문제
알고리즘 분류
- 그리디 알고리즘
- 문자열
IDEA
- 문제 설명을 보고 헷갈릴 수 있는데, 전체를 뒤집는 경우는 생각하지 않아도 된다.
- 예제를 보면 이해하기가 쉬운데,
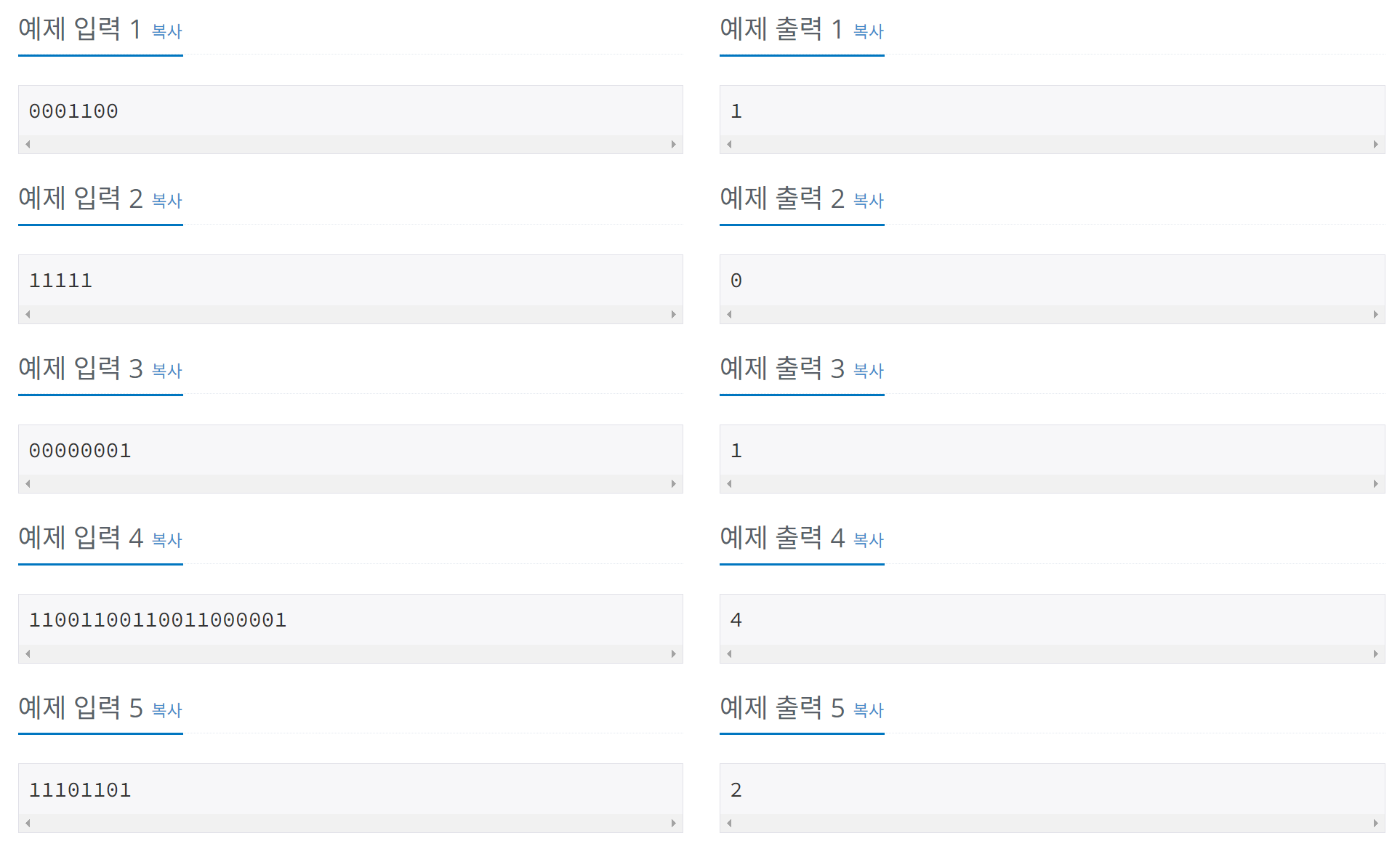
(1) 예제2의 '11111'을 보면 뒤집을 필요가 없으므로 출력은 0이다.
(2) 예제3의 '00000001'을 보면 1을 0으로, 즉 1번 뒤집으면 되므로 출력은 1이다.
(3) 예제1의 '0001100'을 보면 1을 0으로, 즉 1번 뒤집으면 되므로 출력은 1이다.
(4) 예제4의 '11001100110011000001'을 보면 0을 1로 4번 뒤집으면 되므로 출력은 4이다.
(5) 예제5의 '11101101'를 살펴보면, 각각 나뉘어있는 0을 1로 변경하면 되므로 출력은 2이다.
=> (1)을 보면, 연속된 수가 끊기지 않는다면 출력은 0이다.
(2). (3)를 보면, 연속된 수가 1번 또는 2번 끊겼다면 출력은 0이다.
(4), (5)를 보면, 연속된 수가 3번 이상 끊길 경우, 끊긴 횟수 n를 2로 나누면 된다. (n이 홀수라면 올림)
풀이
1. 입력, 연속된 수가 끊기는 횟수 확인
- 이전 글자를 저장해두고, 그 수와 다르면 끊긴 횟수를 증가시킴
String str = br.readLine();
char before = str.charAt(0);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 1; i<str.length(); i++){
if(str.charAt(i) != before) {
count++;
before = str.charAt(i);
}
}2. 횟수에 따른 조건문
- 끊기지 않는 경우 (예제2에 해당) 0 출력
- 1번 또는 2번 끊긴 경우 (예제 1, 3에 해당) 1 출력
- 3번 이상 끊긴 경우 (예제 4, 5에 해당) 2로 나눈 값을 출력 (홀수라면 올림)
if (count == 0 )
System.out.println(0);
else if (count == 1 || count == 2)
System.out.println(1);
else System.out.println(count/2 + count%2);전체 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readLine();
char before = str.charAt(0);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 1; i<str.length(); i++){
if(str.charAt(i) != before) {
count++;
before = str.charAt(i);
}
}
if (count == 0 )
System.out.println(0);
else if (count == 1 || count == 2)
System.out.println(1);
else System.out.println(count/2 + count%2);
}
}