
문제
You are given a list of bombs.
The range of a bomb is defined as the area where its effect can be felt.
This area is in the shape of a circle with the center as the location of the bomb.
The bombs are represented by a 0-indexed 2D integer array bombs where bombs[i] = [xi, yi, ri].
xi and yi denote the X-coordinate and Y-coordinate of the location of the ith bomb,
whereas ri denotes the radius of its range.
You may choose to detonate a single bomb.
When a bomb is detonated,
it will detonate all bombs that lie in its range.
These bombs will further detonate the bombs that lie in their ranges.
Given the list of bombs, return the maximum number of bombs that can be detonated
if you are allowed to detonate only one bomb.당신에게 폭탄의 리스트가 주어집니다.
각각의 폭탄은 x축과 y축이 주어지며, 고유의 반지름을 가집니다.
폭발의 영향력은 중심점으로부터 반지름의 원만큼이며, 그 안에 있던 다른 폭탄도 영향 지대에 있을시 터지게 됩니다.
개별 폭탄들은 1차원 배열로 표현되는데 [xi, yi, ri] 가 각각 x축, y축, 반지름을 의미합니다.
단 하나의 폭탄만을 터뜨렸을때 최대로 터질수 있는 폭탄의 수를 리턴하시오.
예시
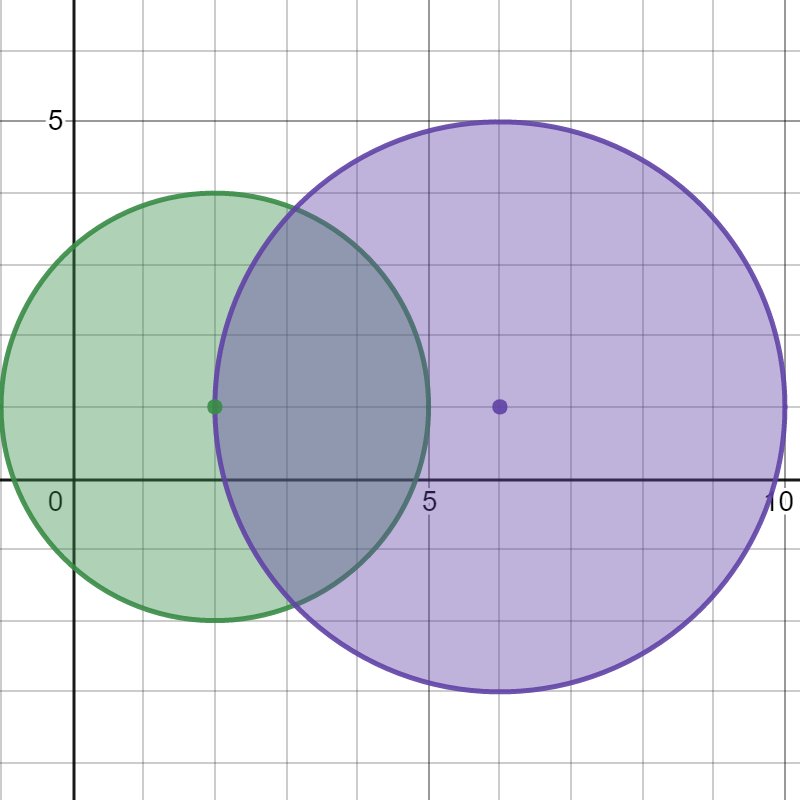
Input: bombs = [[2,1,3],[6,1,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation: 초록색 폭탄이 터지면 자신만 터지지만, 보라색 폭탄이 터지면 초록색이 반경에 위치해 터지나,
총 2개의 폭탄이 터지게 된다.제한
- 1 <= bombs.length <= 100
- bombs[i].length == 3
- 1 <= xi, yi, ri <= 10^5
풀이법
각각의 폭탄으로 부터 BFS를 돌려 순회되는 폭탄의 갯수를 확인해
가장 큰 값을 리턴하면 된다.
여기서 BFS를 순회하는 기준을 트리의 자식이 아닌 아직 폭발하지 않았고 반경 내에 있는 폭탄으로 하면 된다.
def count(bombs: List[List[int]], start: int):
check = [0 for _ in range(len(bombs))]
q = deque()
count = 0
q.append([bombs[start], start])
check[start] = 1
while len(q) != 0:
node = q.popleft()
count += 1
x = node[0][0]
y = node[0][1]
r = node[0][2]
for i, v in enumerate(bombs):
if check[i] == 0 and ((x - v[0])**2 + (y-v[1])**2)**0.5 <= r:
q.append([v, i])
check[i] = 1
return count
class Solution:
def maximumDetonation(self, bombs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
cnt = 1
for i in range(len(bombs)):
cnt = max(cnt, count(bombs, i))
return cnt속도 향샹
폭탄이 한번 터진 전적이 있으면 그 폭탄은 굳이 시작점으로 할 필요가 없다.
폭탄이 터진적이 없는것만 시작점으로 bfs를 하면 bfs의 횟수를 많이 줄여 더 빨라진다.
def count(bombs: List[List[int]], start: int, gc):
check = [0 for _ in range(len(bombs))]
q = deque()
count = 0
q.append([bombs[start], start])
check[start] = 1
gc[start] = 1
while len(q) != 0:
node = q.popleft()
check[node[1]] = 1
gc[node[1]] = 1
count += 1
x = node[0][0]
y = node[0][1]
r = node[0][2]
for i, v in enumerate(bombs):
if check[i] == 0 and ((x - v[0])**2 + (y-v[1])**2)**0.5 <= r:
q.append([v, i])
check[i] = 1
gc[i] = 1
return count
class Solution:
def maximumDetonation(self, bombs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
cnt = 1
gc = [0 for _ in range(len(bombs))]
for i in range(len(bombs)):
if gc[i] == 1: continue
cnt = max(cnt, count(bombs, i, gc))
return cnt