
본 문서는 https://www.udemy.com/course/master-the-coding-interview-big-tech-faang-interviews/ 강의를 참조하여 작성되었습니다.
문제
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list
that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer.
Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node
that tail's next pointer is connected to.
Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.링크드 리스트 head가 주어질때,
사이클이란 어떤 노드가 다른 노드에 의해 여러번 next로 지정될때 형성됩니다.
cycle의 존재 여부를 리턴하세요.
예시
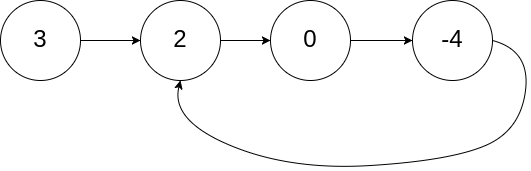
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: 2, 0, -4로 이루어진 cycle이 존재한다.제한
- 링크드 리스트 내 노드의 갯수 범위 [0, 10^4]
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
- pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
풀이법
1. 전부 순회하기
주어진 Head 노드가 null / None 이 될 때 까지 순회하면서 검사합니다.
한번 순회한 노드는 set에 넣고, 다음 노드를 순회할때 이 노드가 한번 순회 되었던 것인지를 확인합니다.
null 까지 도착한다면 사이클이 없는것이고, 그 전에 중복 순회가 발견되면 사이클이 있는것입니다.
코드는 아래와 같습니다.
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
tortoise = head
hare = head
while tortoise != None and hare != None:
tortoise = tortoise.next
if tortoise == None:
return False
hare = hare.next
if hare == None:
return False
hare = hare.next
if tortoise == hare:
return True
return False
시간복잡도는 linear search 이기에 O(N) 이며, 공간복잡도는 set에 원소들을 넣어 놓기에 O(N)입니다.
2. 플로이드의 거북이와 토끼 알고리즘 Floyd's tortoise and hare algorithm
위 알고리즘과는 비슷하나 공간복잡도를 O(1)로 줄입니다.
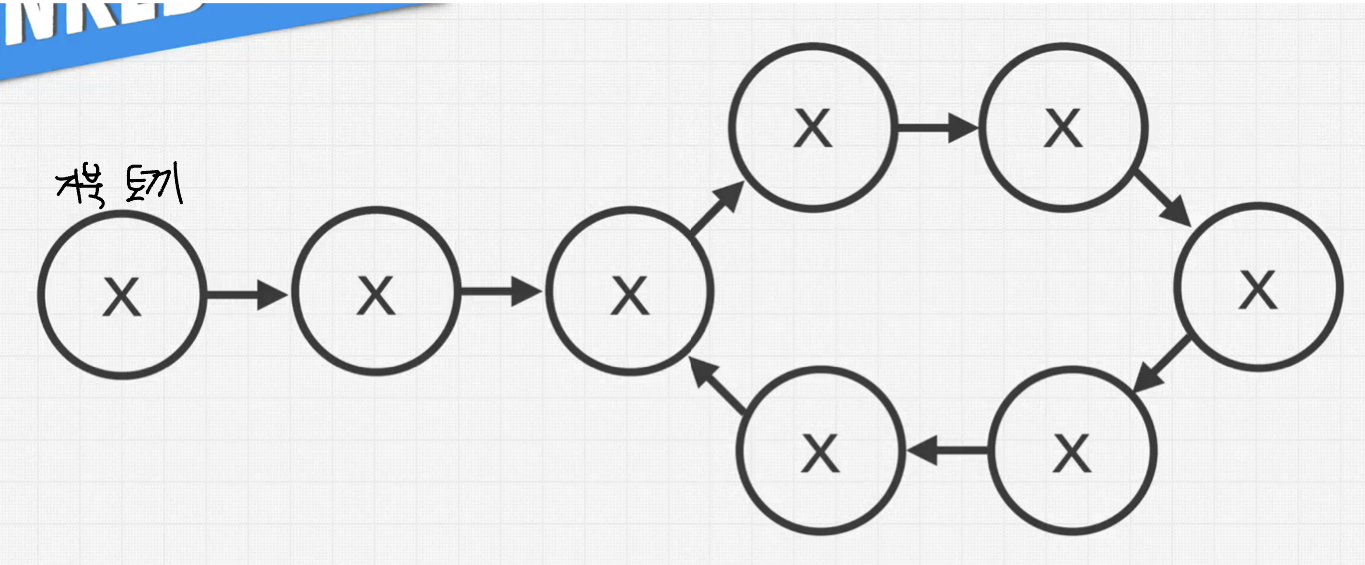
위와 같이 거북이와 토끼에 해당하는 포인터를 두개 둡니다.
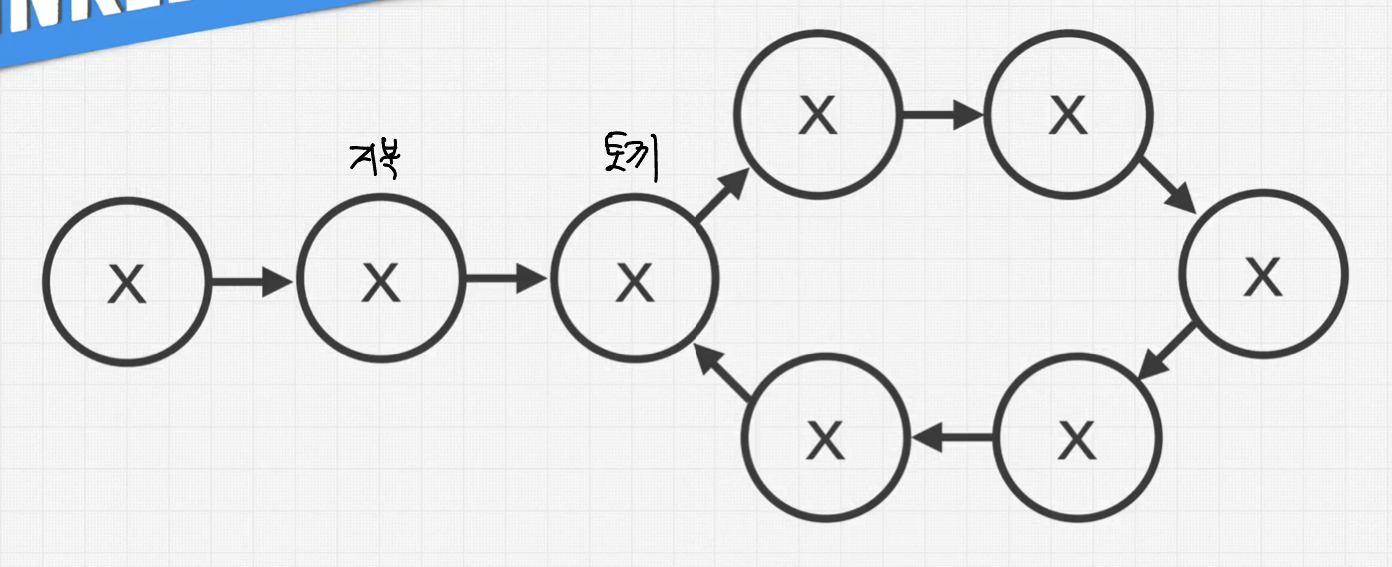
거북이는 한번에 1 node 를 이동하며, 토끼는 한번에 2 node를 이동합니다.
이렇게 이동을 계속 하다가 거북이와 토끼의 포인터가 같아지면 사이클이 있는것이고
거북이든 토끼든 null에 도달하면 사이클이 없는것입니다.
코드는 아래와 같습니다.
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
tortoise = head
hare = head
while tortoise != None and hare != None:
tortoise = tortoise.next
if tortoise == None:
return False
hare = hare.next
if hare == None:
return False
hare = hare.next
if tortoise == hare:
return True
return False포인터 두개만 사용되기 때문에 공간복잡도가 O(1)이 됩니다.
( 2024 / 11 / 23 )
복기
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
def move_next(node: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
return node.next if node else None
tortoise = head
hare = head
while True:
tortoise = move_next(tortoise)
if not tortoise:
return False
hare = move_next(hare)
if not hare:
return False
hare = move_next(hare)
if not hare:
return False
if tortoise == hare:
return True
