문제
You are given an integer matrix isWater of size m x n that represents a map of land and water cells.
If isWater[i][j] == 0, cell (i, j) is a land cell.
If isWater[i][j] == 1, cell (i, j) is a water cell.
You must assign each cell a height in a way that follows these rules:
The height of each cell must be non-negative.
If the cell is a water cell, its height must be 0.
Any two adjacent cells must have an absolute height difference of at most 1. A cell is adjacent to another cell if the former is directly north, east, south, or west of the latter (i.e., their sides are touching).
Find an assignment of heights such that the maximum height in the matrix is maximized.
Return an integer matrix height of size m x n where height[i][j] is cell (i, j)'s height. If there are multiple solutions, return any of them.문제 설명
정수형 행렬 isWater(m x n 크기)가 주어집니다. 이 행렬은 땅과 물 셀을 나타내는 지도를 나타냅니다.
- isWater[i][j] == 0인 경우, 셀 (i, j)는 땅입니다.
- isWater[i][j] == 1인 경우, 셀 (i, j)는 물입니다.
다음 규칙을 만족하도록 각 셀에 높이를 할당해야 합니다:
- 각 셀의 높이는 0 이상의 정수여야 합니다.
- 물 셀의 높이는 반드시 0이어야 합니다.
- 인접한 두 셀의 높이 차의 절댓값은 1을 넘지 않아야 합니다. (인접한 셀이란, 북, 동, 남, 서 방향으로 연결된 셀을 의미합니다.)
주어진 조건을 만족하면서 행렬 내의 최대 높이값을 최대화하는 높이 할당을 찾으세요.
반환값
크기가 m x n인 정수형 행렬 height를 반환하세요. 여기서 height[i][j]는 셀 (i, j)의 높이를 나타냅니다. 여러 가지 해가 존재할 경우, 그중 하나를 반환하면 됩니다.
예시
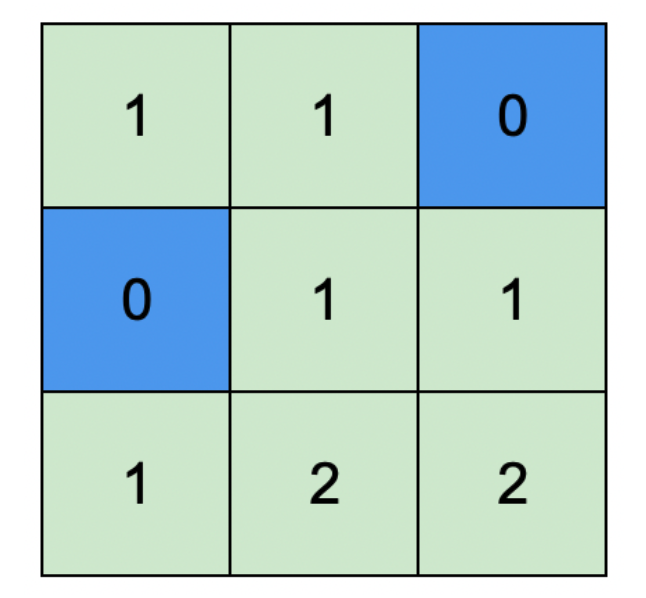
다음 그림은 위의 예시 입력에 대한 출력 결과를 나타냅니다:
- 파란색 칸은 물 셀을 나타내며, 높이가 항상 0입니다.
- 초록색 칸은 땅 셀을 나타내며, 높이는 인접한 셀과의 차이가 1을 넘지 않습니다.
제한
- 주어진 배열은 0 혹은 1로만 이루어져 있다.
- 최소 1개의 셀은 1이다.
풀이
-
결과 배열 초기화
- 정답이 될 배열 ans를 전부 -1로 초기화하고, 주어진 isWater 배열과 크기를 동일하게 만듭니다.
- -1은 아직 방문하지 않은 셀을 나타냅니다.
-
물 셀 초기화
- isWater 배열을 순회하면서 물이 있는 좌표를 모두 큐(queue)에 추가합니다.
- 물 셀의 높이는 항상 0이므로, ans 배열의 해당 좌표를 0으로 설정합니다.
-
BFS를 통한 높이 계산
- 큐에서 좌표를 하나씩 꺼내고, 해당 셀의 상하좌우 인접한 셀을 확인합니다.
- 아직 방문하지 않은 셀(-1로 초기화된 셀)의 경우, 현재 셀의 높이에 1을 더한 값을 할당합니다.
- 새롭게 높이가 할당된 셀을 큐에 추가하여, BFS를 계속 진행합니다.
-
범위와 조건 확인
- 인접한 셀이 배열 범위를 벗어나는지 확인합니다.
- 이미 높이가 할당된 셀은 건너뜁니다.
-
결과 반환
- BFS가 종료된 후, ans 배열이 조건을 만족하는 최종 높이 배치를 담고 있으므로 이를 반환합니다.
위 방법을 통해 모든 물 셀에서 동시에 시작하여, 각 땅 셀까지의 최소 높이를 계산하며 조건을 만족하는 배열을 생성합니다.
class Solution:
def highestPeak(self, isWater: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
R = len(isWater)
C = len(isWater[0])
q = deque()
directions = [
[0, 1],
[0, -1],
[1, 0],
[-1, 0]
]
ans = [
[-1] * C for _ in range(R)
]
for r in range(R):
for c in range(C):
if isWater[r][c] == 1:
ans[r][c] = 0
q.append((r, c))
while q:
row, col = q.popleft()
for dr, dc in directions:
tr, tc = row + dr, col + dc
if min(tr, tc) < 0 or tr >= R or tc >= C or ans[tr][tc] != -1:
continue
ans[tr][tc] = ans[row][col] + 1
q.append((tr, tc))
return ans
