Primitive vs. Wrapper
기본형(primitive type)과 참조형(reference type)
- 기본형(primitive type) : 계산을 위한 실제 값을 저장한다.
- 논리형(booldean), 문자열(char), 정수형(byte short, int, long) 실수형(float, doyble)
- 참조형(reference type) : 객체의 주소를 저장한다.
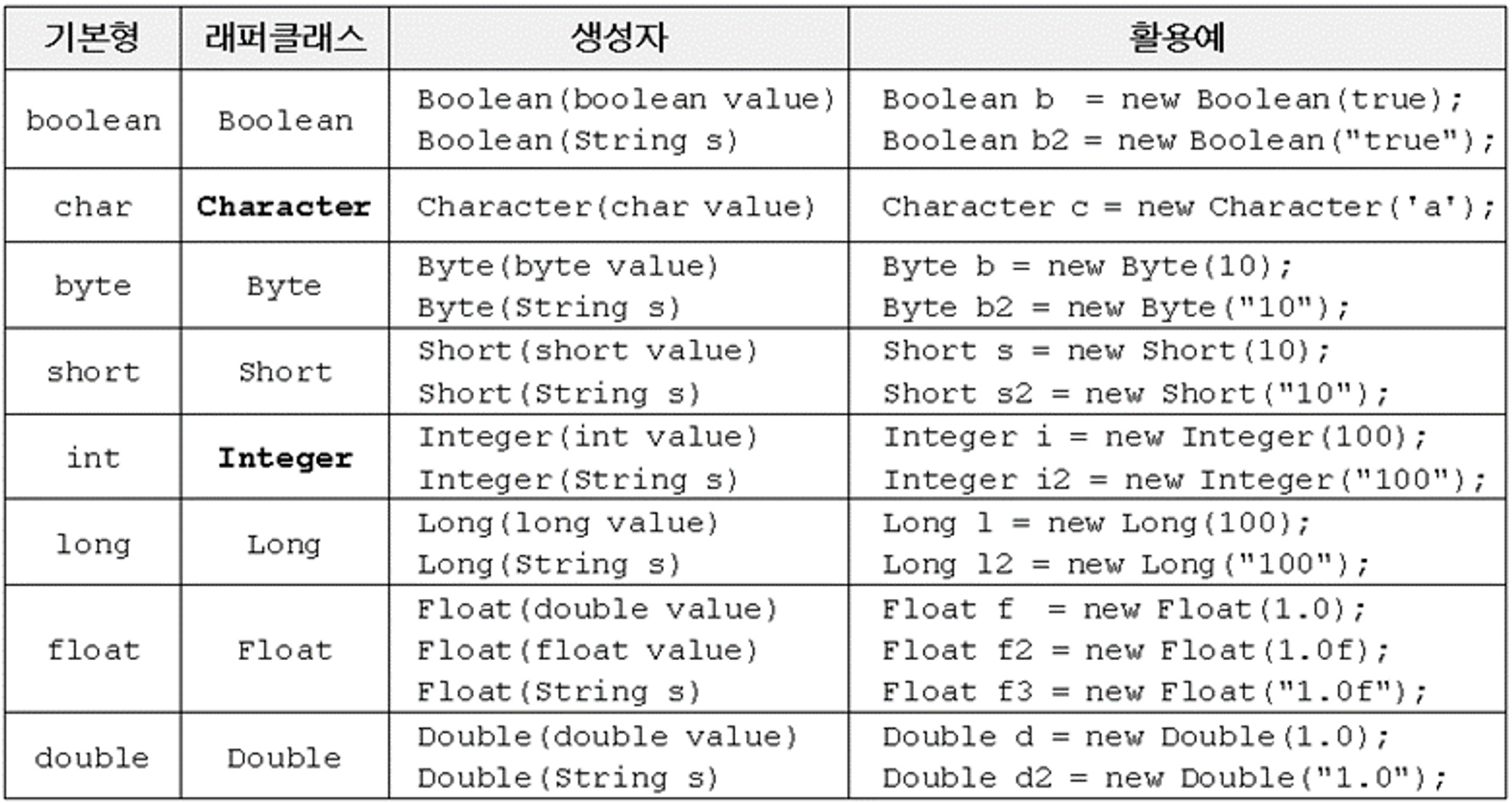
래퍼 클래스(Wrapper class)란?
- 기본형 데이터 타입(primitive type)을 객체로 변환한 클래스
- wrapper 클래스를 사용하면 기본형(primitive) 값을 객체로 다룰 수 있다.
- 객체 생성 시, 기본형 데이터 타입을 저장하는 필드가 존재한다.
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable {
...
private int value;
...
}
래퍼 클래스(Wrapper Class) 사용 이유
- 기본형 데이터 타입(primitive data type)을 객체(Object)로 변환할 수 있다.
- primitive type을 객체로 만들어 null을 넣거나 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
- java.util 패키지의 클래스는 객체만 처리하므로 래퍼 클래스가 필요하다.
- Date, Calendar 클래스
- Collection Framework 관련 인터페이스와 클래스
- Collection Framework의 데이터 구조는 기본 타입(primitivie type)이 아닌 객체만 저장한다.
- Genetics 타입에 primitive는 사용할 수 없다.
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Boxing과 UnBoxing
- 박싱(Boxing) : 기본형 데이터 타입(primitive type) -> 래퍼 클래스(wrapper class)의 인스턴스로 변환
- 언박싱(UnBoxing) : 래퍼 클래스(wrapper class) -> 기본형 타입(primitive type)으로 변환
래퍼 클래스(Wrapper Class)의 메서드
- 래퍼 클래스들은 모두
equals()가 오버라이딩되어 있다. → 주소값이 아닌 객체로 값을 비교
- 래퍼 클래스와 기본형 타입을 서로 비교할 때는
==, equals() 모두 사용 가능하다. → 오토 박싱, 언박싱
- 비교 연산자 사용 불가 →
compareTo() 사용
toString() 도 오버라이딩되어 있다. → 객체가 갖고 있는 값 문자열 반환 가능


