콜백(Callback) 함수란?
매개변수로 함수 객체를 전달하여, 호출 함수 내에서 매개변수로 쓰인 함수를 실행하는 것을 말한다.
콜백 함수(callback function) 는 다른 함수의 인자로 전달되어, 특정 작업이 완료되거나 특정 이벤트가 발생했을 때 호출되는 함수이다. 콜백 함수는 비동기 작업을 처리하거나, 코드의 흐름을 제어하는 데 주로 사용된다. 자바스크립트에서 콜백 함수는 특히 중요하며, 비동기 프로그래밍을 이해하는 데 필수적이다.
일반적으로, 함수는 파라미터로 값을 전달받지만, 콜백 함수는 함수 자체를 전달하는 것이다. 또한, 어차피 매개변수에 함수를 전달해 일회용으로 사용하기 때문에, 굳이 함수의 이름을 명시할 필요가 없어, 보통 콜백 함수 형태로 함수를 넘겨줄 대 함수의 이름이 없는 '익명 함수'형태로 넣어준다.
// 1초 후에 메시지를 출력하는 함수
function delayedGreeting(name, callback) {
setTimeout(function() {
const greeting = 'Hello, ' + name + '!';
callback(greeting);
}, 1000);
}
// 익명 함수를 콜백으로 전달
delayedGreeting('Alice', function(message) {
console.log(message);
});
// Hello, Alice!위 코드에서, 익명함수는 console.log(message)가 된다.
콜백함수의 특징
- 함수의 인자로 전달됨
- 콜백 함수는 다른 함수의 인자로 전달된다.
- 호출된 함수 내에서 콜백 함수가 호출된다.
- 지정된 시점에 호출됨
- 콜백 함수는 특정 작업이 완료되거나 특정 조건이 만족되었을 때 호출된다.
- 비동기 작업 처리
- 콜백 함수는 비동기 작업을 처리하는 데 자주 사용된다. 예를 들어, 파일 읽기, 네트워크 요청, 타이머 등에서 사용된다.
콜백함수 예제
1. 기본 예제
function greet(name, callback) {
console.log('Hello, ' + name + '!');
callback();
}
function sayGoodbye() {
console.log('Goodbye!');
}
greet('Alice', sayGoodbye);
// Hello, Alice!
// Goodbye!위 예제에서 greet 함수는 name과 callback을 인자로 받는다. sayGoodbye 함수는 callback으로 전달되고, greet 함수 내에서 호출된다.
2. 비동기 예제
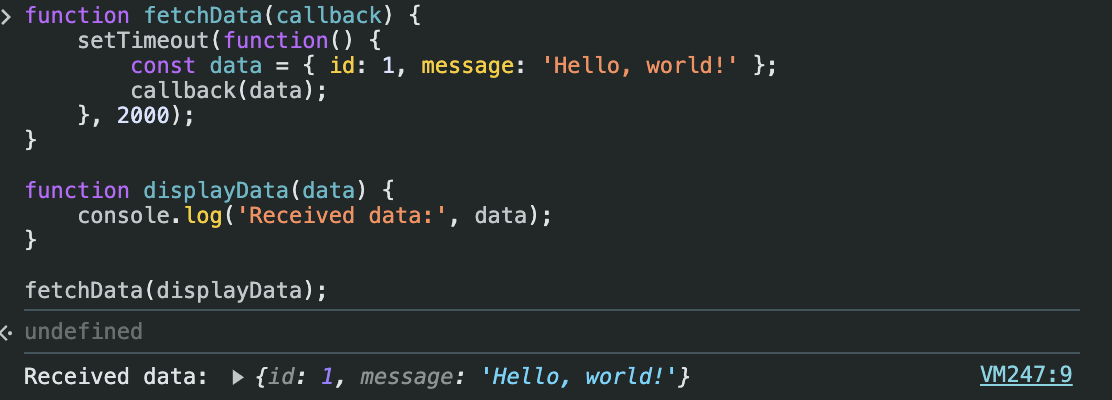
function fetchData(callback) {
setTimeout(function() {
const data = { id: 1, message: 'Hello, world!' };
callback(data);
}, 2000);
}
function displayData(data) {
console.log('Received data:', data);
}
fetchData(displayData);이 예제에서는 fetchData 함수가 비동기 작업을 시뮬레이션하기 위해 setTimeout을 사용했다. 2초 후에 callback 함수가 호출되며, data 객체가 전달됩니다. 출력 결과는 다음과 같다.
3. 익명 함수 사용
보통 콜백 함수는 호출 함수에 일회용으로 사용되는 경우가 많아, 코드의 간결성을 위해 이름이 없는 '익명의 함수'를 사용한다. 함수의 내부에서 매개변수를 통해 실행되기 때문에 이름을 붙이지 않아도 되기 때문이다.
function sayHello(name, callback) {
const words = 'Hello, My name is ' + name + '.';
callback(words); //
}
sayHello("Alice", function (message) {
console.log(message);
});위 예제에서 sayHello 함수는 name과 callback을 인자로 받는다. 익명 함수가 콜백으로 전달되어 words를 인자로 받아 출력한다. callback(words)에 의하여, console.log(message)에 words가 전달된다.
익명 함수는, 함수 이름을 정의하지 않음으로서 다른 변수명이나 함수명과의 이름 충돌을 피하게 해준다.
4. 화살표 함수 사용
콜백 함수를 익명 함수로 정의함으로써 코드의 간결성을 얻었지만, 더 간결하게 만들기 위해 화살표 함수를 사용하여 '익명 화살표 함수'형태로 사용할 수 있다.
// 1초 후에 메시지를 출력하는 함수
function delayedGreeting(name, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
const greeting = 'Hello, ' + name + '!';
callback(greeting);
}, 1000);
}
// 화살표 함수를 콜백으로 전달
delayedGreeting('Alice', (message) => {
console.log(message);
});5. 함수의 이름 넘기기
자바스크립트는 일급 객체의 특성을 갖고 있기 때문에, 자바스크립트는 null과 undefined타입을 제외하고 모든 것응 객체로 다룬다. 그래서 매개변수에 일반적인 변수나 상수값 뿐만 아니라, 함수 자체를 객체로서 전달이 가능하다.
그러므고, 콜백 함수가 일회용이 아닌 여러 호출 함수에 재활용으로 자주 이용될 경우, 별도로 함수를 정의하고 함수의 이름만 호출 함수의 인자에 저달하는 식으로 사용이 가능하다.
// 콜백 함수를 별도의 함수로 정의
function greet(name) {
console.log("Hello, " + name);
}
function sayHello(callback) {
var name = "Alice";
callback(name); // 콜백 함수 호출
}
function sayHello2(callback) {
var name = "Inpa";
callback(name); // 콜백 함수 호출
}
// 콜백 함수의 이름만 인자로 전달
sayHello(greet); // Hello, Alice
sayHello2(greet); // Hello, Inpa6. 이벤트 리스너
콜백 함수로서 많이 활용하는 곳은, 이벤트 리스너로 사용하는 것이다.
addEventListener는 특정 이벤트가 발생했을 때, 콜백 함수를 실행하는 메서드이다.
// 버튼 요소를 선택합니다.
const button = document.getElementById('myButton');
// 클릭 이벤트 리스너를 버튼에 추가합니다.
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('Button was clicked!');
});콜백 함수의 장점
- 비동기 코드 작성 가능
- 콜백 함수를 사용하면, 비동기 작업을 처리하는 코드 작성이 가능해진다.
- 예를 들어, 네트워크 요청이 완료된 후에 실행될 코드를 작성할 수 있다. (비동기 처리)
- 코드의 재사용성 증가
- 콜백 함수를 사용하면, 동일한 함수 내에서 다양한 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 코드를 재사용할 수 있다.
- 유연성 증가
- 함수가 수행해야 할 작업을 동적으로 정의할 수 있어 코드의 유연성이 증가한다.
콜백 함수의 단점
- 콜백 함수를 많이 사용하면 코드가 복잡해지고 가독성이 떨어질 수 있다. 이를 "콜백 헬(callback hell)"이라고 부른다.
- 여러 단계의 비동기 콜백이 중첩되면 에러 처리가 어려울 수 있다.
이러한 단점을 보완하기 위해 ES6부터는 Promise와 async/await가 도입되었다. 하지만 콜백 함수는 여전히 자주 사용되는 중요한 개념이다.
콜백 지옥 예시
function getUser(userId, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('User retrieved');
callback(null, { userId: userId, username: 'JohnDoe' });
}, 1000);
}
function getPosts(userId, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Posts retrieved');
callback(null, [{ postId: 1, content: 'Hello World' }, { postId: 2, content: 'Another post' }]);
}, 1000);
}
function getComments(postId, callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Comments retrieved');
callback(null, [{ commentId: 1, content: 'Great post!' }, { commentId: 2, content: 'Nice article' }]);
}, 1000);
}
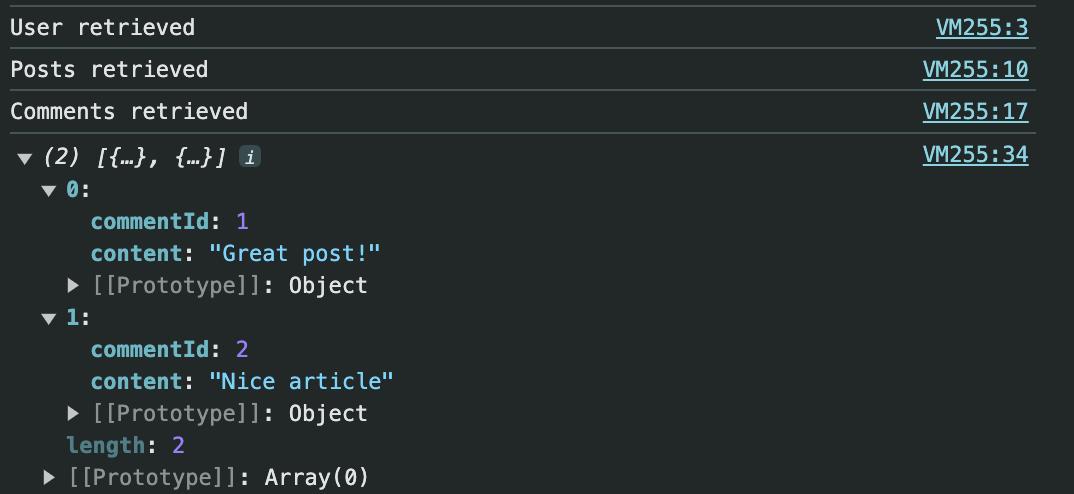
getUser(1, (err, user) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
getPosts(user.userId, (err, posts) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
getComments(posts[0].postId, (err, comments) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log(comments);
}
});
}
});
}
});출력은 아래와 같다.
콜백 지옥 개선: Promise와 async/await 사용
Promise
function getUser(userId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('User retrieved');
resolve({ userId: userId, username: 'JohnDoe' });
}, 1000);
});
}
function getPosts(userId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Posts retrieved');
resolve([{ postId: 1, content: 'Hello World' }, { postId: 2, content: 'Another post' }]);
}, 1000);
});
}
function getComments(postId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Comments retrieved');
resolve([{ commentId: 1, content: 'Great post!' }, { commentId: 2, content: 'Nice article' }]);
}, 1000);
});
}
getUser(1)
.then(user => getPosts(user.userId))
.then(posts => getComments(posts[0].postId))
.then(comments => console.log(comments))
.catch(error => console.error(error));async/await
function getUser(userId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('User retrieved');
resolve({ userId: userId, username: 'JohnDoe' });
}, 1000);
});
}
function getPosts(userId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Posts retrieved');
resolve([{ postId: 1, content: 'Hello World' }, { postId: 2, content: 'Another post' }]);
}, 1000);
});
}
function getComments(postId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Comments retrieved');
resolve([{ commentId: 1, content: 'Great post!' }, { commentId: 2, content: 'Nice article' }]);
}, 1000);
});
}
async function fetchUserData() {
try {
const user = await getUser(1);
const posts = await getPosts(user.userId);
const comments = await getComments(posts[0].postId);
console.log(comments);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
fetchUserData();