함수 호출방법
1. Call by value - 값에 의한 호출
2. Call by reference - 참조에 의한 호출
Call by Value
- Call by value는 메서드 호출 시에 사용되는 인자의 메모리에 저장되어 있는 값(value)을 복사하여 보낸다.
- 값에 의한 호출
- 함수에 매게 변수를 복사해서 처리
- 복사해서 처리하기 때문에 원래의 값이 보존된다.
- 복사하기 때문에 메모리량이 늘어난다.
public class CallByValue {
public static void swap(int x, int y){
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(" 호출 전 : a = " + a + " b = " + b);
swap(a,b);
System.out.println(" 호출 후 : a = " + a + " b = " + b);
}
}결과
호출 전 : x = 10 y = 20
호출 후 : x = 10 y = 20
*main() 에 선언된 변수 a와 b가 메모리에 할당된다.
swap()메서드 호출 시 할당 된 메모리 주소가 아닌 메모리에 담겨져 있던 값만 복사되어 x와 y의 메모리 주소에 담겨지게 된다.swap()메서드가 수행하는 동안 사용되는 변수는main()에 존재하는 a,b가 아닌 새로 생성된 x,y이기 때문에 수행 후에도 값에 변화가 없다.
Call by Reference
- Call by reference는 메서드 호출 시에 사용되는 인자가, 값이 아닌 주소(Address)를 넘겨줌으로써, 주소를 참조(Reference)하여 데이터를 변경할 수 있다.
- 참조에 의한 호출
- 인자로 받은 값의 주소를 참조해 직접 값에 영향을 주는 것
- 복사하지 않고 직접 참조를 하기 때문에 빠르다.
- 직접 참조를 하기 때문에 원래 값이 영향을 받는다.
public class CallByReference {
int value;
CallByReference(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public static void swap(CallByReference x, CallByReference y) {
int temp = x.value;
x.value = y.value;
y.value = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CallByReference a = new CallByReference(10);
CallByReference b = new CallByReference(20);
System.out.println(" 호출 전 : a = " + a.value + " b = " + b.value);
swap(a, b);
System.out.println(" 호출 후 : a = " + a.value + " b = " + b.value);
}
}결과
호출 전 : a = 10 b = 20
호출 후 : a = 20 b = 10
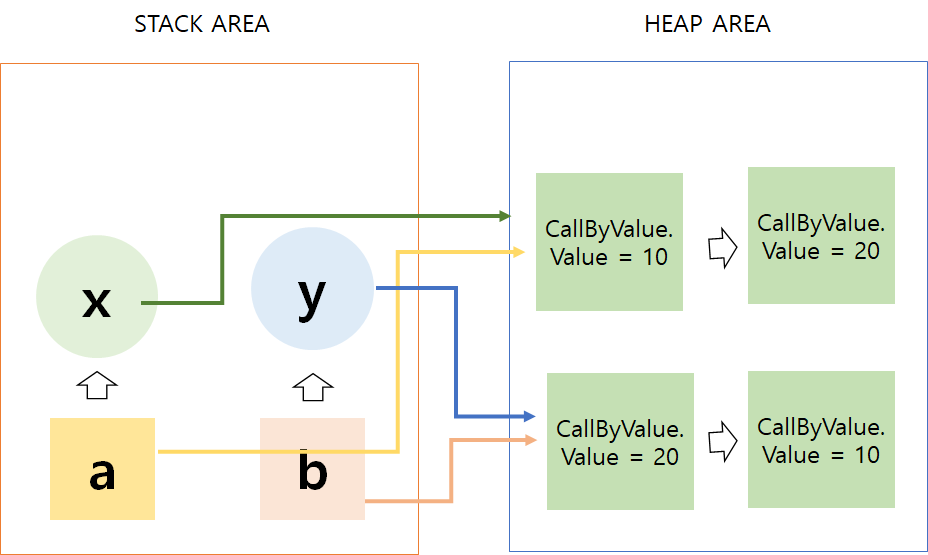
stack area에는 객체들이 저장되고Heap Area에는 값들이 저장된다.- 메서드를 호출했을 때 주소 값을 복사 해서 넘긴다.
- 값이 변경될 때 x와 y가 가지고있는 주소 값을 통해서 value의 값을 변경한다.
- 같은 주소값을 가진 a뫄b의 값이 변경된 것처럼 보여진다.
Java의 경우 Call by value이며, java는 객체를 메서드로 넘길 때 참조하는 지역번수의 실제 주소를 넘기는 것이 아니고 지역변수가 가리키고 있는 Heep영역의 객체를 가리키는 새로운 지역변수를 생성하여 그것을 통하여 같은 객체를 가리키도록 하는 방식이다.
