▶️ 혼공학습단 ▶️ 도서 정보 ▶️ 심화자료 ▶️ 유튜브 강의
기본 미션
p. 185 확인 문제 3번
Q. 다음 설명을 읽고 SRAM에 대한 설명인지 DRAM에 대한 설명인지 쓰세요.
A.
- 주로 캐시 메모리로 활용됩니다.
SRAM- 주로 주기억장치로 활용됩니다.
DRAM- 대용량화하기 유리합니다.
DRAM- 집적도가 상대적으로 낮습니다.
SRAM
SRAMwill hold its data permanently in the presence of power, while data inDRAMdecays in seconds and thus must be periodically refreshed.SRAMis faster thanDRAMbut it is more expensive in terms of silicon area and cost.SRAMis typically used for the cache and internal registers of a CPU whileDRAMis used for a computer's main memory.
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit.
SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed.
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology.
The electric charge on the capacitors gradually leaks away; without intervention the data on the capacitor would soon be lost. To prevent this, DRAM requires an external memory refresh circuit which periodically rewrites the data in the capacitors, restoring them to their original charge. This refresh process is the defining characteristic of dynamic random-access memory, in contrast to static random-access memory (SRAM) which does not require data to be refreshed.
Unlike flash memory, DRAM is volatile memory (vs. non-volatile memory), since it loses its data quickly when power is removed.
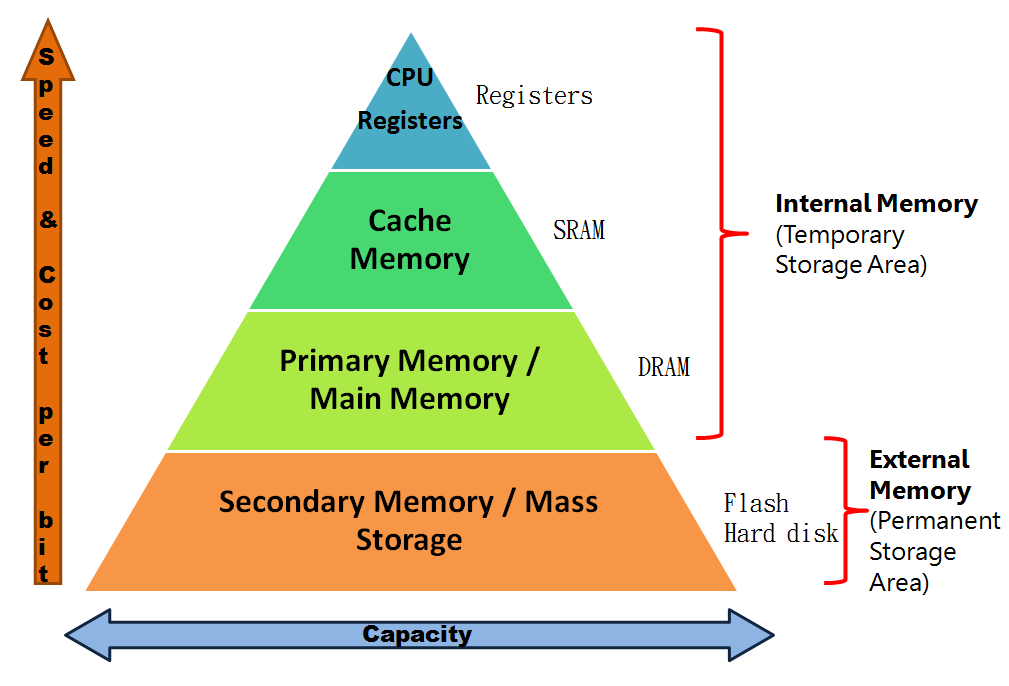
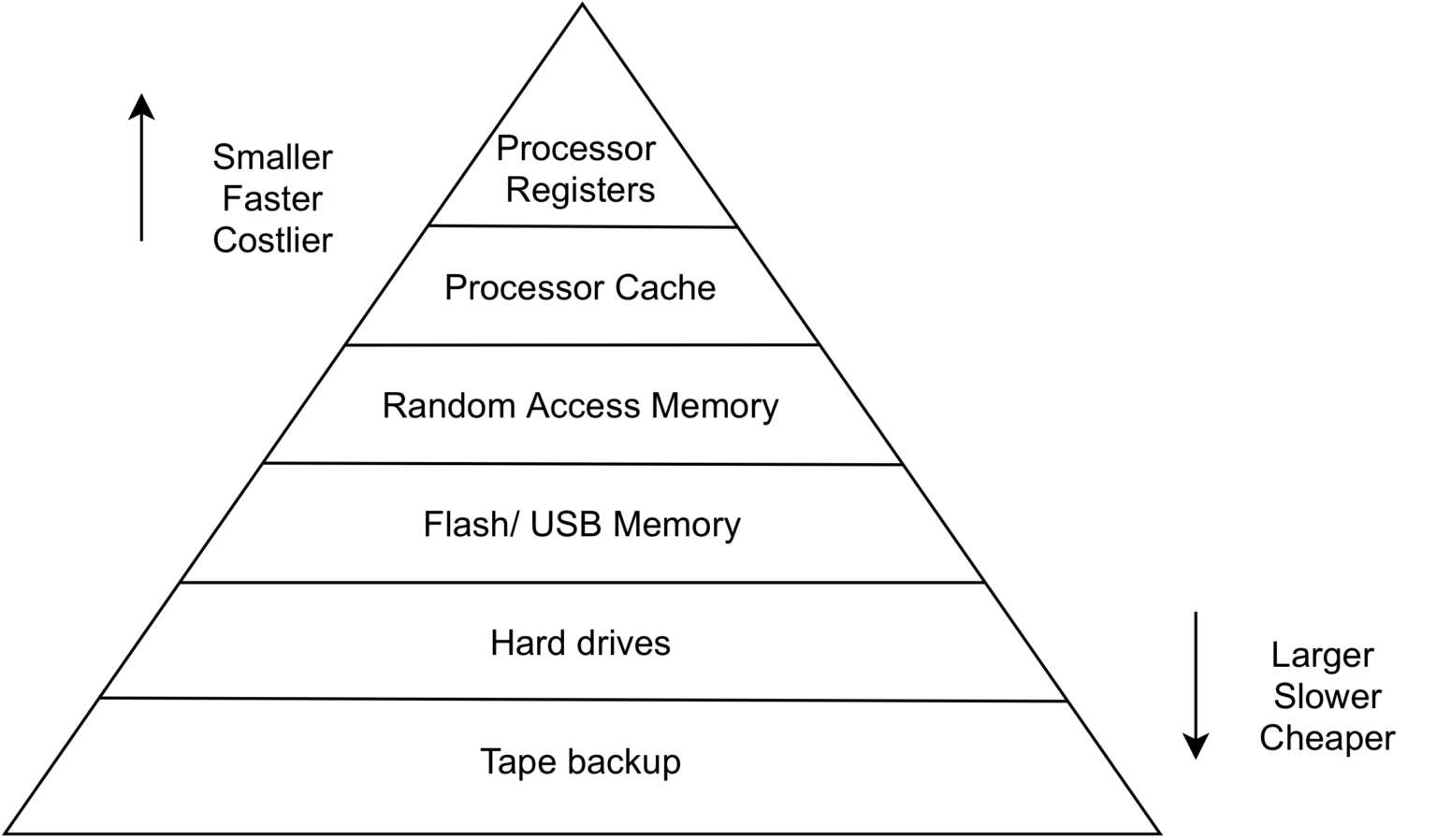
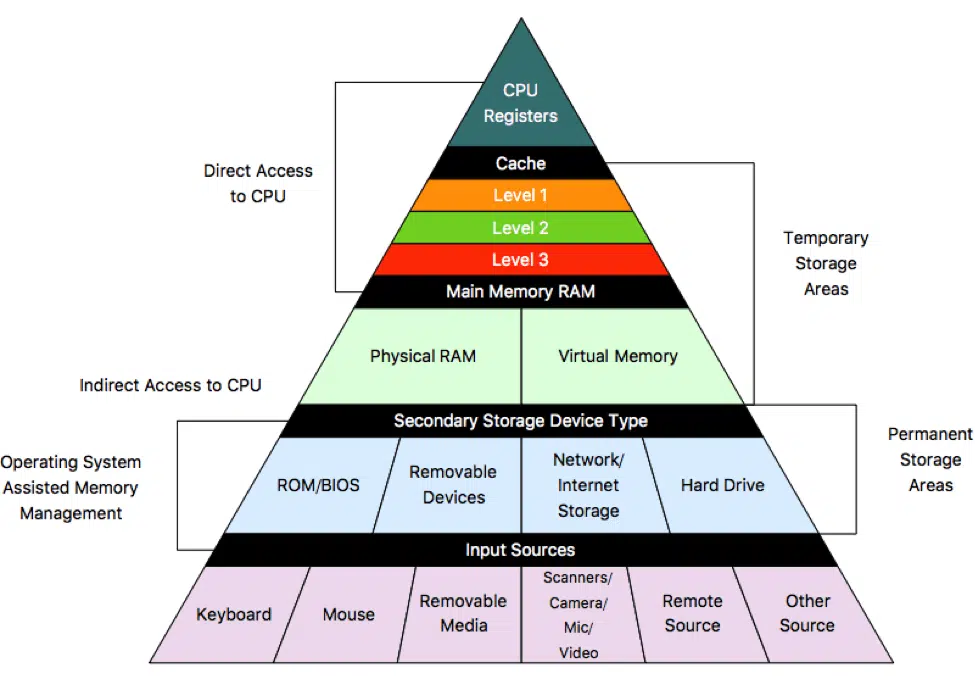
p. 205 확인 문제 1번
Q. 다음 보기에 있는 저장 장치들로 저장 장치 계층 구조 도식도를 채우세요.
보기메모리, 보조기억장치, 캐시메모리, 레지스터
A.
레지스터
Registers
캐시 메모리Cache Memory
메모리Main Memory RAM
보조기억장치Secondary Memory
선택 미션
RAID
RAID (
redundant array of inexpensive disksorredundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both.
Standard RAID levels
| RAID 0 | RAID 1 | RAID 4 | RAID 5 | RAID 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
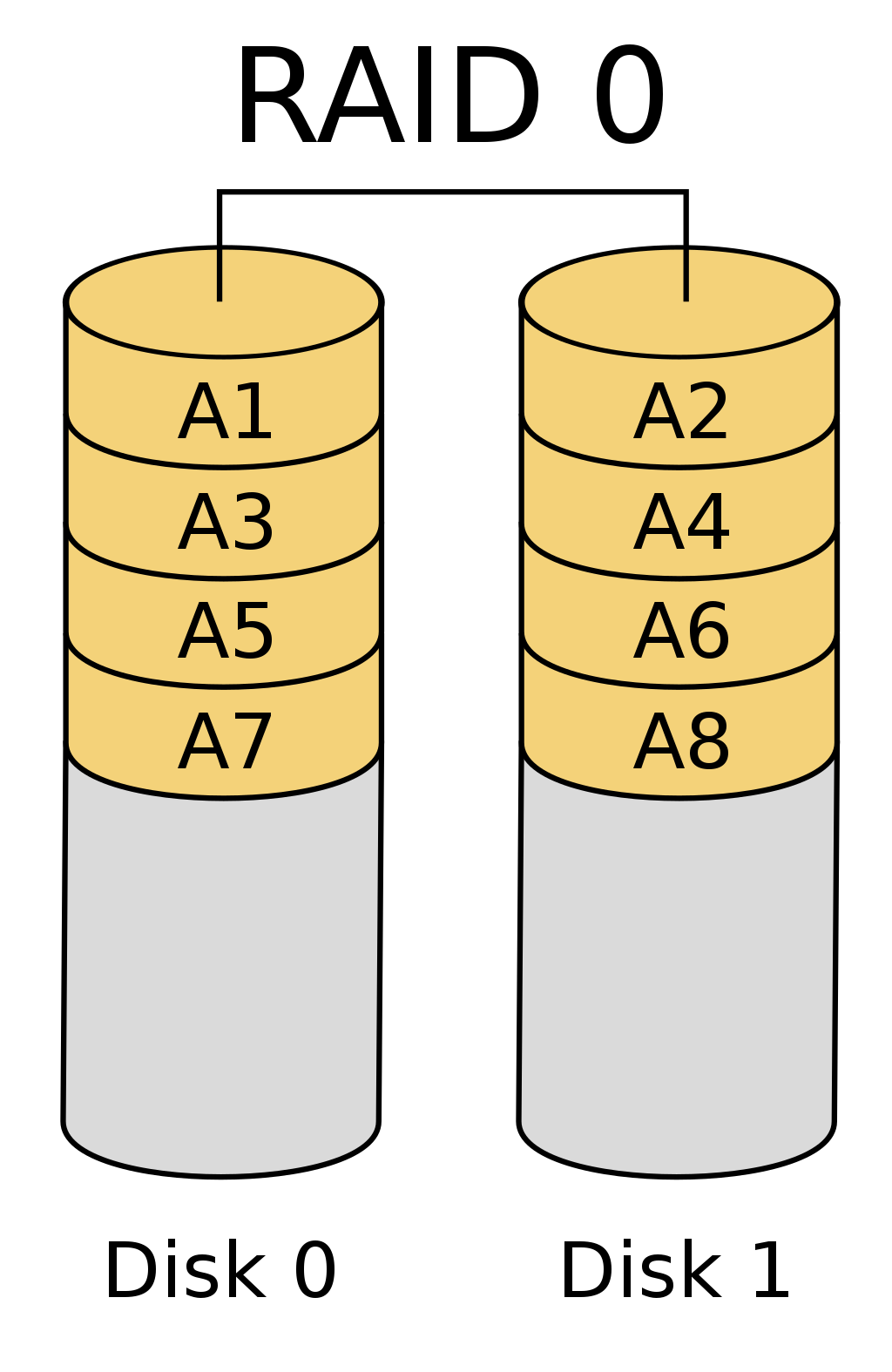 | 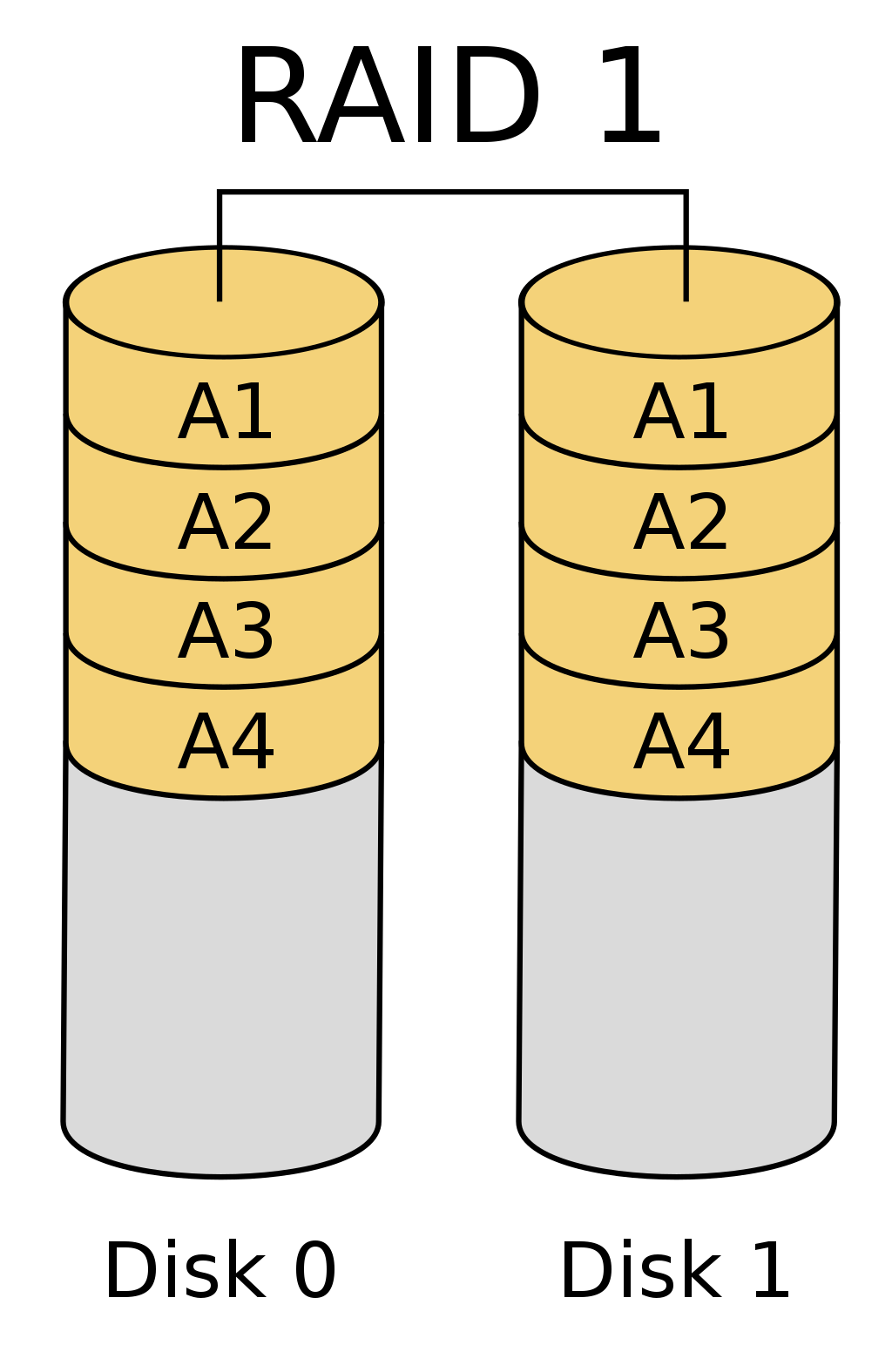 | 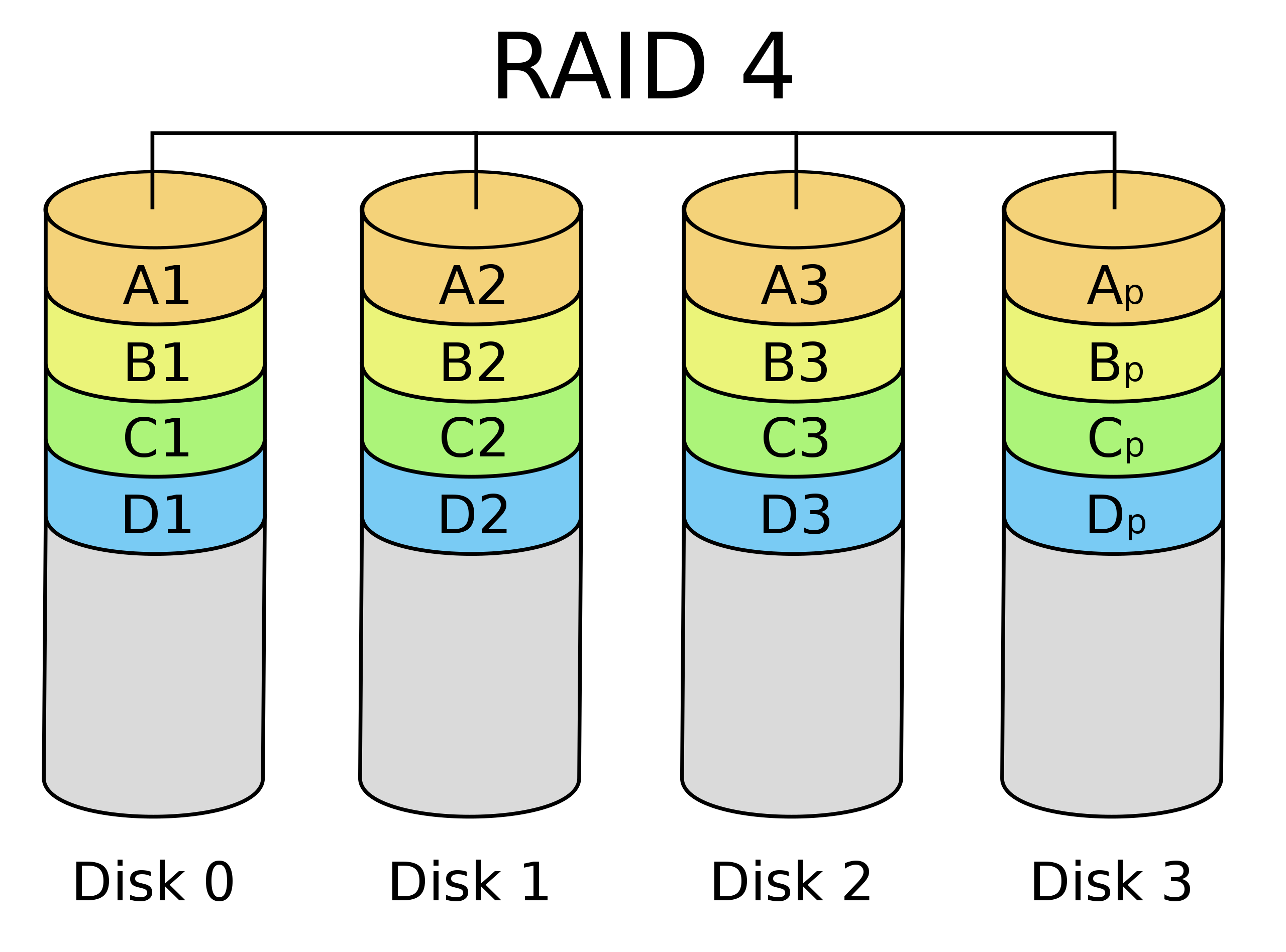 | 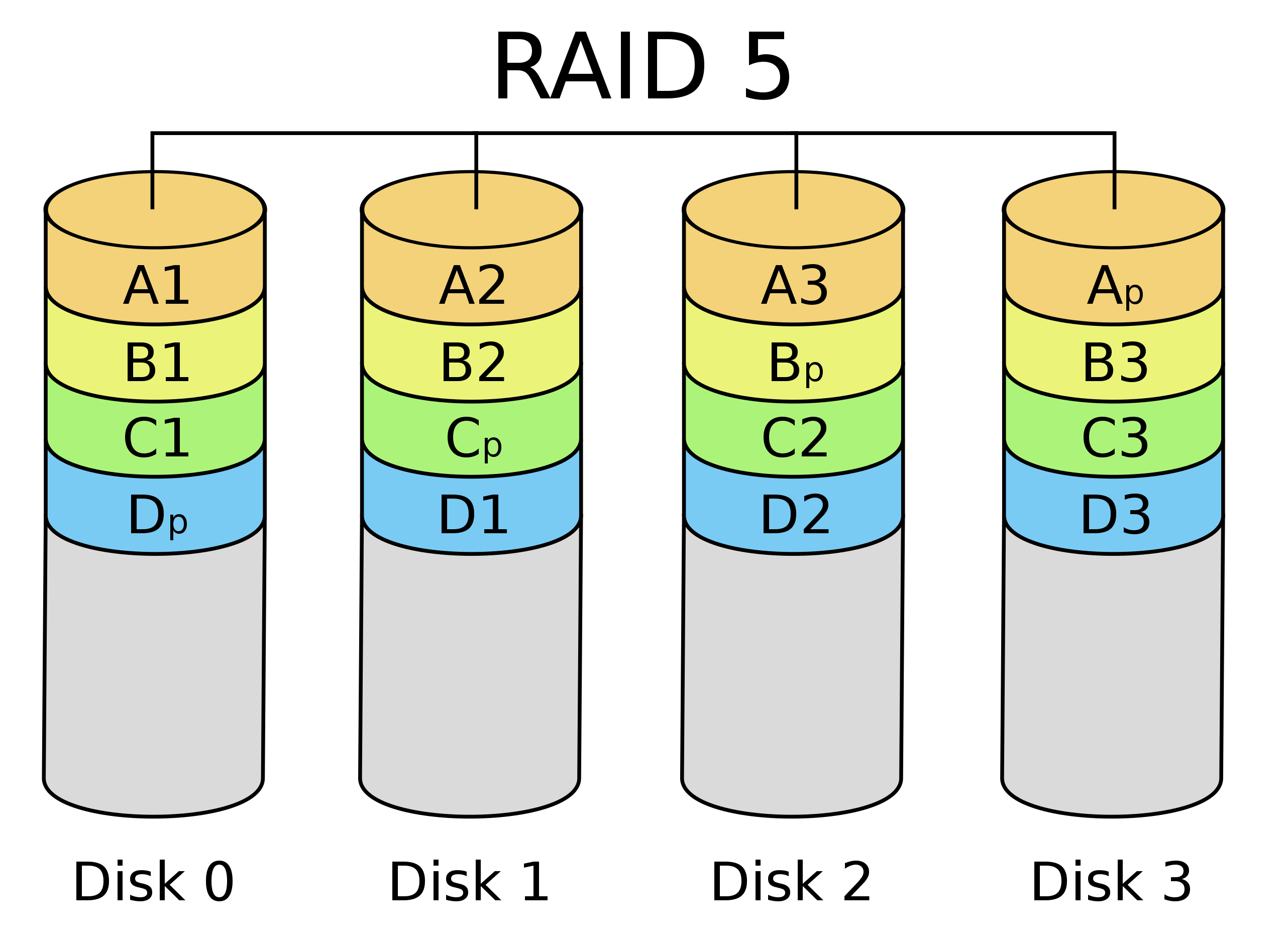 | 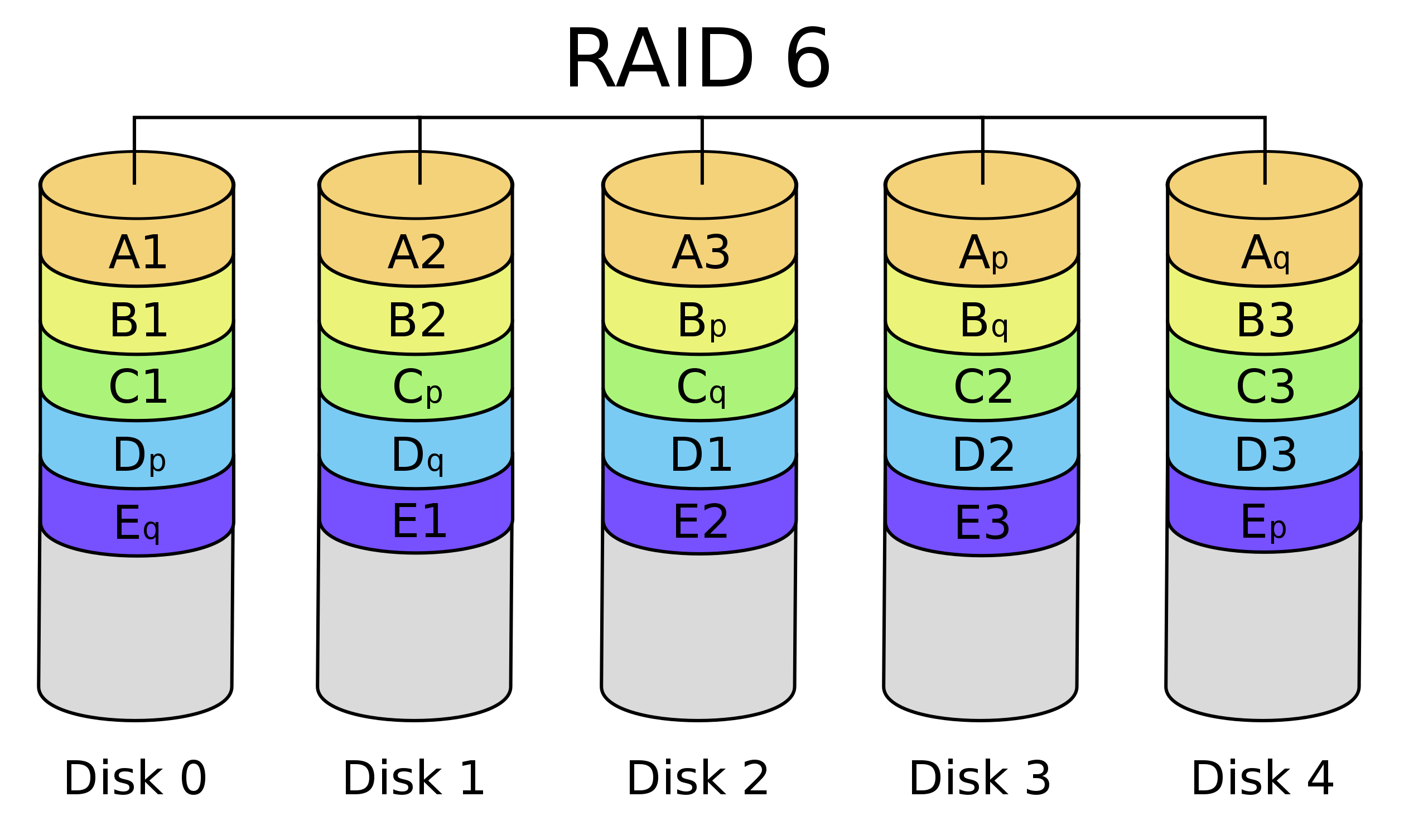 |
| RAID 0 splits ("stripes") data evenly across two or more disks, without parity information, redundancy, or fault tolerance. | RAID 1 consists of an exact copy (or mirror) of a set of data on two or more disks; | RAID 4 consists of block-level striping with a dedicated parity disk. | RAID 5 consists of block-level striping with distributed parity. Unlike in RAID 4, parity information is distributed among the drives. | RAID 6 extends RAID 5 by adding another parity block; thus, it uses block-level striping with two parity blocks distributed across all member disks. |
[Chapter 06 ~ 08]
컴퓨터 핵심 부품 4
Latency Numbers Every Programmer Should Know
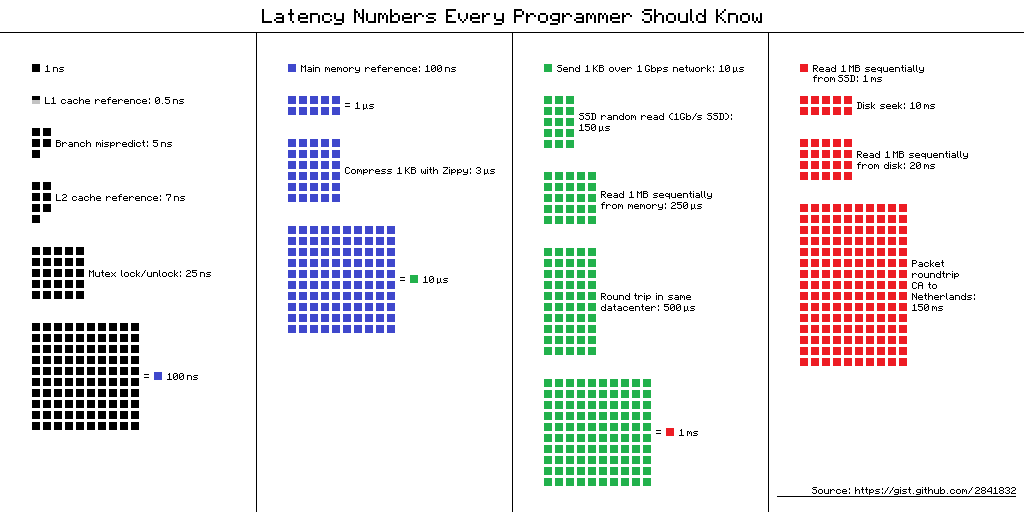
DO YOU KNOW HOW MUCH YOUR COMPUTER CAN DO IN A SECOND?
By
Peter Norvig
By
Jeffrey DeanSoftware Engineering Advice from Building Large-Scale Distributed Systems
Designs, Lessons and Advice from Building Large
Distributed Systems
Hard Drive
Hard drive running
Hard drive in slow motion
혼공컴운
| # | 진도 | 기본 미션 | 선택 미션 | ☑️ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1주차 (1/2 ~ 1/7) | Chapter 01 ~ 03 | p. 51의 확인 문제 3번, p. 65의 확인 문제 3번 풀고 인증하기 | p. 100의 스택과 큐의 개념을 정리하기 | ☑️ |
| 2주차 (1/8 ~ 1/14) | Chapter 04 ~ 05 | p. 125의 확인 문제 2번, p. 155의 확인 문제 4번 풀고 인증하기 | Ch.05(05-1) 코어와 스레드, 멀티 코어와 멀티 스레드의 개념을 정리하기 | ☑️ |
| 3주차 (1/15 ~ 1/21) | Chapter 06 ~ 08 | p. 185의 확인 문제 3번, p. 205의 확인 문제 1번 풀고 인증하기 | Ch.07(07-1) RAID의 정의와 종류를 간단히 정리해 보기 | ☑️ |
| 4주차 (1/22 ~ 1/28) | Chapter 09 ~ 11 | p. 304의 확인 문제 1번 풀고 인증하기 | Ch.11(11-2) 준비 큐에 A,B,C,D 순으로 삽입되었다고 가정했을 때, 선입 선처리 스케줄링 알고리즘을 적용하면 어떤 프로세스 순서대로 CPU를 할당받는지 풀어보기 | |
| 5주차 (1/29 ~ 2/4) | Chapter 12 ~ 13 | p. 363의 확인 문제 1번 풀고 인증하기 | Ch.12(12-1) 임계 구역, 상호 배제 개념을 정리하기 | |
| 6주차 (2/5 ~ 2/12) | Chapter 14 ~ 15 | p. 400의 확인 문제 1번 풀고 인증하기 | Ch.14(14-3) 프로세스가 사용할 수 있는 프레임이 3개 있고, 페이지 참조열이 '2313523423' 일 때 LRU 페이지 교체 알고리즘으로 이 페이지를 참조한다면 몇 번의 페이지 폴트가 발생하는지 풀어보기 |