ArrayList
ArrayList란 기존 Java Array의 한계를 극복한 Array 객체이다.
Pros & Cons
장점
- Runtime동안 Array length를 동적으로 바꿀 수 있음
- 앞 뒤로 데이터를 추가할 수 있고, insert도 가능
- Not square bracket notation (대괄호 사용 안 함)
단점
- 기존 array에 비해 비효율적
- Object type만 저장가능하고, primitive type은 불가능
- ArrayList도 array를 사용
Create Instance of ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList; // must imported
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<String>(20); //길이 설정
Methods of ArrayList
// Constructor
public ArrayList<Base_Type>()
public ArrayList<Base_Type>(int initialCapacity)
// Add : push_back()
public boolean add(Base_Type newElement)
// Insert : index에 element를 삽입
public boolean add(int index, Base_Type newElement)
/* 필요한 경우, capacity()를 증가 */
/* Throws IndexOutOfBoundException이 포함된 Method */
// Get : 해당 Index 값을 Return
public Base_Type get(int index)
// Get : 해당 Index 값을 element으로 변경
public Base_Type set(int index, Base_Type element)
// Remove : Index
public Base_Type remove(int index)
// Remove : element가 앞에서부터 처음 등장한 경우 제거
public boolean remove(Object element)
/* Add와 동일한 Exception 적용 */
/* size() 1 감소*/Programming Example
ArrayList 내용 For-each 탐색
for(String s : toDoList)
System.out.println(s);capacity()를 size()만큼 줄임
ArrayList.trimToSize()
/* Trims the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be the list's current size */Deep Copy
ArrayList.clone()Parameterized Classes, Generic Data Types
Generic 개념
Possible to declare our own classes which use types as
parameters
클래스 내부에서 지정하는 것이 아닌 외부에서 사용자에 의해 지정되는 것을 의미ArrayList<Template> toDoList = new ArrayList<Template>();
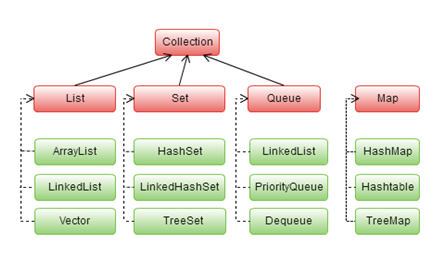
Collection interface
The Collection interface specifies how objects can be
added, removed, or accessed from a Collection
다수의 데이터를 쉽고 효과적으로 처리할 수 있는 표준화된 방법을 제공하는 클래스의 집합
Hashmap
Used like a database to efficiently map from a key to an
object
key, value(Object) 쌍으로 이루워진 Data Structure 형식
HashMap<String, Integer> mountains = new HashMap<String, Integer>();printMap()
public void printMap(HashMap<String, Integer> map)
{
System.out.println("Map contains:");
for (String keyMountainName : map.keySet())
{
Integer height = map.get(keyMountainName);
System.out.println(keyMountainName +
" --> " + height.intValue() + " feet.");
}
System.out.println();
}Hashset
HashSet is used to store a set of object(no equal element is stored)
If you use HashSet of your own class, it must override
hashCode() and equals()
HashSet은 Object Set을 저장하는 데이터 구조 중 하나이고, 각 요소들은 중복되지 않는다.
HashSet에 동일학 객체를 넣어도 중복되어 Set에 입력이 되는 경우를 막기위해서 해당 class의 hashCode와 equals를 override를 수정해주어야 한다.
Define Hashset
HashSet<Integer> integers = new HashSet<Integer>();Override hashCode( ), equals( )
Object는 hashCode와 equals method가 탑재되어 있는데,
아래와 같은 형태로 되어 있다.
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
return (this == obj);
}'==' 연산은 메모리 주소값이 같은지 따지는 연산이라 Object 필드의 값이 다 같은지 확인하려면 equals를 바꾸어 주어야 한다.
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if(obj instanceof this)
{
Car tmp = (Car) obj
if(tmp.name == this.name) return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean hashCode()
{ // 기존에는 memory address return
return this.name.hashCode() + this.year;
// 이런 식으로 hash function을 수정해주어야 한다.
}