Handling unknown number of arguments
만약에 A라는 자동차는 옵션 사항이 40개정도 되다고 가정했을 떄
A라는 자동차를 구입하는 함수를 구현한다고 했을때, 모든 옵션 사항을 parameter로 받으려면 parameter의 수가 40개가 된다. 따라서 함수의 정의도 그 만큼 늘어 날 것이다.
그리고 A라는 자동차는 계속해서 업그레이드 되므로 전에 없던 옵션이 생길 수 도 있다.
그럴경우 함수를 다시 만들어야하는 상황이 올 수 있다.
그렇다면 이렇게 사전에 정확히 필요한 paramter 수와 구조를 알수 없는 경우 어떻게 함수를 구성해야 할까?
가장 간단한 방법은 Dictionary를 Parameter로 받아서 사용하는 것이다.
## dictionary parameter function
def buy_A_car(options):
print(f"다음 사양의 자동차를 구입하십니다:")
for option in options:
print(f"{option} : {options[option]}")
options = {"seat" : "가죽", "blackbox" : "최신"}
buy_A_car(options)
# >> 다음 사양의 자동차를 구입하십니다:
# >> seat : 가죽
# >> blackbox : 최신Keyworded Variables length of arguments
위 같은 경우 항상 parameter를 dictionary형태로만 받아야한다는 제한이 있다.
때로는 parameter를 다른 type의 value, 예를들어 string으로 넘겨주는 경우 오류가 발생한다
따라서 파이썬에서는 Keyworded Variables length of arguments 라는 기능이 있다.
말그대로 keyword arguments 인데, 그 수가 정해지지 않고 유동적으로 변할 수 있는 keyword arguments이다.
keyword arguments는 parameter 앞에 **로 시작해야한다.
그리고 함수를 호출할때 일반적인 Keyword arguments 처럼 사용하면 된다
그리고 keyKeyworded variable length of arguments를 사용할때 일반적으로 argument 이름을 kwargs 라고 짓습니다. 그래서 대부분 **kwargs 라고 parameter 이름을 정한다
일반적인 keyword arguments와의 차이점은:
- Argument 수를 0부터 N까지 유동적으로 넘길수 있다.
- Keyword가 미리 정해져 있지 않기 때문에 원하는 Keyword를 유동적으로 사용할 수 있다.
- Keyworded variable length of arguments는 dictionary 형태로 지정됩니다.
## Keyworded Variables length of arguments example
def buy_A_car(**kwargs):
print(f"다음 사양의 자동차를 구입하십니다:")
for option in kwargs:
print(f"{option} : {kwargs[option]}")
buy_A_car(seat="가죽", blackbox="최신", tint="yes")
# >> {'seat': '가죽', 'blackbox': '최신', 'tint': 'yes'}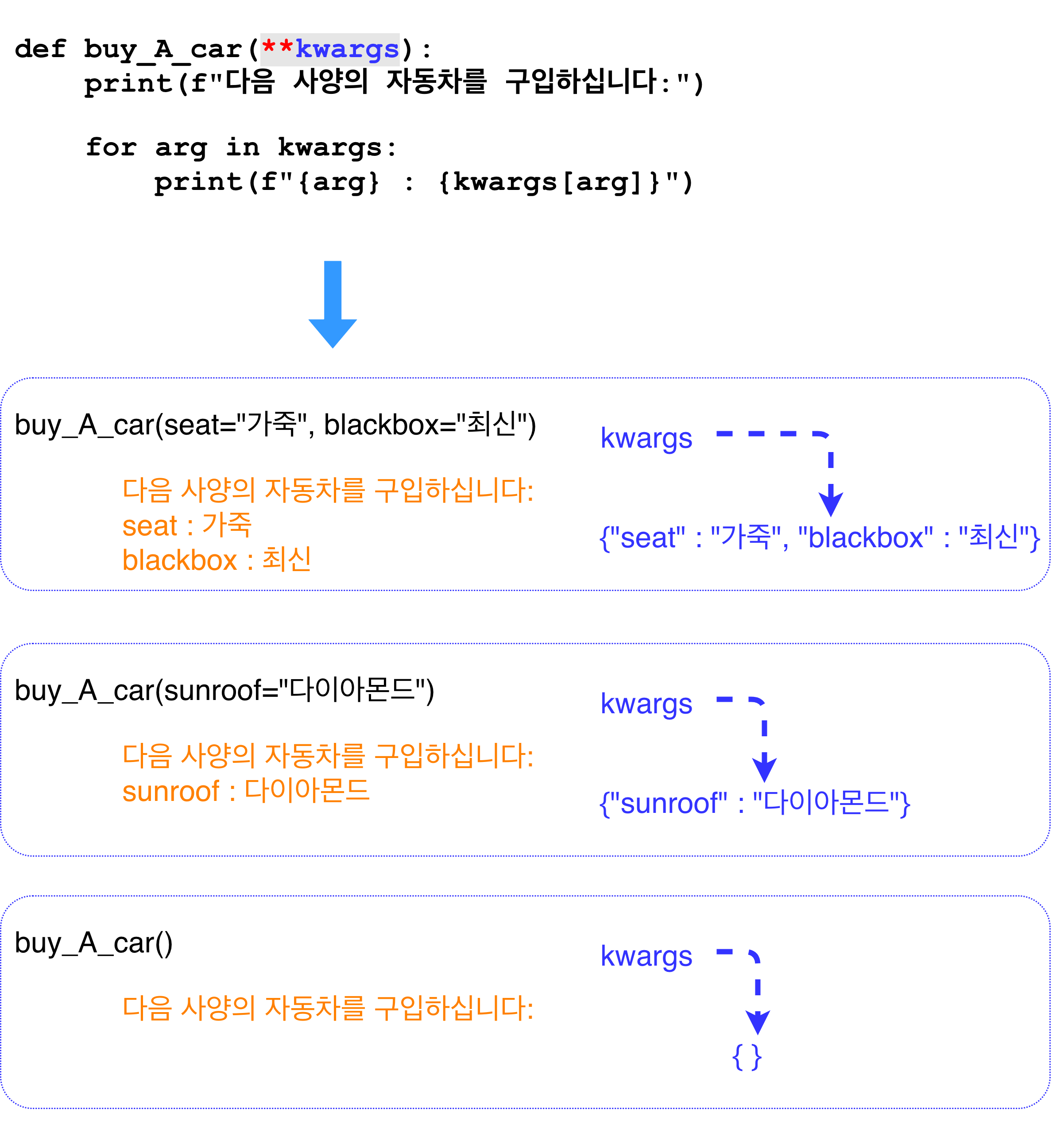
Non-keyworded variable length of arguments
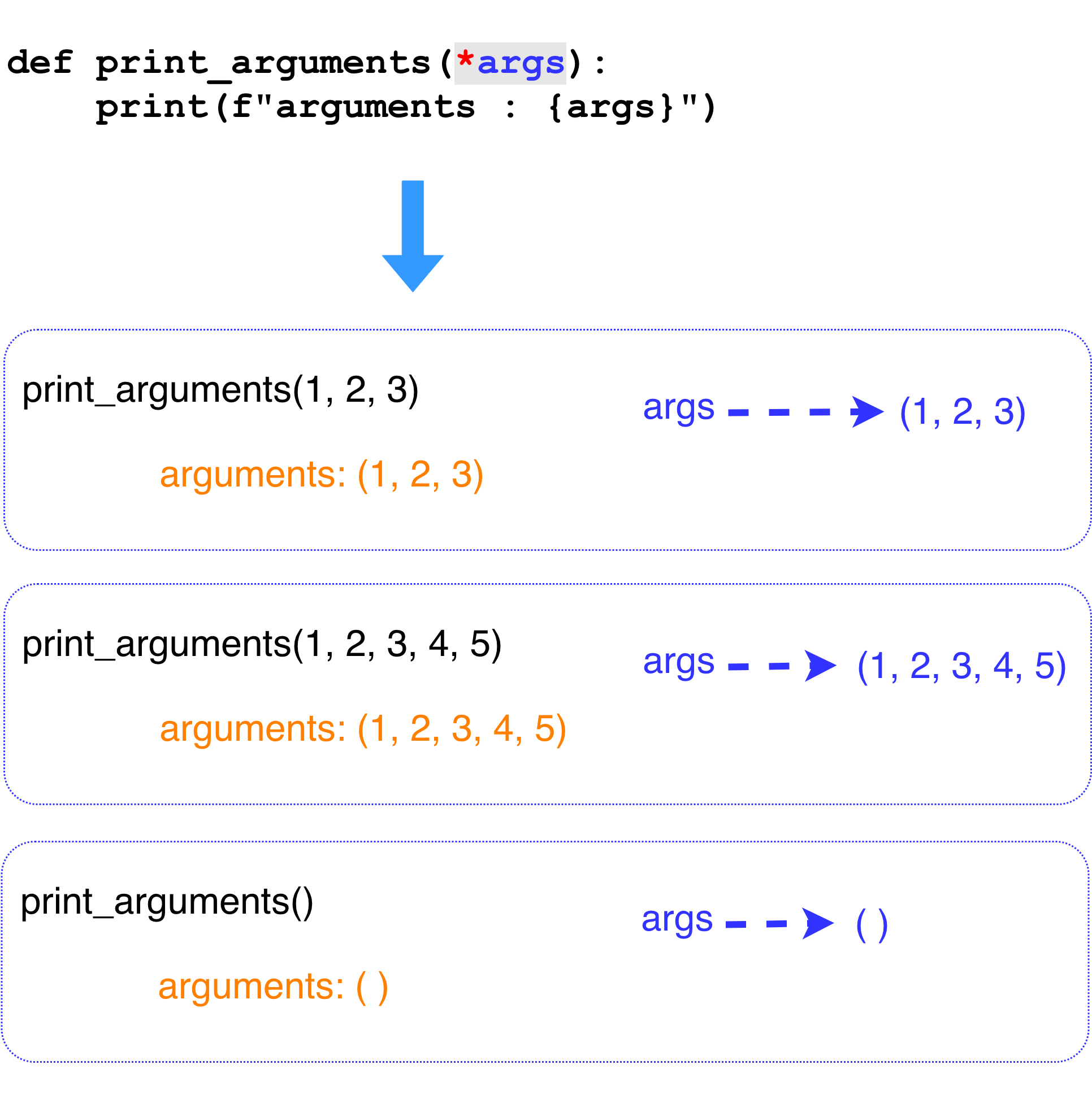
Keyworded variable length of arguments와 동일하지만 keyword 를 사용하지 않고 순서대로 값을 전달하는 방식도 가능하다.
Non-keyworded variable length of arguments 혹은 그냥 variable length of arguments 라고 한다. 더 간단하게 variable arguments 라고 하기도 한다.
Variable arguments를 선언하는 방법은 별표 2개 대신에 1개를 사용해서 선언한다.
그리고 variable arguments는 tuple로 변환되어 함수에 전달된다.
Mixing args and kwargs
Variable arguments와 keyworded variable arguments 둘다 사용하여 함수를 정의할 수 도 있다.
## Mixing args and kwargs example
def do_something(*args, **kwargs):
## some code here...
....
do_something(1, 2, 3, name="정우성", age=45)
do_something(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "hello", {"주소" : "서울", "국가" : "한국"})
do_something(name="정우성", gender="남", height="187")
do_something(1)
do_something()둘다 사용하면 어떠한 형태와 수의 argument도 허용 가능한 함수가 된다.
즉, parameter에 있어서 굉장히 유동적인 함수가 되는것이다.
Assignment
함수 2개를 구현해주세요. 함수의 이름은 다음과 같아야 합니다.
- sum_of_numbers
- what_is_my_full_name
함수 sum_of_numbers는 arugment로 주어지는 모든 수를 합한 값을 리턴해야 합니다.
예를 들어, sum_of_numbers(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) 는 15를 리턴해야 하고 sum_of_numbers(1,2)는 3을 리턴해야 합니다.
만일 parameter가 주어지지 않으면 0을 리턴해야 합니다.
what_is_my_full_name 함수는 주어진 parameter중 first_name 과 last_name 이라는 parameter를 조합하여 full name을 리턴해주어야 합니다.
예를 들어, first_name이 "우성" 이고 last_name 이 "정" 이면 "정 우성" 라고 리턴하면 됩니다.
Last name과 first name 사이에 space(빈칸)이 들어가 있어야 합니다.
만일 last_name이 없거나 first_name이 없으면 둘 중하나만 리턴하면 됩니다.
예를 들어, last_name이 없으면 "우성" 이라고 이름만 리턴하면 됩니다,
마지막으로, last_name과 first_name 둘다 없으면 "Nobody" 라고 리턴하면 됩니다.
## sum_of_numbers My Solution
def sum_of_numbers(*args):
sum = 0
if args == 0:
return 0
for i in args:
sum += i
return sum## what_is_my_full_name My Solution
def what_is_my_full_name(**kwargs):
name={}
for option in kwargs:
name[option] = kwargs[option]
if 'first_name' not in name and 'last_name' not in name :
return("Nobody")
elif 'first_name' not in name :
return(f"{name['last_name']}")
elif 'last_name' not in name:
return(f"{name['first_name']}")
else:
return(f"{name['last_name']} {name['first_name']}")## sum_of_numbers Model Solution
def sum_of_numbers(*numbers):
return sum(numbers)## what_is_my_full_name Model Solution
def what_is_my_full_name(**kwargs):
print(kwargs.keys())
if "first_name" in kwargs and "last_name" in kwargs:
return f"""{kwargs["last_name"]} {kwargs["first_name"]}"""
elif "first_name" in kwargs and "last_name" not in kwargs:
return f"""{kwargs["first_name"]}"""
elif "first_name" not in kwargs and "last_name" in kwargs:
return f"""{kwargs["last_name"]}"""
else:
return "Nobody"
print(what_is_my_full_name(first_name="우성", last_name="정"))