문제
Design an algorithm that collects daily price quotes for some stock and returns the span of that stock's price for the current day.
The span of the stock's price in one day is the maximum number of consecutive days (starting from that day and going backward) for which the stock price was less than or equal to the price of that day.
For example, if the prices of the stock in the last four days is [7,2,1,2] and the price of the stock today is 2, then the span of today is 4 because starting from today, the price of the stock was less than or equal 2 for 4 consecutive days.
Also, if the prices of the stock in the last four days is [7,34,1,2] and the price of the stock today is 8, then the span of today is 3 because starting from today, the price of the stock was less than or equal 8 for 3 consecutive days.정수 배열 prices가 주어졌을때,
next함수를 호출하면 지금까지 자신에게 next로 주어졌던 값들보다 작거나 같았던 값의 갯수에 자기자신의 갯수를 더해 리턴한다.
단 작거나 같았던 숫자들은 연속해서 위치해야 한다.
Ex. (30, 50, 40) -> 40보다 작거나 같은 수는 자기 자신 포함 1개
(30, 40, 50) -> 50보다 작거나 같은 수는 자기 자신 포함 3개
next를 구현하시오.
예시
Input
["StockSpanner", "next", "next", "next", "next", "next", "next", "next"]
[[], [100], [80], [60], [70], [60], [75], [85]]
Output
[null, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 6]
100 보다 작거나 같은건 자기자신 -> 1
85 보다 작거나 같은건 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 80 -> 6제한
- next 함수는 최소 번 호출된다.
풀이
- 스택을 사용한다.
- prices 배열에 [100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85] 순으로 숫자가 들어온다고 가정한다.
- 항상 top 에 있는 튜플의 두번째 값 ( 작거나 같은 수 ) 를 리턴하면된다.
- 스택에는 자기 자신의 값과 자기 자신보다 작거나 같은 숫자의 갯수를 저장한다.
(값, 작거나 같은 갯수)
- 100을 스택에 집어 넣는다.
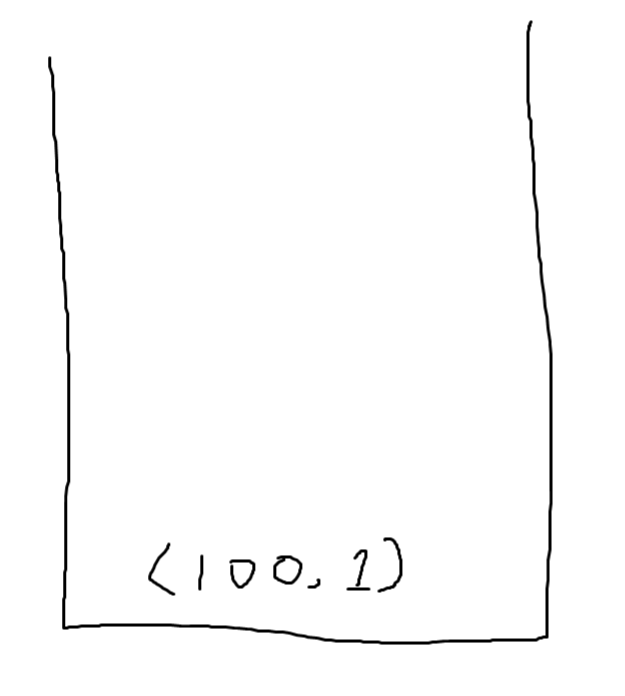
- 현재 100보다 작거나 같은 값은 없기에 1이 된다.
- 80을 스택에 집어 넣는다.
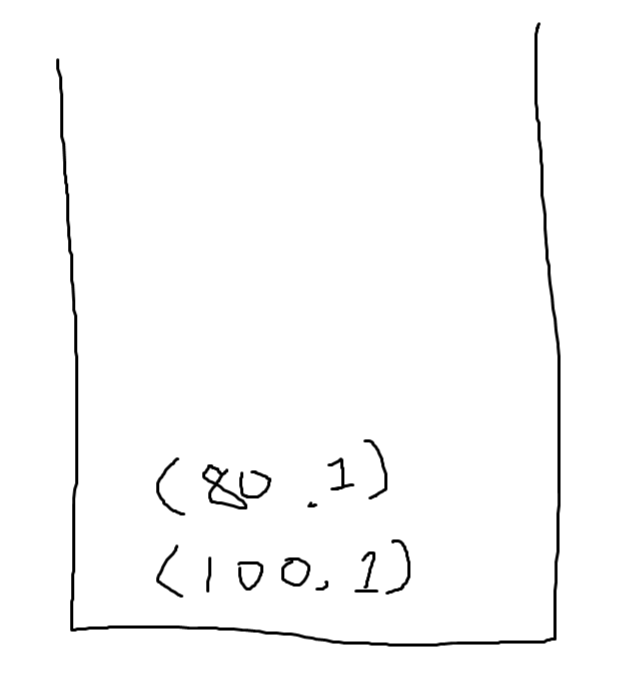
- 현재 80보다 작거나 같은 값은 없기에 1이 된다.
- 60을 스택에 집어 넣는다.
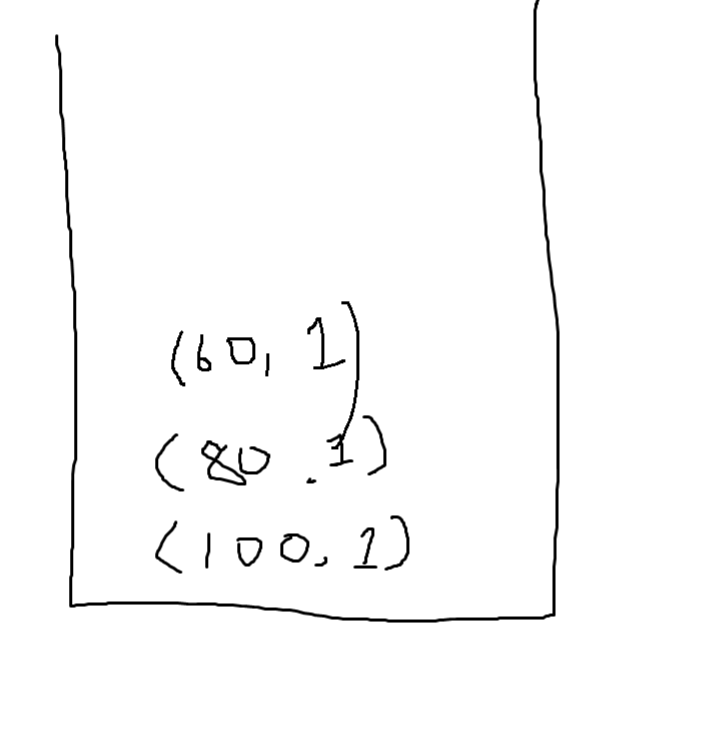
- 현재 60보다 작거나 같은 값은 없기에 1이 된다.
- 70을 스택에 집어 넣는다.
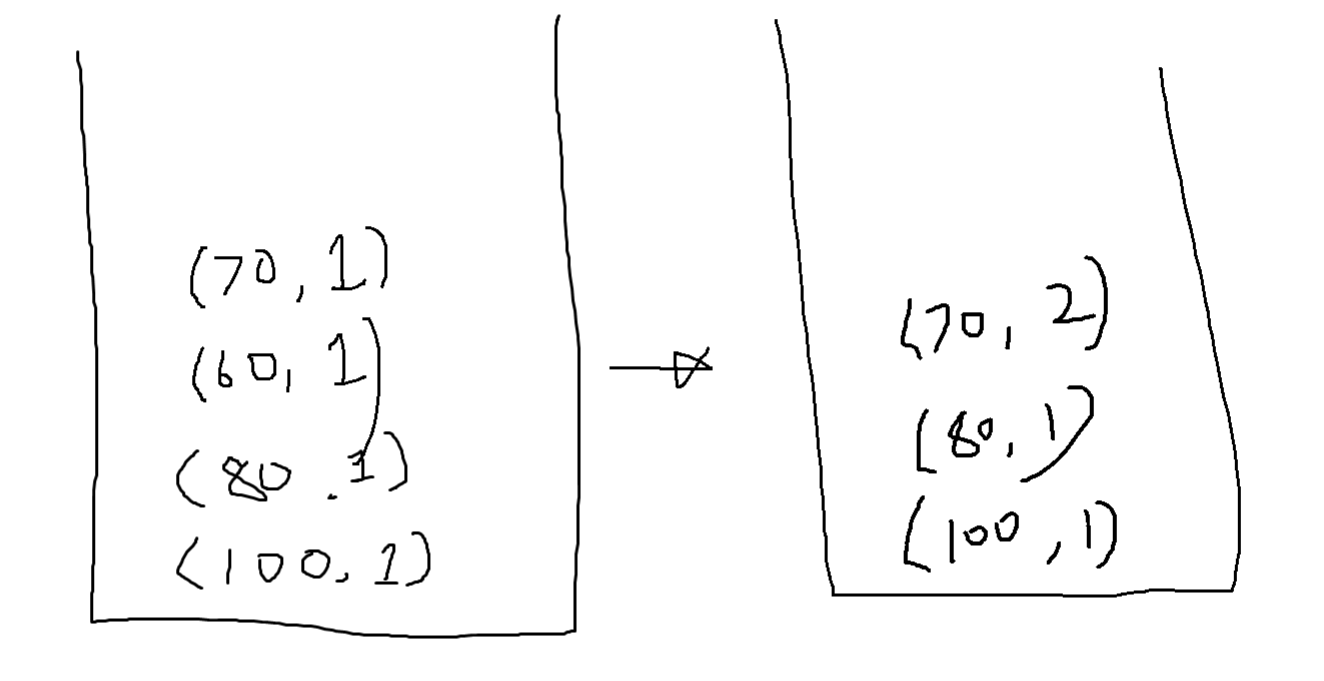
- 60은 70보다 작다! 그렇기에 60을 pop 하고 70의 count 에 1이 추가된다.
- 즉 자신보다 앞에 있는 값이 작을 경우는 pop하고 pop된 값을 추가해주면 된다!
from typing import Tuple
class StockSpanner:
def __init__(self):
self.stack: List[Tuple[int, int]] = []
def next(self, price: int) -> int:
count = 1
while self.stack and self.stack[-1][0] <= price:
count += self.stack.pop()[1]
self.stack.append((price, count))
return self.stack[-1][1]
# Your StockSpanner object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = StockSpanner()
# param_1 = obj.next(price)