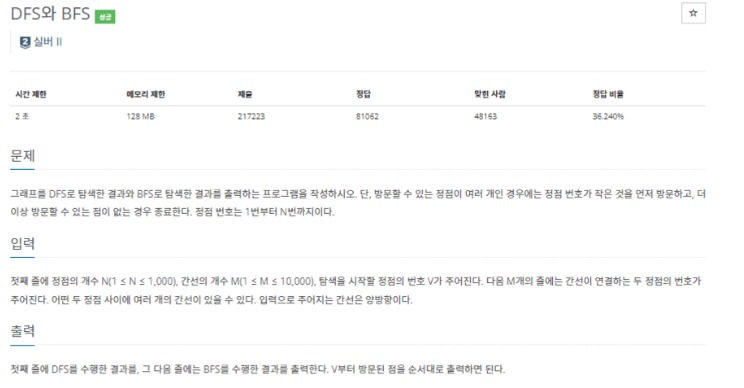
-
DFS구현은 재귀를 활용하는 방법을 사용 (스택도 가능)
- 재귀를 통해서 만약 arr이 ==1이라면 간선이 있다는걸 의미, 그다음 check가 false라면 탐색하지 않았던 노드를 의미한다.
- 해당 노드에 걸리게 되면 DFS가 바로 실행이 되며, 더 깊이 파고든다.
-
BFS 큐를 통해 구현
- 큐의 처음 삽입한 노드를 빼주고 그 노드와 연결되어있는 (ARR 배열) 노드들을 탐색하여 Q에 넣습니다.
- 큐를 반복해서 꺼내 주다가 큐가 비어지면 끝이난다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static boolean[] check;
static int[][] arr;
static Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
static int point, line, start;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
point = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
line = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
check = new boolean[point + 1];
arr = new int[point + 1][point + 1];
// 노드 간의 간서을 표현해주기 위한 2차원 배열 생성
for (int i = 0; i < line; i++) {
StringTokenizer s = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(s.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(s.nextToken());
arr[a][b] = arr[b][a]=1;
}
dfs(start);
sb.append("\n");
check = new boolean[point + 1];
bfs(start);
System.out.println(sb);
}
static void dfs(int start) {
check[start] =true;
sb.append(start + " ");
for (int i = 0; i <= point; i++) {
if(arr[start][i] == 1 && !check[i])
dfs(i);
}
}
public static void bfs(int start) {
q.add(start);
check[start] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
start = q.poll();
sb.append(start + " ");
for (int i = 1; i <= point; i++) {
if (arr[start][i] == 1 && !check[i]) {
q.add(i);
check[i] = true;
}
}
}
}}