 사용될 수 있다.
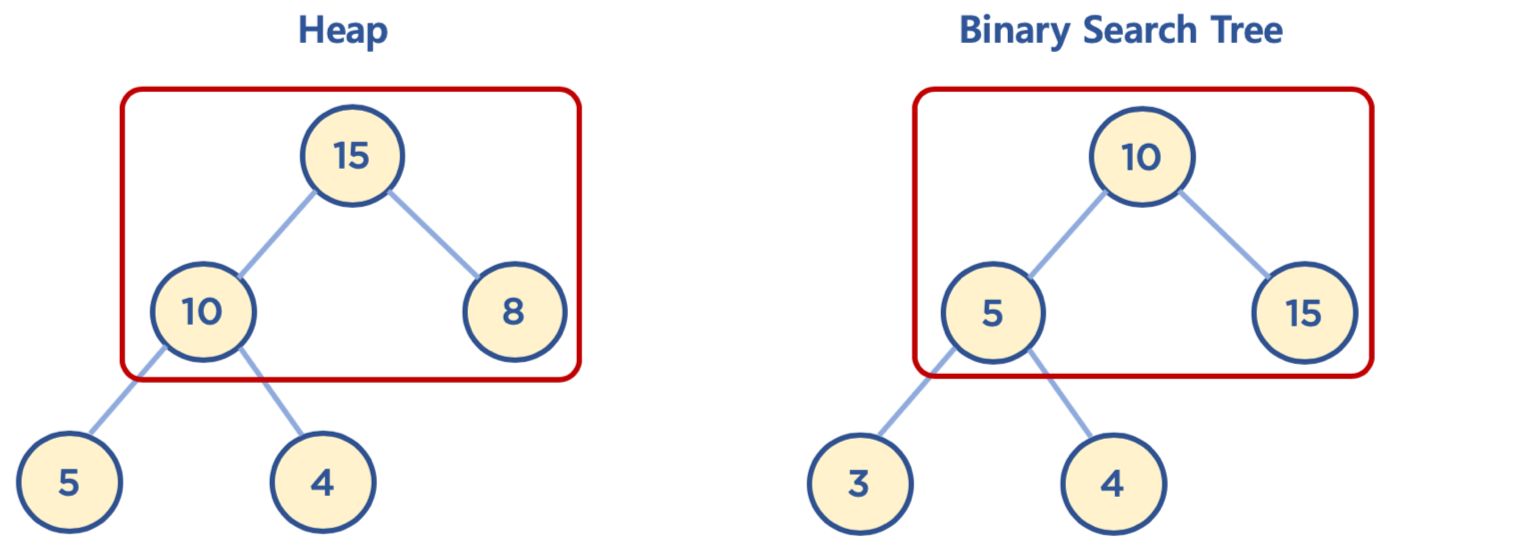
힙과 이진 탐색 트리의 공통점과 차이점
- 공통점: 힙과 이진 탐색 트리는 모두 이진 트리임
- 차이점:
- 힙은 각 노드의 값이 자식 노드보다 크거나 같음(Max Heap의 경우)
- 이진 탐색 트리는 왼쪽 자식 노드의 값이 가장 작고, 그 다음 부모 노드, 그 다음 오른쪽 자식 노드 값이 가장 큼
- 힙은 이진 탐색 트리의 조건인 자식 노드에서 작은 값은 왼쪽, 큰 값은 오른쪽이라는 조건은 없음
- 힙의 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 자식 노드의 값은 오른쪽이 클 수도 있고, 왼쪽이 클 수도 있음
- 이진 탐색 트리는 탐색을 위한 구조, 힙은 최대/최소값 검색을 위한 구조 중 하나로 이해하면 됨
힙과 이진 탐색 트리의 차이점 : 힙과 이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree, BST)는 모두 트리 기반의 자료구조다. 하지만, 차이점이 있는데, BST에서는 노드의 왼쪽 하위 트리에는 노드의 값보다 작은 값들이 오고, 오른쪽 하위 트리에는 노드의 값보다 큰 값들이 위치하는 반면, 힙은 노드의 값이 자식 노드들의 값보다 크거나 같은(최대 힙의 경우) 또는 작거나 같은(최소 힙의 경우) 구조를 가지고 있다.
3. 힙 (Heap) 동작
데이터가 어떻게 힙에 삽입되고 삭제되는지 알아본다.
삽입 작업과 삭제 작업을 설명하면 다음과 같다.
- 삽입 작업:
- 이진 힙에 요소를 삽입하면, 그 요소는 일단 트리의 마지막 위치에 추가된다. 그런 다음, 새 요소는 그 부모와 비교되어 힙 속성을 만족하도록 적절한 위치로 "거품이 올라가" (또는 "위로 이동") 합니다. 이 과정을 "업힙" (up-heap) 또는 "버블업" (bubble-up)이라고도 부른다.
- 삭제 작업:
- 힙에서 요소를 제거할 때는, 일반적으로 루트 요소를 제거한다. 그런 다음 힙의 마지막 요소가 루트로 이동하고, 이 요소는 자식 노드와 비교되며 힙 속성을 만족하도록 적절한 위치로 "아래로 내려갑니다". 이 과정을 "다운힙" (down-heap) 또는 "버블다운" (bubble-down)이라고도 부른다.
이러한 과정에서 힙은 두 가지 주요 속성, 즉 "완전 이진 트리"의 형태를 유지하고 "부모가 자식보다 크거나 작다"는 (최대 힙 또는 최소 힙에 따라 다름) 힙 속성을 유지한다.
힙은 이러한 동작을 통해 효과적으로 최대값 (또는 최소값)을 추적하며, 이를 통해 우선순위 큐와 같은 고급 데이터 구조를 구현하는 데 사용될 수 있다.
- 데이터를 힙 구조에 삽입, 삭제하는 과정을 그림을 통해 선명하게 이해해보자.
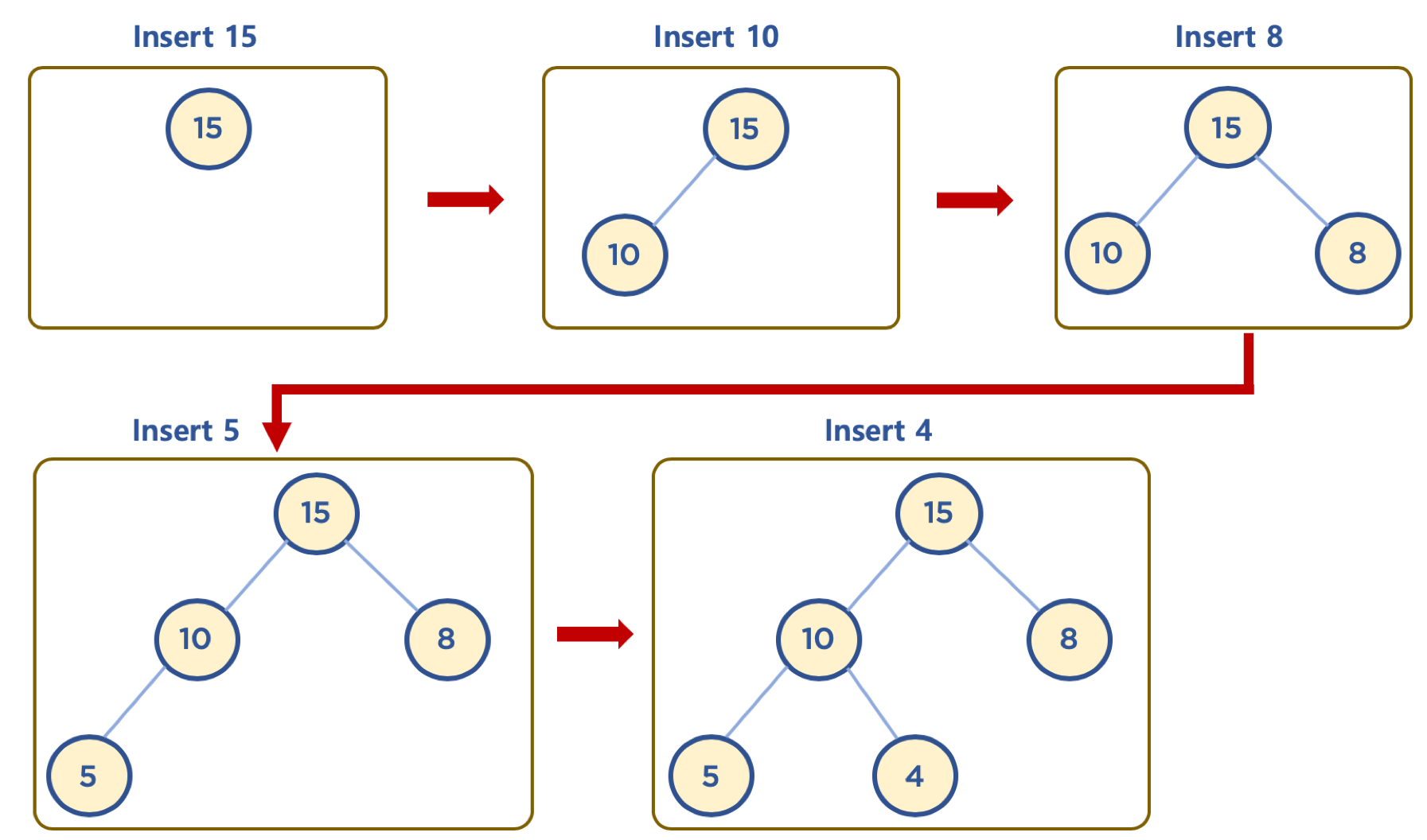
힙에 데이터 삽입하기 - 기본 동작
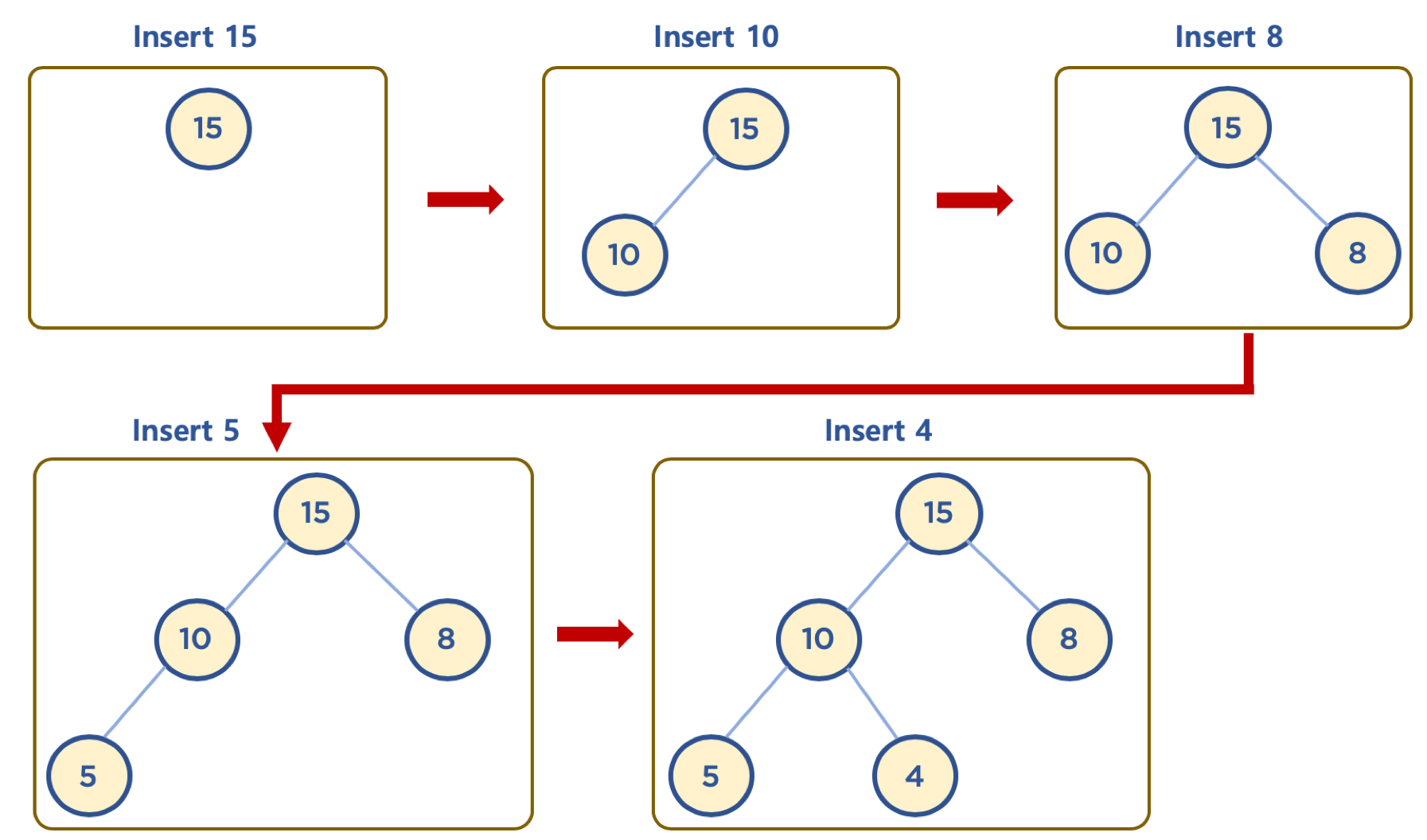
- 힙은 완전 이진 트리이므로, 삽입할 노드는 기본적으로 왼쪽 최하단부 노드부터 채워지는 형태로 삽입한다.
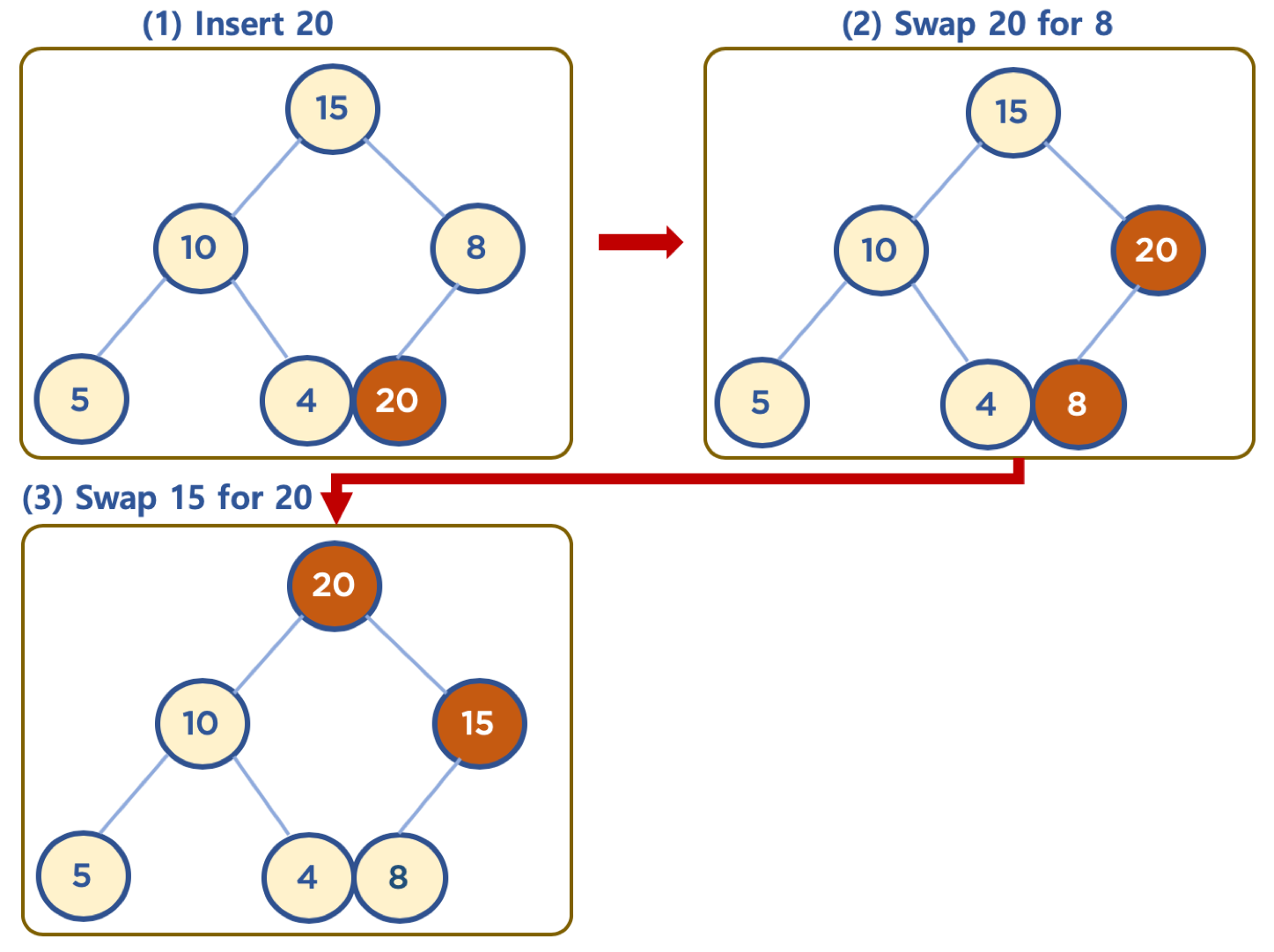
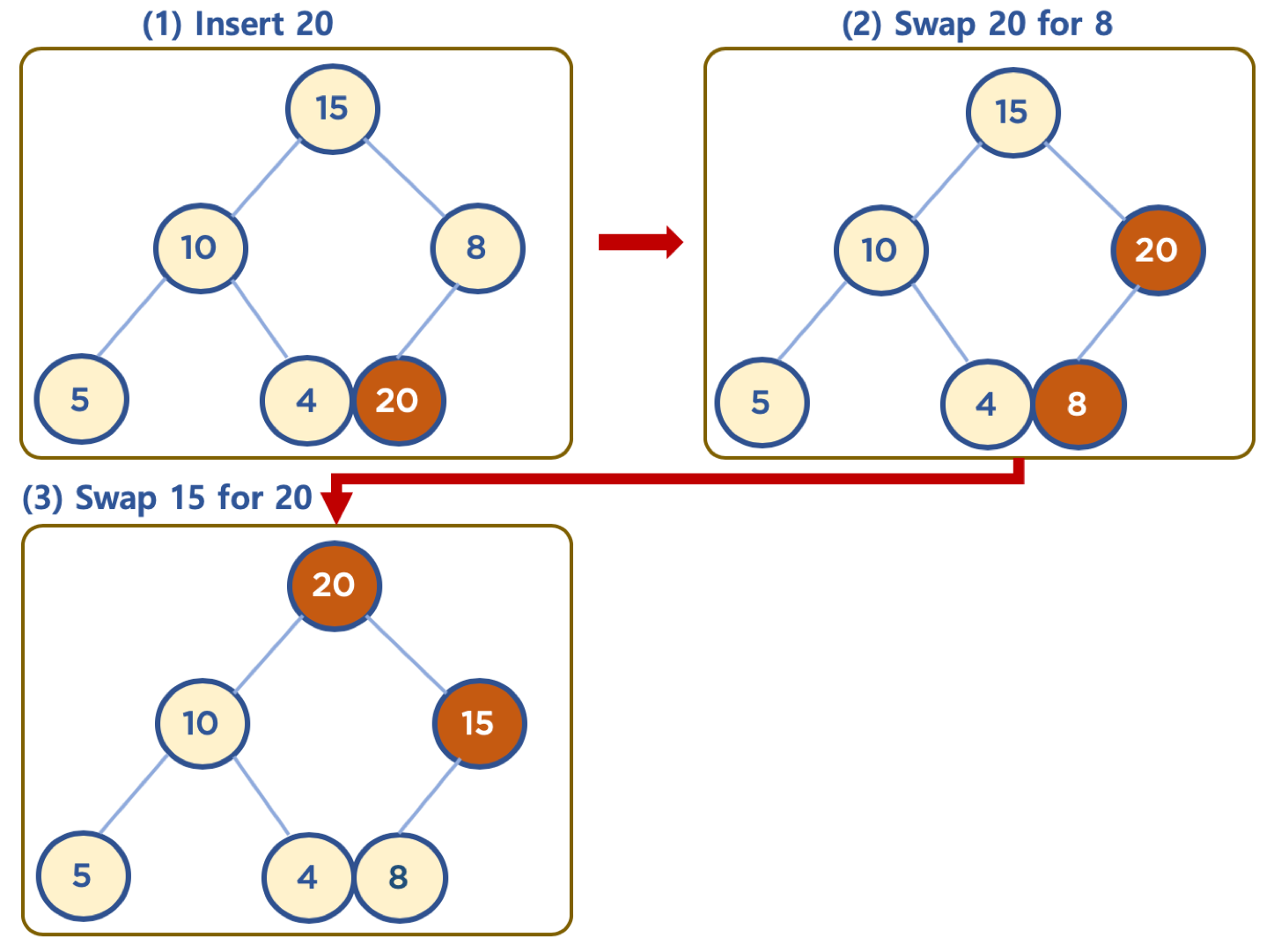
힙에 데이터 삽입하기 - 삽입할 데이터가 힙의 데이터보다 클 경우 (Max Heap 의 예)
- 먼저 삽입된 데이터는 완전 이진 트리 구조에 맞추어, 최하단부 왼쪽 노드부터 채워진다.
- 채워진 노드 위치에서, 부모 노드보다 값이 클 경우, 부모 노드와 위치를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복한다. (swap)
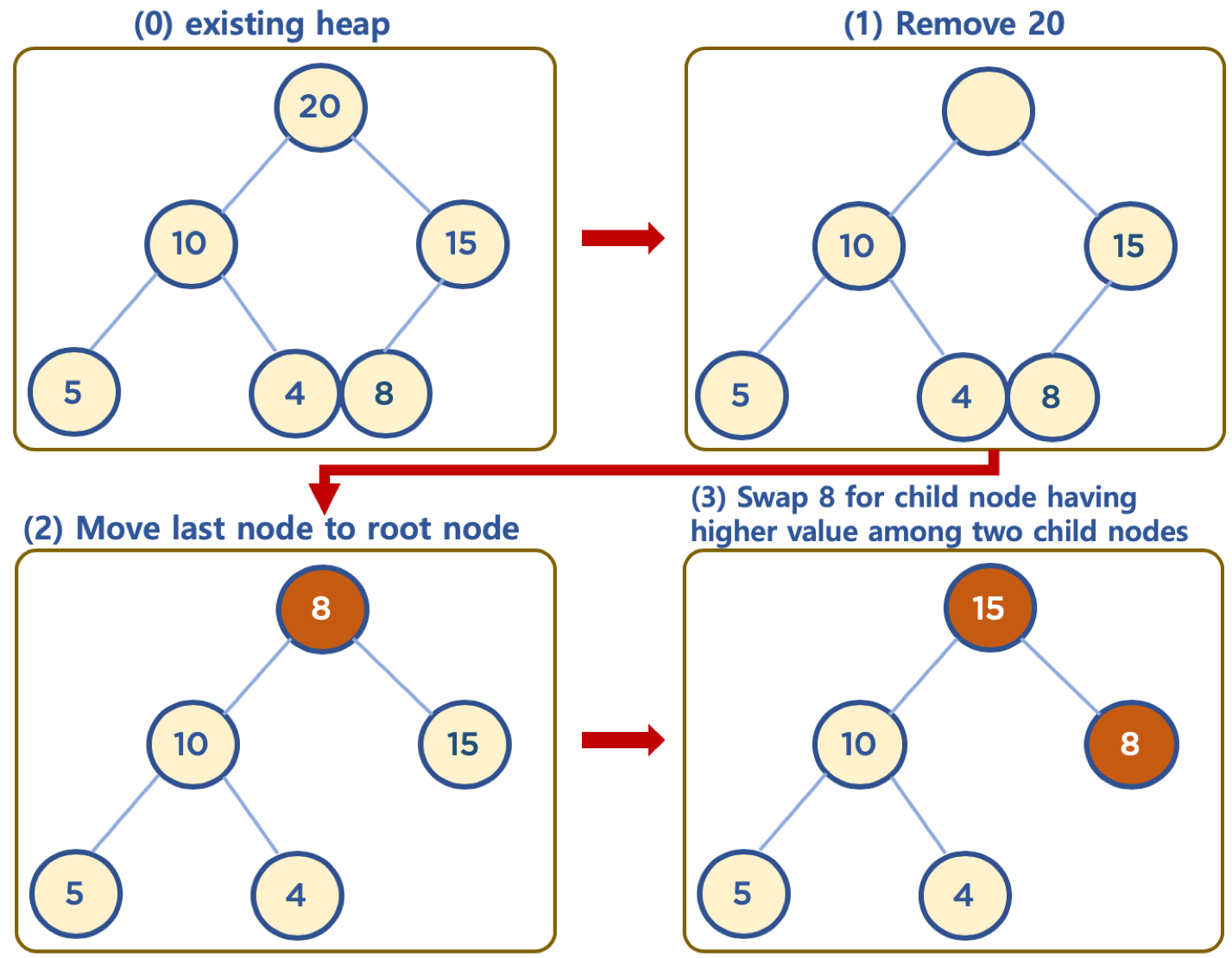
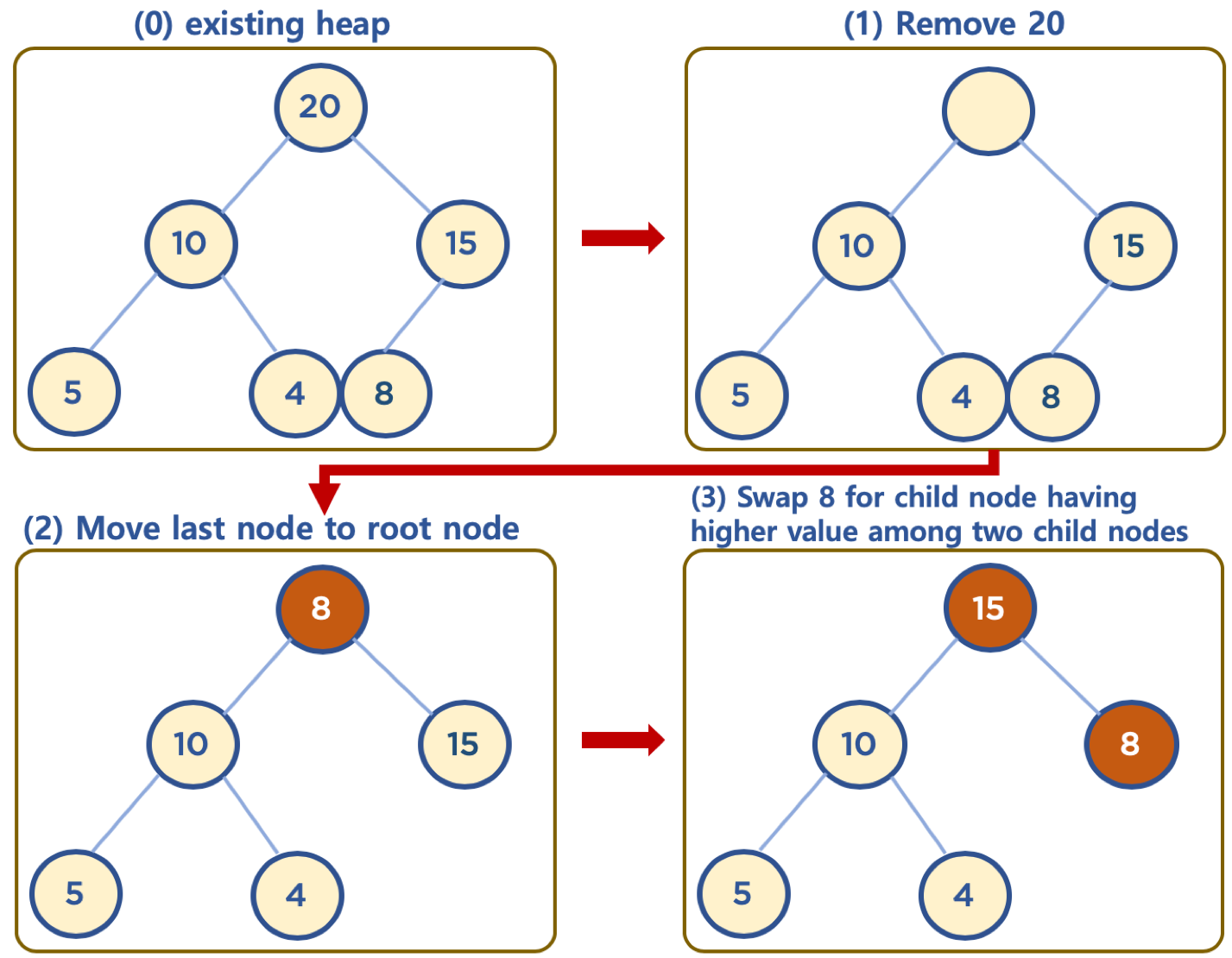
힙의 데이터 삭제하기 (Max Heap 의 예)
- 보통 삭제는 최상단 노드 (root 노드)를 삭제하는 것이 일반적임
- 힙의 용도는 최대값 또는 최소값을 root 노드에 놓아서, 최대값과 최소값을 바로 꺼내 쓸 수 있도록 하는 것임
- 상단의 데이터 삭제시, 가장 최하단부 왼쪽에 위치한 노드 (일반적으로 가장 마지막에 추가한 노드) 를 root 노드로 이동
- root 노드의 값이 child node 보다 작을 경우, root 노드의 child node 중 가장 큰 값을 가진 노드와 root 노드 위치를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복함 (swap)
힙 구현
힙과 배열
- 일반적으로 힙 구현시 배열 자료구조를 활용한다.
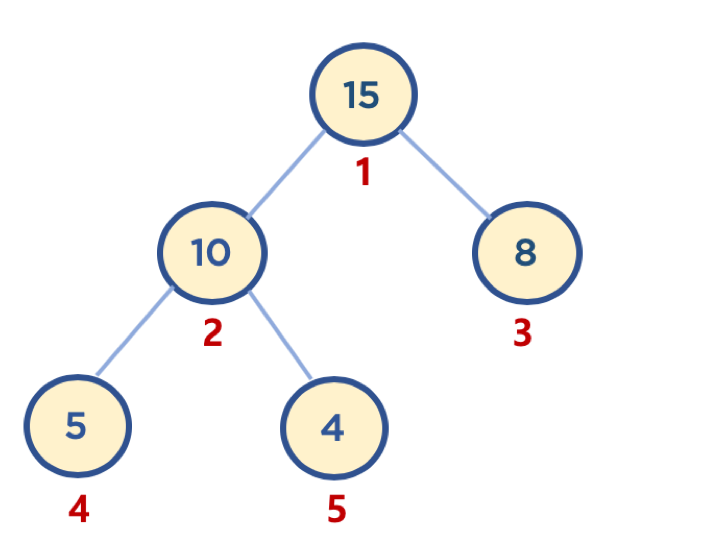
- 배열은 인덱스가 0번부터 시작하지만, 힙 구현의 편의를 위해, root 노드 인덱스 번호를 1로 지정하면, 구현이 좀더 수월하다.
- 즉, 배열 기반의 힙에서 첫번째 요소 (인덱스 0)는 보통 무시하고, 루트 노드는 인덱스 1에 위치시키는 것이 일반적이다. 이렇게 하면 부모 노드와 자식 노드 사이의 관계를 쉽게 찾을 수 있다.
- 힙의 노드 간 관계는 다음과 같다.
- 부모 노드의 인덱스가 i일 때,
- 왼쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스는 2 * i이다.
- 오른쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스는 2 * i + 1이다.
- 반대로 자식 노드의 인덱스가 j일 때,
- 그 노드의 부모 노드의 인덱스는 j // 2이다.
- 부모 노드의 인덱스가 i일 때,
힙에 데이터 삽입 구현 (Max Heap 예)
힙 클래스 구현1
class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)heap = Heap(1)
heap.heap_array # [None, 1]이 코드는 Heap이라는 클래스를 구현하는 부분이다. Heap 클래스는 힙을 구현하기 위한 기본적인 구조를 가지고 있다.
__init__ 메서드는 Heap 클래스의 인스턴스를 초기화하는 역할을 한다. data라는 매개변수를 받아, 이를 힙에 첫 번째 데이터로 추가한다.
self.heap_array는 힙의 모든 요소를 저장하는 배열이다. 배열의 첫 번째 요소는 None으로 설정하여, 인덱스 1부터 실제 데이터가 저장되도록 한다. 이렇게 하는 이유는 배열 기반의 힙에서 첫 번째 요소(인덱스 0)는 무시하고 루트 노드는 인덱스 1에 위치시키는 것이 일반적이기 때문이다.
self.heap_array.append(data) 라인은 인스턴스를 초기화할 때 주어진 데이터를 heap_array에 추가한다. 이로써 첫 번째 데이터가 힙에 저장된다.
마지막에 보여주는 heap = Heap(1)과 heap.heap_array는 Heap 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하고, 그 인스턴스의 heap_array를 출력하는 예시다. 이 경우, heap_array는 [None, 1]이 출력된다.
힙 클래스 구현2 - insert1
인덱스 번호는 1번부터 시작하도록 변경
class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
def insert(self, data):
if len(self.heap_array) == 0:
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
return True
self.heap_array.append(data)
return True 이 코드는 Heap 클래스에 새로운 데이터를 삽입하는 insert 메소드를 추가한 것이다.
- insert 메서드는 새로운 데이터를 힙의 마지막 위치에 삽입하는 기본적인 동작을 수행한다.
- 먼저 if len(self.heap_array) == 0: 조건문을 통해 힙 배열의 길이가 0인 경우, 즉 힙이 비어있는 경우를 처리한다. 이 때는 배열에 None을 추가하고, 그 다음에 입력받은 data를 추가합니다. 삽입이 성공하면 True를 반환한다.
- 위의 조건문에 해당하지 않는 경우, 즉 힙이 이미 데이터를 가지고 있는 경우에는 self.heap_array.append(data)를 통해 새로운 데이터를 힙의 마지막에 추가한다. 이후에도 True를 반환한다.
이러한 방식으로 새로운 데이터를 힙에 삽입하는 기본적인 기능을 구현했다. 이 코드는 아직 힙의 속성(최대 힙의 경우 부모 노드는 자식 노드보다 크거나 같다는 속성 등)을 유지하는 로직은 없다. 즉, 단순히 데이터를 배열에 추가하는 동작만을 수행하고 있다. 힙의 속성을 유지하려면 추가적인 로직이 필요하다.
힙 클래스 구현3 - insert2
- 삽입한 노드가 부모 노드의 값보다 클 경우, 부모 노드와 삽입한 노드 위치를 바꿈
- 삽입한 노드가 루트 노드가 되거나, 부모 노드보다 값이 작거나 같을 경우까지 반복
특정 노드의 관련 노드 위치 알아내기
- 부모 노드 인덱스 번호 (parent node's index) = 자식 노드 인덱스 번호 (child node's index) // 2
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 번호 (left child node's index) = 부모 노드 인덱스 번호 (parent node's index) * 2
- 오른쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 번호 (right child node's index) = 부모 노드 인덱스 번호 (parent node's index) * 2 + 1
heap = Heap(15)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(8)
heap.insert(5)
heap.insert(4)
heap.insert(20)
heap.heap_array # [None, 20, 10, 15, 5, 4, 8]class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
def move_up(self, inserted_idx):
if inserted_idx <= 1:
return False
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
if self.heap_array[inserted_idx] > self.heap_array[parent_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def insert(self, data):
if len(self.heap_array) == 0:
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
return True
self.heap_array.append(data)
inserted_idx = len(self.heap_array) - 1
while self.move_up(inserted_idx):
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
self.heap_array[inserted_idx], self.heap_array[parent_idx] = self.heap_array[parent_idx], self.heap_array[inserted_idx]
inserted_idx = parent_idx
return True이 코드는 최대 힙의 속성을 유지하도록 새로운 데이터를 힙에 삽입하는 로직을 추가한 것이다.
- move_up 메서드는 새로 삽입된 노드를 부모 노드와 비교하여, 만약 새로 삽입된 노드의 값이 부모 노드의 값보다 큰 경우 위치를 바꿔야 하는지를 결정한다. 만약 삽입된 노드의 인덱스가 1 이하인 경우 (즉, 삽입된 노드가 루트 노드인 경우) False를 반환하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 부모 노드와 삽입된 노드의 값을 비교하여 삽입된 노드의 값이 더 큰 경우 True, 그렇지 않은 경우 False를 반환한다.
- insert 메서드는 새로운 데이터를 힙에 삽입하는 역할을 한다. 기본적인 삽입 동작은 이전과 동일하며, 새로운 데이터를 힙의 마지막에 추가하는 방식으로 이루어진다.
- 새로운 데이터를 힙에 추가한 후, move_up 메서드를 통해 삽입된 노드와 부모 노드의 값들을 비교하며, 필요한 경우 위치를 교환한다. 이 과정은 삽입된 노드가 루트 노드가 되거나 (즉, 삽입된 노드의 인덱스가 1이 되거나), 삽입된 노드의 값이 부모 노드의 값보다 작거나 같을 때까지 반복된다.
이렇게 함으로써 새로운 데이터를 힙에 삽입하면서도 힙의 속성 (즉, 모든 노드는 자식 노드들보다 크거나 같다는 속성)을 유지하도록 보장한다.
힙에 데이터 삭제 구현 (Max Heap 예)
힙 클래스 구현4 - delete1
- 보통 삭제는 최상단 노드 (root 노드)를 삭제하는 것이 일반적임
- 힙의 용도는 최대값 또는 최소값을 root 노드에 놓아서, 최대값과 최소값을 바로 꺼내 쓸 수 있도록 하는 것임
class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
def pop(self):
if len(self.heap_array) <= 1:
return None
returned_data = self.heap_array[1]
return returned_data이 코드는 힙에서 가장 큰 값을 반환하는 기본적인 동작을 구현한 것이다. 힙의 구조 상 가장 큰 값은 루트 노드에 위치하므로, pop 메서드를 호출하면 루트 노드의 값을 반환한다.
그러나 현재 코드는 데이터를 삭제하는 동작은 포함하지 않았으며, 오직 루트 노드의 값을 반환만 한다. 그리고 힙 배열의 길이가 1 이하일 경우, 즉 힙에 데이터가 없을 경우에는 None을 반환한다.
힙에서 데이터를 제대로 삭제하려면 루트 노드를 삭제한 뒤에 힙의 속성을 유지하도록 다시 조정하는 작업이 필요하다. 이 작업은 일반적으로 마지막 노드를 루트 노드로 이동시킨 뒤, 루트 노드에서부터 아래로 내려가며 자식 노드들과 비교하여 필요한 경우 위치를 교환하는 방식으로 이루어진다. 이러한 동작은 아직 구현되지 않았다.
힙 클래스 구현4 - delete2
- 상단의 데이터 삭제시, 가장 최하단부 왼쪽에 위치한 노드 (일반적으로 가장 마지막에 추가한 노드) 를 root 노드로 이동
- root 노드의 값이 child node 보다 작을 경우, root 노드의 child node 중 가장 큰 값을 가진 노드와 root 노드 위치를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복함 (swap)
특정 노드의 관련 노드 위치 알아내기
- 부모 노드 인덱스 번호 (parent node's index) = 자식 노드 인덱스 번호 (child node's index) // 2
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 번호 (left child node's index) = 부모 노드 인덱스 번호 (parent node's index) * 2
- 오른쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 번호 (right child node's index) = 부모 노드 인덱스 번호 (parent node's index) * 2 + 1
heap = Heap(15)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(8)
heap.insert(5)
heap.insert(4)
heap.insert(20)
heap.heap_array # [None, 20, 10, 15, 5, 4, 8]heap.pop() # 20heap.heap_array # [None, 15, 10, 8, 5, 4]class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
def move_down(self, popped_idx):
left_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2
right_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2 + 1
# case1: 왼쪽 자식 노드도 없을 때
if left_child_popped_idx >= len(self.heap_array):
return False
# case2: 오른쪽 자식 노드만 없을 때
elif right_child_popped_idx >= len(self.heap_array):
if self.heap_array[popped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
# case3: 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식 노드 모두 있을 때
else:
if self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx] > self.heap_array[right_child_popped_idx]:
if self.heap_array[popped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
else:
if self.heap_array[popped_idx] < self.heap_array[right_child_popped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def pop(self):
if len(self.heap_array) <= 1:
return None
returned_data = self.heap_array[1]
self.heap_array[1] = self.heap_array[-1]
del self.heap_array[-1]
popped_idx = 1
while self.move_down(popped_idx):
left_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2
right_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2 + 1
# case2: 오른쪽 자식 노드만 없을 때
if right_child_popped_idx >= len(self.heap_array):
if self.heap_array[popped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx]:
self.heap_array[popped_idx], self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx] = self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx], self.heap_array[popped_idx]
popped_idx = left_child_popped_idx
# case3: 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식 노드 모두 있을 때
else:
if self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx] > self.heap_array[right_child_popped_idx]:
if self.heap_array[popped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx]:
self.heap_array[popped_idx], self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx] = self.heap_array[left_child_popped_idx], self.heap_array[popped_idx]
popped_idx = left_child_popped_idx
else:
if self.heap_array[popped_idx] < self.heap_array[right_child_popped_idx]:
self.heap_array[popped_idx], self.heap_array[right_child_popped_idx] = self.heap_array[right_child_popped_idx], self.heap_array[popped_idx]
popped_idx = right_child_popped_idx
return returned_data
def move_up(self, inserted_idx):
if inserted_idx <= 1:
return False
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
if self.heap_array[inserted_idx] > self.heap_array[parent_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def insert(self, data):
if len(self.heap_array) == 1:
self.heap_array.append(data)
return True
self.heap_array.append(data)
inserted_idx = len(self.heap_array) - 1
while self.move_up(inserted_idx):
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
self.heap_array[inserted_idx], self.heap_array[parent_idx] = self.heap_array[parent_idx], self.heap_array[inserted_idx]
inserted_idx = parent_idx
return True이 코드는 힙 자료구조에서 데이터를 삭제하는 로직을 구현한 것이다. 데이터 삭제는 일반적으로 루트 노드(가장 큰 값 혹은 가장 작은 값)를 삭제하는 것이며, 삭제 후에는 힙의 속성이 유지되도록 재정렬이 이루어져야 한다.
구체적으로 pop 메서드를 보면, 먼저 가장 마지막에 추가한 노드(배열의 마지막 요소)를 루트 노드로 이동시키고, 원래의 루트 노드(배열의 첫 번째 요소)는 삭제합니다. 그런 다음, 루트 노드부터 아래로 내려가면서 루트 노드가 자식 노드보다 작을 경우, 두 노드의 위치를 바꿉니다. 이를 move_down 메서드를 통해 수행한다.
move_down 메서드는 삭제된 노드의 인덱스를 매개변수로 받아, 해당 노드의 왼쪽 자식 노드와 오른쪽 자식 노드의 인덱스를 구합니다. 그런 다음, 세 가지 경우를 검사한다.
- 왼쪽 자식 노드도 없을 때: 이 경우는 현재 노드가 리프 노드(자식이 없는 노드)라는 의미이므로, 더 이상 내려가지 않아도 된다. 따라서 False를 반환한다.
- 오른쪽 자식 노드만 없을 때: 이 경우는 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있으므로, 현재 노드와 왼쪽 자식 노드의 값을 비교하여 왼쪽 자식 노드가 더 크면 True를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 False를 반환한다.
- 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식 노드 모두 있을 때: 이 경우는 두 자식 노드 중에서 더 큰 노드와 현재 노드의 값을 비교하여, 자식 노드가 더 크면 True를 반환하고, 그렇지 않으면 False를 반환한다.
이렇게 move_down 메서드를 통해 루트 노드부터 아래로 내려가면서 힙의 속성이 유지되도록 노드를 교환한다. 이 과정을 통해 삭제 작업이 완료되고, 삭제된 노드의 값을 반환한다.
마지막으로, insert 메서드는 데이터를 힙에 삽입하는 로직을 구현한 것으로, 새 데이터를 배열의 마지막에 추가하고 move_up 메서드를 통해 힙의 속성이 유지되도록 노드를 교환한다. 이 과정을 통해 삽입 작업이 완료된다.
힙 (Heap) 시간 복잡도
- depth (트리의 높이) 를 h라고 표기한다면,
- n개의 노드를 가지는 heap 에 데이터 삽입 또는 삭제시, 최악의 경우 root 노드에서 leaf 노드까지 비교해야 하므로 에 가까우므로, 시간 복잡도는
- 참고: 빅오 표기법에서 에서의 log의 밑은 10이 아니라, 2입니다.
- 한번 실행시마다, 50%의 실행할 수도 있는 명령을 제거한다는 의미. 즉 50%의 실행시간을 단축시킬 수 있다는 것을 의미함
