MySQL 설치
API와 MySQL을 연결하기 위해서 기본적으로 MySQL을 설치하여야 한다.
우분투에서는 apt, apt-get 혹은 apt install 패키지 매니저를 사용하여 MySQL를 설치할 수 있다.
mysql-server
(base) $ sudo apt update
(base) $ sudo apt install mysql-serversudo: super 유저 권한을 가져와서 다음 명령어를 실행 할 수 있다.update: 현재 local ubuntu의 모든 패키지들을 최신화 update한다apt install mysql-server: apt install 패키지 명령어로 mysql-server 패키지를 가져와서 설치를 시작한다- 설치과정가운데 password를 입력하는데 mysql root계정의 비밀번호이다.
service mysql start, status, stop
(base) $ sudo service mysql start
[sudo] inyong의 암호:
# mysql -u root -p
$ mysql -u root -p
Enter password: -
sudo: mysql를 시작할 수 있다. -
mysql -u root -p: mysql root계정으로 접속 시 mysql 접속하게 된다. 접속 시 비밀번호는 설치당시 입력한 비밀번호 이다. -
-u: MySQL에 접속할 사용자의 아이디를 명시하는 옵션. 여기서는 root계정으로 접속한다. -
-p: 비빌번호를 직접 입력하겠다는 옵션.
(base) $ service mysql status
● mysql.service - MySQL Community Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; vendor pres
Active: active (running) since Fri 2020-01-31 12:20:34 KST; 3min 15s ag
Process: 9177 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize --pid-file=/run/mys
Process: 9148 ExecStartPre=/usr/share/mysql/mysql-systemd-start pre (cod
Main PID: 9179 (mysqld)
Tasks: 28 (limit: 4915)
(base) $ service mysql stop
(base) $ service mysql status
● mysql.service - MySQL Community Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; vendor pres
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2020-01-31 12:25:21 KST; 1s ago
Process: 9177 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/mysqld --daemonize --pid-file=/run/mys
Process: 9148 ExecStartPre=/usr/share/mysql/mysql-systemd-start pre (cod
Main PID: 9179 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
...
...-
service mysql status: mysql service 가 구동중인지를 확인 할 수 있는 명령어.Active:이 active 이면 mysql service가 실행 중이고, inactive이면 service가 중지 상태이다. -
service mysql stop: mysql service를 중지 시키는 명령어
API에 데이터베이스 연동하기
Minitter schema
데이터베이스 즉 MySQL를 설치 완료하였으면, 우리가 그 전 블로그에서 만들었던 Minitter API와 연동할 준비를 한다.
먼저 Minitter의 schema를 구현하도록 한다
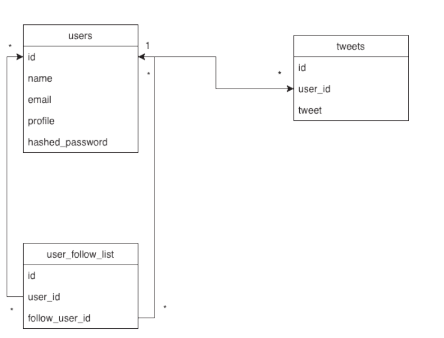
-
users테이블 : name, email, profile, hashed_password 등의 사용자 정보를 저장하는 테이블이다. -
user_follow_list테이블 : 사용자들이 다른 사용자들을 팔로우하는 리스트를 저장한다 -
users-user_follow_list는 한 사용자가 여러사용자를 팔로우/언팔로우 할수 있고, 여러사용자가 한 사용자를 팔로우/언팔로우 할 수 있다.
따라서 many to many 관계이며,users테이블의 id를 통한 외부키(foreign key)로 연결되어 있다. -
tweets테이블 : 사용자들의 트윗들을 저장하는 테이블이다. -
users-tweets는 한 사용자가 여러 트윗들을 할 수 있다.
따라서 one to many 관계이며,users테이블의 id를 통한 외부키로 연결되어 있다.
MySQL 접속
(base) $ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 2
Server version: 5.7.28-0ubuntu0.18.04.4 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2019, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> MySQL Database create(생성)
mysql> CREATE DATABASE minitter;
mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| minitter |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> USE minitter;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> connect minitter;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Connection id: 3
Current database: minitter
mysql> -
CREATE DATABASE: 데이터베이스를 생성. 생성 시 charset등 여러가지 옵션들이 다양하다. -
SHOW DATABASES;: 데이터베이스들을 확인한다. -
USEorCONNECT: 데이터베이스에 접속 또는 사용한다
MySQL TABLE CREATE(생성)
위 minitter의 schema에 해당하는 database table를 만들려면 다음과 같이 SQL문을 입력하면 된다.
mysql > CREATE TABLE users(
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, # 1)
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
hashed_password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
profile VARCHAR(2000) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, # 2)
updated_at TIMESTAMP NULL DEFAULT NULL ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, # 3)
PRIMARY KEY (id), # 4)
UNIQUE KEY email (email) # 5)
);
CREATE TABLE users_follow_list(
user_id INT NOT NULL,
follow_user_id INT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (user_id, follow_user_id),
CONSTRAINT users_follow_list_user_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id), # 6)
CONSTRAINT users_follow_list_follow_user_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (follow_user_id) REFERENCES users(id)
);
CREATE TABLE tweets(
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_id INT NOT NULL,
tweet VARCHAR(300) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, PRIMARY KEY (id),
CONSTRAINT tweets_user_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id)
);
1) NOT NULL : 해당 컬럼은 null 값이 될 수 없다는 뜻으로, 항상 값이 있어야 한다.
1) AUTO_INCREMENT : 해당 칼럼의 값이 자동으로 1씩 증가한다는 듯으로, 주로 id 값을 자동으로 생성하기 위해 사용된다.
**2) DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP : 만일 칼럼의 값이 없으면 디폴트 값으로 현재 시간(TIMESTAMP) 값을 사용하라는 뜻이다. created_at 처럼 해당 값이 생성된 시점을 기록하는 칼럼에 주로 사용된다.
3) ON UPDATE CURRENT TIMESTAMP : 해당 로우(row)의 값이 업데이트, 즉 수정이 되면 해당 칼럼의 값을 수정이 이루어진 시간값으로 자동 생성해 준다는 뜻이다.
**4) PRIMARY KEY : 구문을 통해 고유 키로 사용될 칼럼을 정해준다. 고유키는 한 개의 칼럼으로 정할 수도 있지만, 여러 칼럼을 정할 수도 있다. 여러 칼럼을 고유 키로 정해주면 해당 칼럼 값들을 합한 값이 고유키가 된다.
5) UNIQUE KEY : 해당 칼럼의 값이 중복되는 로우가 없어야 한다는 뜻이다.
(Ex. Email일 경우 이미 등록된 Email이 있으면, 중복되지 않기 때문에 UNIQUE KEY 설정을 하여 시스템적으로 방지해 둘 수 있다)
**6) CONSTRAINT...FOREIGN KEY...REFERENCES... : 외부키를 걸수 있다. users_follow_list테이블과 tweets테이블 둘다 users테이블에 외부키를 통해 연결된다.
더 자세한 SQL문은 Database - SQL 기초에서 확인 할 수 있다.
MySQL TABLE 확인(SHOW, EXPLAIN, DESC..)
위에서 table들을 생성하면 show명령어로 다음과 같이 table들을 확인 할 수 있다.
mysql> show tables;
+--------------------+
| Tables_in_minitter |
+--------------------+
| tweets |
| users |
| users_follow_list |
+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)users TABLE
mysql> explain users;
+-----------------+---------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------+---------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | NO | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(255) | NO | UNI | NULL | |
| hashed_password | varchar(255) | NO | | NULL | |
| profile | varchar(2000) | NO | | NULL | |
| created_at | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | |
| updated_at | timestamp | YES | | NULL | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+-----------------+---------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)users_follow_list TABLE
mysql> explain users_follow_list;
+----------------+-----------+------+-----+-------------------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------------+-----------+------+-----+-------------------+-------+
| user_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| follow_user_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| created_at | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | |
+----------------+-----------+------+-----+-------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)tweets TABLE
mysql> explain tweets;
+------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| user_id | int(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | |
| tweet | varchar(300) | NO | | NULL | |
| created_at | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | |
+------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+----------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)